Enable Autonomous Data Guard
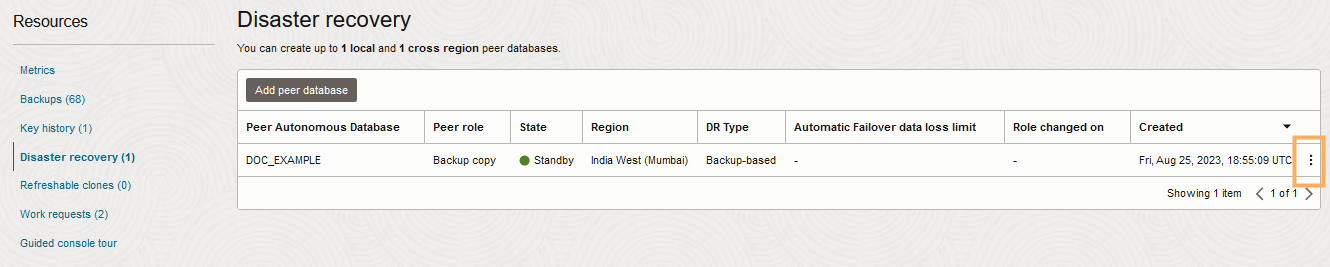
By default and at no additional cost, Autonomous AI Database provides a local backup copy peer for each Autonomous AI Database instance. You enable Autonomous Data Guard by changing the disaster recovery type to use a standby database. Autonomous Data Guard provides a lower Recovery Time Objective (RTO), compared to using a backup copy peer, and provides for automatic failover to a local standby when the primary database is not available.
When you change your disaster recovery type to use a local standby database, you also have the option to add a second cross-region disaster recovery option, either a cross-region Autonomous Data Guard standby database or a cross-region backup copy peer.
Perform the following prerequisite steps as necessary:
-
Open the Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Console by clicking the
 next to Cloud.
next to Cloud.
-
From the Oracle Cloud Infrastructure left navigation menu click Oracle Database and then click Autonomous AI Database.
-
On the Autonomous AI Database page, select your Autonomous AI Database from the links under the Display name column.
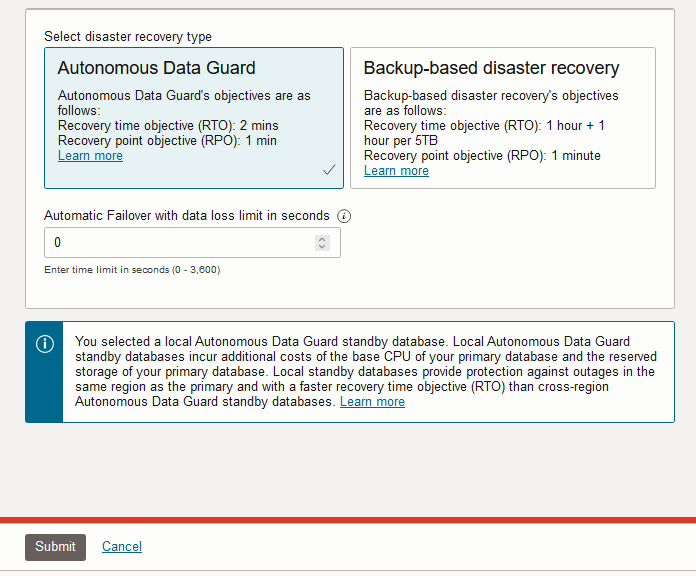
To change your disaster recovery type to add a local Autonomous Data Guard standby database:
Notes for changing the disaster recovery type to a local Autonomous Data Guard standby database:
-
Autonomous AI Database generates an Enable Autonomous Data Guard work request. To view the request, on the details page, select the Work requests tab.
You may need to wait for the work request to complete to 100% before you see Autonomous Data Guard in the DR type column on the Disaster recovery tab. The provisioning process takes several minutes.
-
While you add a local standby database, when the Lifecycle state field shows Updating, the following actions are disabled for the primary database:
-
Move Resource. See Move an Autonomous AI Database to a Different Compartment for information on moving an instance.
-
Stop. See Stop Autonomous AI Database for information on stopping an instance.
-
Restart. See Restart Autonomous AI Database for information on restarting an instance.
-
Restore. See Restore and Recover your Autonomous AI Database for information on restoring.
-