Implicit Grant Type
Use this grant type when the custom application can't keep client credentials confidential and receives an access token directly from an authorization request rather than through an intermediate authorization code.
The following diagram displays the Implicit Grant Type flow.
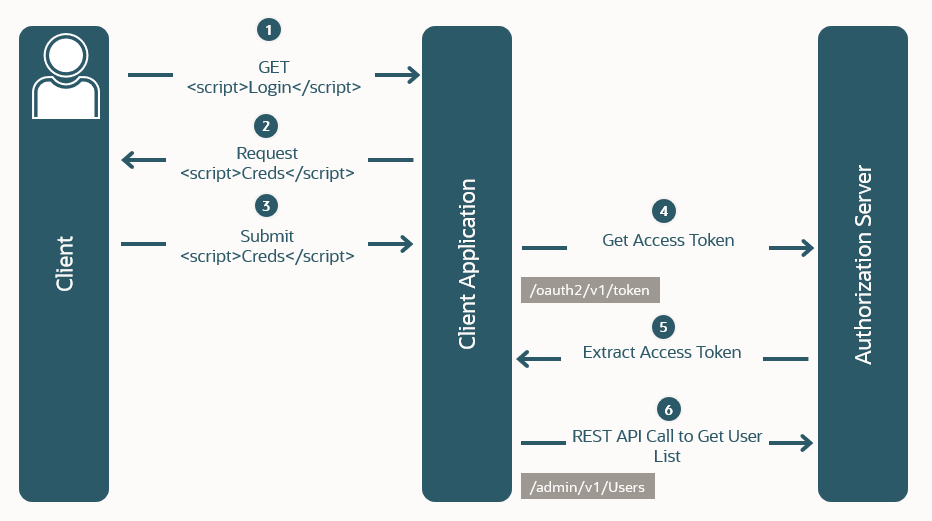
In this OAuth flow:
-
A custom application, for example, is implemented in a client-side application using a scripting language such as JavaScript or implemented for a mobile device. The user requests authentication and authorization through the application.
-
The client application prompts the user to provide their credentials.
-
The user enters their credentials.
-
If authorized, the user is redirected to a URL that contains the access token in a URL fragment.
-
The application extracts the access token from the URL.
-
The application uses the access token in a request for protected resources, such as a list of users.
| Function | Available |
|---|---|
| Requires client authentication | No |
| Requires client to know user credentials | No |
| Browser-based end-user interaction | Yes |
| Can use an external Identity Provider for authentication | Yes |
| Refresh token is allowed | No |
| Access token is in the context of the end user | Yes |
See an example Implicit Grant Type authorization flow.
Implicit Grant Type Authorization Flow Example
This Implicit grant type authorization example describes the authorization flow for applications that are implemented in a Web browser using a scripting language such as JavaScript or implemented on a mobile device. An access token is returned to the client through a browser redirect in response to the resource owner authorization request (rather than an intermediate authorization code).
When you create an application for client-side application authorization in the identity domain Console:
-
Specify that this is a Mobile Application type.
-
Select Implicit as the grant type. This type of application cannot keep a secret and runs on an unauthenticated web browser or a mobile device.
See Implicit Grant Type for more information on the Implicit grant type and an authorization flow diagram.
Processing Steps
-
A user clicks a sign-in link in their browser application or taps a sign-in button on their device, requesting access to protected resources from a client application.
-
The client redirects the browser to the OAuth Authorization Server with a request for authorization.
The sign-in URL contains query parameters that indicate the type of access being requested:
Example Requesthttps://acme.identity.us.oraclecloud.com/oauth2/v1/authorize?client_id=<client-id>&response_type=token&redirect_uri=<client-redirect-uri>&scope=<scope>&nonce=<nonce-value>Note
A nonce value is a cryptographically strong random string that you use to prevent intercepted responses from being reused.Example Request Using mTLS
To find out how to get the
secureDomainURL, see Access Grant Types.curl -v \ --cert cert.crt \ --key key.key \ --cacert ca.crt \ --location '<secureDomainURL>/oauth2/v1/token' \ --header 'Authorization: Basic <base64Encoded clientid:secret>' --header 'Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded' \ --data-urlencode 'grant_type=client_credentials' \ --data-urlencode 'client_id=<client-id>' \ --data-urlencode 'scope=urn:opc:idm:_myscopes_' -
If the user isn't already logged in, the OAuth Authorization Server challenges the user to authenticate. The OAuth Authorization Server authenticates the user and provides a consent page for the user to authorize the sharing of information.
-
After the user authorizes, the OAuth Authorization Server redirects the browser to the requesting site with an access token.Note
If the user doesn't authenticate, an error is returned rather than the access token. -
The access token is returned containing all applicable scopes based on the privileges represented by the application roles granted to the requesting client application and the user being specified by the client's request (if present).
-
The requesting site uses the access token in an API call to obtain protected data.