Reference for Network Load Balancer
This guide lists the predefined objects in Resource Analytics for Network Load Balancer. You can find information about views, entity relationships, subject areas and sample queries.
Views
| View Name | View Description |
|---|---|
| NLB_NETWORK_LOAD_BALANCER_DIM_V | This view stores information about the properties of a network Load Balancer. |
| NLB_BACKEND_DIM_V | This view stores information about the configuration of a backend server in a network Load Balancer backend set. |
| NLB_BACKEND_SET_DIM_V | This view stores information about the configuration of a network Load Balancer backend set. |
| NLB_HEALTH_CHECKER_DIM_V | This view stores information about the configuration of the health check policy of a network Load Balancer. |
| NLB_LISTENER_DIM_V | This view stores information about the configuration of a network Load Balancer listener. |
| NLB_FACT_V | Fact for network Load Balancer service. Measures include backend set count, backend count, listener count, health checker count, public and private IP count. |
| NLB_RESOURCE_DETAILS_V | Denormalized view that show the backends, listeners, and health checkers associated with each network Load Balancer and backend set combination. |
| NLB_BACKEND_FACT_V | Fact for network Load Balancer backends. Measures include backend count. |
| NLB_HEALTH_CHECKER_FACT_V | Fact for network Load Balancer service. Measures include backend set count, backend count, listener count, health checker count, public and private IP count. |
| NLB_LISTENER_FACT_V | Fact for network Load Balancer listeners. Measures include listener count. |
The suffixes in the view names specify the view type:
- FACT_V: Fact
- DIM_V: Dimension
- _V: Denormalized view
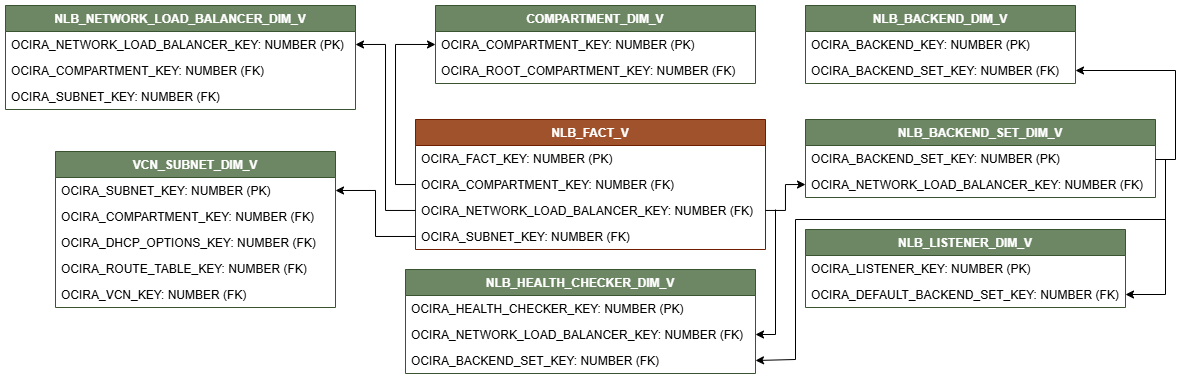
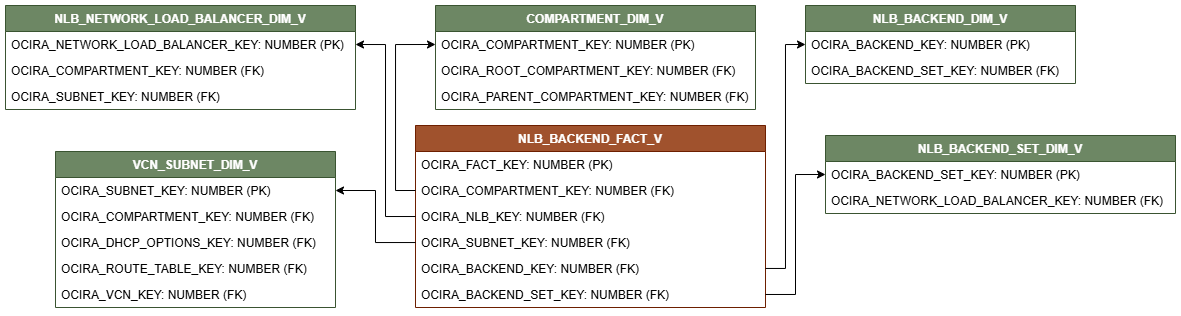
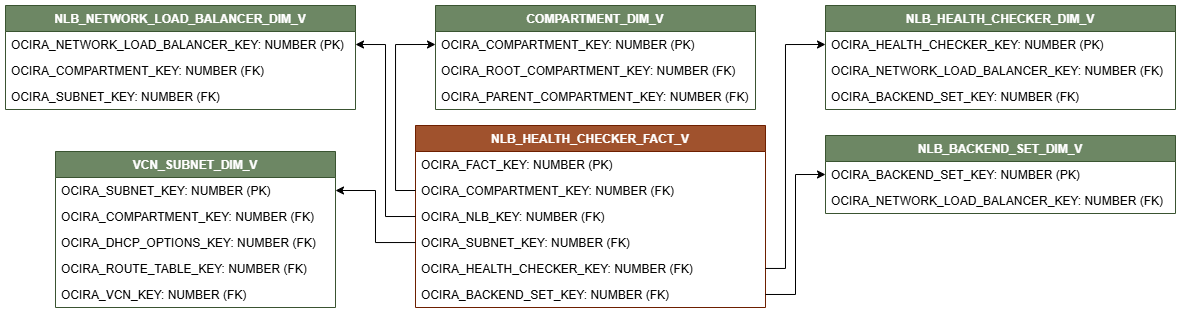
Relationship Diagram
This section provides diagrams that define the logical relationship of a fact table with different dimension tables.
The contents of each view and their relationships are listed in the following file: network load balancer views.

Sample Queries
Sample queries for network Load Balancer.
SELECT BS.BACKEND_SET_NAME, BS.NETWORK_LOAD_BALANCER_ID, L.TIME_CREATED, L.COMPARTMENT_ID, L.REGION, L.LIFECYCLE_STATE
FROM OCIRA.NLB_BACKEND_SET_DIM_V BS
INNER JOIN OCIRA.NLB_NETWORK_LOAD_BALANCER_DIM_V L
ON BS.OCIRA_NETWORK_LOAD_BALANCER_KEY = L.OCIRA_NETWORK_LOAD_BALANCER_KEY;SELECT B.BACKEND_NAME, L.ID, L.TIME_CREATED, L.COMPARTMENT_ID, L.REGION, L.LIFECYCLE_STATE
FROM OCIRA.NLB_BACKEND_DIM_V B
INNER JOIN OCIRA.NLB_BACKEND_SET_DIM_V BS
ON B.OCIRA_BACKEND_SET_KEY = BS.OCIRA_BACKEND_SET_KEY
INNER JOIN OCIRA.NLB_NETWORK_LOAD_BALANCER_DIM_V L
ON BS.OCIRA_NETWORK_LOAD_BALANCER_KEY = L.OCIRA_NETWORK_LOAD_BALANCER_KEY;SELECT H.HEALTH_CHECKER_NAME, L.TIME_CREATED, L.COMPARTMENT_ID, L.REGION, L.LIFECYCLE_STATE
FROM OCIRA.NLB_HEALTH_CHECKER_DIM_V H
INNER JOIN OCIRA.NLB_BACKEND_SET_DIM_V BS
ON H.OCIRA_BACKEND_SET_KEY = BS.OCIRA_BACKEND_SET_KEY
INNER JOIN OCIRA.NLB_NETWORK_LOAD_BALANCER_DIM_V L
ON BS.OCIRA_NETWORK_LOAD_BALANCER_KEY = L.OCIRA_NETWORK_LOAD_BALANCER_KEY;SELECT LS.LISTENER_NAME, L.ID, L.TIME_CREATED, L.COMPARTMENT_ID, L.REGION, L.LIFECYCLE_STATE
FROM OCIRA.NLB_LISTENER_DIM_V LS
INNER JOIN OCIRA.NLB_BACKEND_SET_DIM_V BS
ON LS.OCIRA_DEFAULT_BACKEND_SET_KEY = BS.OCIRA_BACKEND_SET_KEY
INNER JOIN OCIRA.NLB_NETWORK_LOAD_BALANCER_DIM_V L
ON BS.OCIRA_NETWORK_LOAD_BALANCER_KEY = L.OCIRA_NETWORK_LOAD_BALANCER_KEY;SELECT F.NLB_ID, D.DISPLAY_NAME
FROM OCIRA.NLB_FACT_V F
LEFT JOIN OCIRA.NLB_NETWORK_LOAD_BALANCER_DIM_V D
ON F.OCIRA_NLB_KEY = D.OCIRA_NETWORK_LOAD_BALANCER_KEY
WHERE F.LIFECYCLE_STATE IN ('FAILED');SELECT F.NLB_ID, BS.BACKEND_SET_NAME, B.BACKEND_NAME
FROM OCIRA.NLB_FACT_V F
LEFT JOIN OCIRA.NLB_BACKEND_SET_DIM_V BS
ON F.OCIRA_NLB_KEY = BS.OCIRA_NETWORK_LOAD_BALANCER_KEY
LEFT JOIN OCIRA.NLB_BACKEND_DIM_V B
ON BS.OCIRA_BACKEND_SET_KEY = B.OCIRA_BACKEND_SET_KEY;SELECT F.NLB_ID, H.BACKEND_SET_NAME, H.HEALTH_CHECKER_NAME, H.INTERVAL_IN_MILLIS, H.PORT,
H.PROTOCOL, H.RESPONSE_BODY_REGEX, H.RESPONSE_DATA, H.RETRIES, H.RETURN_CODE,
H.TIMEOUT_IN_MILLIS, H.URL_PATH
FROM OCIRA.NLB_FACT_V F
LEFT JOIN OCIRA.NLB_HEALTH_CHECKER_DIM_V H
ON H.OCIRA_NETWORK_LOAD_BALANCER_KEY = H.OCIRA_NETWORK_LOAD_BALANCER_KEY;SELECT F.NLB_ID, F.SUBNET_ID, S.DISPLAY_NAME
FROM OCIRA.NLB_FACT_V F
LEFT JOIN OCIRA.VCN_SUBNET_DIM_V S
ON F.OCIRA_SUBNET_KEY = S.OCIRA_SUBNET_KEY;SELECT F.NLB_ID, T.TAG_TYPE, T.TAG_KEY_NAME, T.TAG_VALUE
FROM OCIRA.NLB_FACT_V F
LEFT JOIN OCIRA.TAGS_DIM_V T
ON F.NLB_ID = T.RESOURCE_ID;
Data Lineage
The Customer Experience Semantic Model Lineage spreadsheet and Metric Calculation Logic spreadsheet for network Load Balancer provides an end-to-end data lineage summary report for physical and logical relationships in your data.
For more information, see Data Lineage.
Subject Areas
This section provides information on the subject areas with data you maintain in network Load Balancer. These subject areas, with their corresponding data, are available for you to use when creating and editing analyses and reports. The information for each subject area includes:
-
Description of the subject area.
-
Business questions that can be answered by data in the subject area, with a link to more detailed information about each business question.
-
Job-specific groups and duty roles that can be used to secure access to the subject area, with a link to more detailed information about each job role and duty role.
-
Primary navigation to the work area that's represented by the subject area.
-
Time reporting considerations in using the subject area, such as whether the subject area reports historical data or only the current data. Historical reporting refers to reporting on historical transactional data in a subject area. With a few exceptions, all dimensional data are current as of the primary transaction dates or system date.
-
The lowest grain of transactional data in a subject area. The lowest transactional data grain decides how data are joined in a report.
-
Special considerations, tips, and things to look out for in using the subject area to create analyses and reports.
Other References
This section provides other references related to the Network Load Balancer.