Core Services Concepts
Understand these components of OCI before you get started.
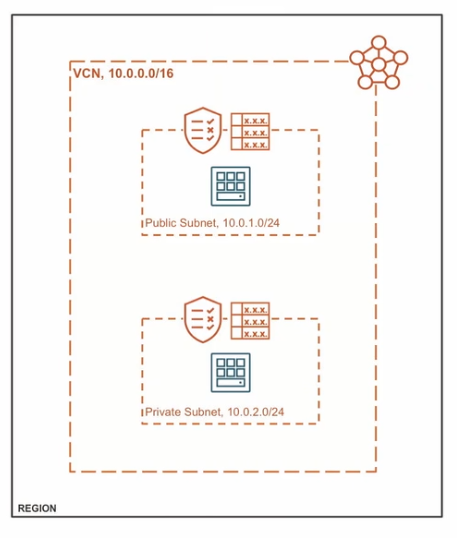
VCN
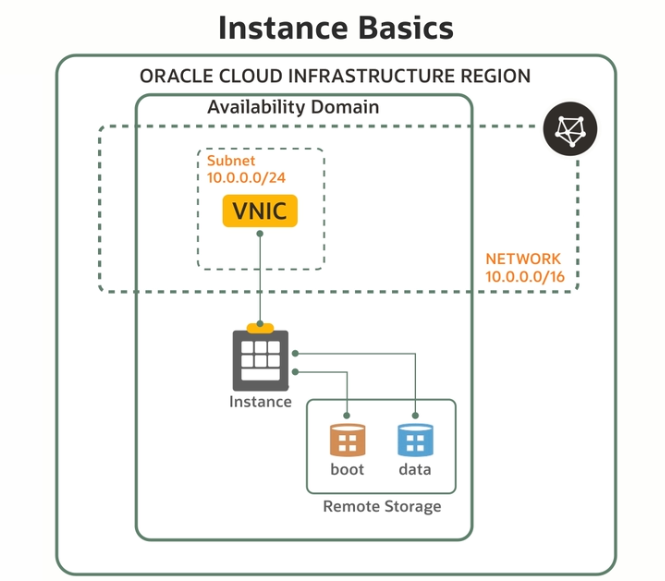
A virtual cloud network is a virtual version of a traditional network—including subnets, route tables, and gateways—on which your instances run. A cloud network resides within a single region but includes all the region's availability domains. Each subnet you define in the cloud network can either be in a single availability domain or span all the availability domains in the region (recommended). You need to set up at least one cloud network before you can launch instances. You can configure the cloud network with an optional internet gateway to handle public traffic, and an optional IPSec connection or FastConnect to securely extend your on-premises network. For details on creating, managing, and deleting VCNs, see Networking.
The image is a template of a virtual hard drive that defines the operating system and other software for an instance, for example, Oracle Linux. When you launch an instance, you can define its characteristics by choosing its image. Oracle provides a set of platform images you can use. You can also save an image from an instance that you have already configured to use as a template to launch more instances with the same software and customizations.
In Compute, the shape specifies the number of CPUs and amount of memory allocated to the instance. Oracle Cloud Infrastructure offers shapes to fit various computing requirements. See the list of compute shapes.
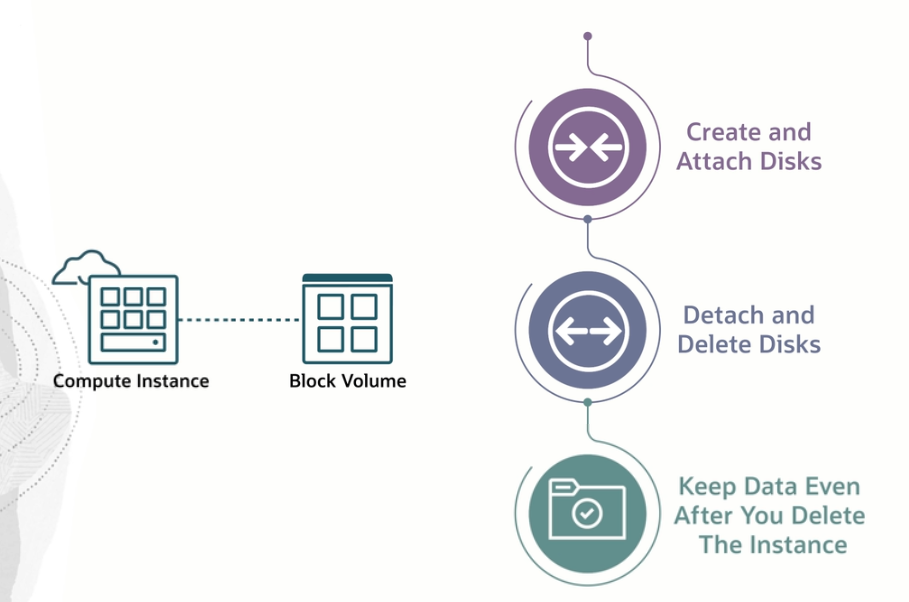
Block volume
A block volume is a virtual disk that provides persistent block
storage space for Oracle Cloud Infrastructure instances. Use a block
volume just as you would a physical hard drive on your computer, for example, to store
data and applications. You can detach a volume from one instance and attach it to
another instance without loss of data.