OpenSearch Pipelines
Create and manage OpenSearch pipelines using Data Prepper to ingest data into an OpenSearch cluster.
Data Prepper is an open source data collector that can filter, enrich, transform, normalize, and aggregate data for downstream analysis and visualization. It's one of the most recommended data ingestion tools for processing large and complex datasets.
The OpenSearch pipelines are compatible with OpenSearch clusters running version 2.x and later.
The OpenSearch Cluster with Data Prepper feature is only available in the OC1 realm.
Required Policies
Complete the policy requirements described in this section before proceeding with the steps described in this topic.
If you're a non-administrator in your tenancy, contact your tenancy administrators to grant these permissions to you. The administrator must update the following users permission to allow non-administrator users to manage and CRUD operations the pipelines
The following policy allows the administrator to grant permission to all users in the respective tenancy:
Allow any-user to manage opensearch-cluster-pipeline in tenancyThe following policy allows the administrator to grant permission for a group in a compartment (recommended)
Allow group <group> to manage opensearch-cluster-pipeline in compartment <compartment>
where
<group>
is all the users inside that group can access the resource.
The following policy allows OpenSearch pipelines to read the secrets from the Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Vault.
Allow any-user to read secret-bundles in compartment <compartment> WHERE ALL {request.principal.type='opensearchpipeline', target.secret.id = '<target-secret-ocid>' }' }
Allow any-user to read secrets in compartment <compartment> WHERE ALL {request.principal.type='opensearchpipeline', target.secret.id = '<target-secret-ocid>' }OpenSearch index names must follow these rules:
- All letters must be lowercase.
- Names can't begin with an underscore ( _ ) or hyphen (-).
- Names can't contain spaces, commas, or any of the following characters: :, ", *, +, /, \, |, ?, #, >, <
- The index name can contain a data prepper expression.
Creating the Secrets in the Vault
All plain text secrets that are required by the OpenSearch pipelines should be passed to it through Vault, as OpenSearch pipelines doesn't accept plain text secrets such as usernames and passwords in the pipelines YAML code.
Perform the following tasks:
- Create a new user with write permissions, in your OpenSearch cluster. For instructions, see the following OpenSearch documentation topics:
- Create secrets (username and password) in Vault for the new user you created. For instructions, see the following Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Vault topics:
- Add the following resource principal policies in your OpenSearch tenancy to allow OpenSearch pipelines to read the secrets from the Vault.
ALLOW ANY-USER to read secrets in compartment '<customer-compartment>' WHERE ALL {request.principal.type='opensearchpipeline', target.secret.id = '<target-secret-ocid>' } ALLOW ANY-USER to read secret-bundles in compartment '<customer-compartment>' WHERE ALL {request.principal.type='opensearchpipeline', target.secret.id = '<target-secret-ocid>' }For more information on see creating policies for Vault, see Details for the Vault Service.
You can perform the following OpenSearch pipeline tasks:
List the OpenSearch pipelines in a compartment.
Create a new OpenSearch pipeline.
Get an OpenSearch pipeline's details.
Supported Processors
The following table list those processors are supported in the pipeline.
PULL Pipelines
Object Storage Policies
These policies are only required for Object Storage source:
The following policy allows OpenSearch pipelines to use a bucket from Object Storage as the source coordination persistence:
Allow any-user to manage objects in compartment <compartment> WHERE ALL {request.principal.type='opensearchpipeline', target.bucket.name='<source-coordination-bucket-name>'}The following policy allows OpenSearch pipelines to ingest objects from Object Storage:
Allow any-user to manage objects in compartment <compartment> WHERE ALL {request.principal.type='opensearchpipeline', target.bucket.name='<bucket_name>'}The following policy allows OpenSearch pipelines to read buckets from Object Storage:
Allow any-user to read buckets in compartment <compartment> WHERE ALL {request.principal.type='opensearchpipeline', target.bucket.name='<bucket_name>'}The following policy allows OpenSearch pipelines to read buckets from the source coordination bucket.
Allow any-user to read buckets in compartment <compartment> WHERE ALL {request.principal.type='opensearchpipeline', target.bucket.name='<bucket_name>'}OCI Streaming and Self-Managed Kafka Policies
These policies are required for OCI Streaming service or self-managed Kafka sources.
Common Network Policies
These policies are not needed for the public OCI Streaming service.
Policies to be added to allow OpenSearch service to create, read, update the delete the private endpoints in the customer subnet.
Allow group SearchOpenSearchAdmins to manage vnics in compartment <network_resources_compartment>
Allow group SearchOpenSearchAdmins to manage vcns in compartment <network_resources_compartment>
Allow group SearchOpenSearchAdmins to manage subnets in compartment <network_resources_compartment>
Allow group SearchOpenSearchAdmins to use network-security-groups in compartment <network_resources_compartment>
OCI Streaming Service Policies (Public and Private)
These policies are only required for the OCI Streaming service.
The following policy allows OpenSearch pipelines to consume the records from the OCI Streaming service.
Allow ANY-USER TO {STREAM_INSPECT, STREAM_READ, STREAM_CONSUME} in compartment '<compartment-name>'
where ALL {request.principal.type='opensearchpipeline', target.streampool.id = '<target-stream-pool-ocid>'}The following policy allows OpenSearch pipelines to read stream pools from OCI streaming service
Allow ANY-USER TO read stream-pools in compartment '<compartment-name>' where ALL {request.principal.type='opensearchpipeline',
target.streampool.id = '<target-stream-pool-ocid>'}Self-Managed Kafka Permission
These permissions are only required for self-managed Kafka sources.
Select the following link to add required permission to list the topics, describe the topics, to join the group and to consume the records from the topic by the OpenSearch pipeline:
Network Security Rules
This configuration is only required for Private OCI Streaming service and Self-managed Kafka. In-case of Public OCI Streaming service, select none.
Add an ingress security rule in the Security List of the subnet or the Network Security Group to all OpenSearch pipelines to communicate to the private OCI Streaming service running in your subnet.
To add the security rule, see Security Rules and Access and Security.
To find the CIDR of your subnet, see Getting a Subnet's Details.
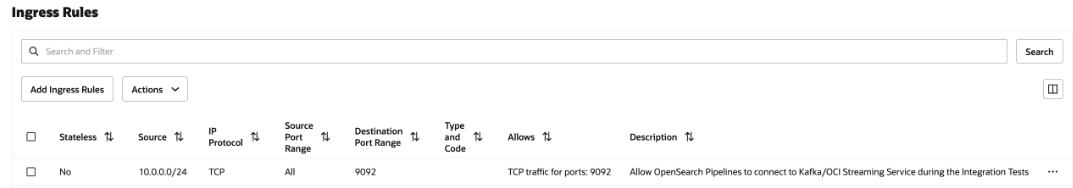
The following image shows the ingress rules for the Network Security Group.
Object Storage and Source Coordination YAML
Object Storage source depends the source coordination configuration. The OpenSearch pipeline support source coordination using Object Storage as persistence. You must provide the Object Storage bucket details from your tenancy.
The following is an example of source coordination:
source_coordination:
store:
oci-object-bucket:
name: <OCI Object storage bucket-name details from their tenancy>
namespace: <namespace>
For information on how to obtain the Object Storage namespace of your tenancy, see Understanding Object Storage Namespaces.
The following is an example of source coordination using Object Storage persistence:
source_coordination:
store:
oci-object-bucket:
name: "dataprepper-test-pipelines" <-- bucket name
namespace: "idee4xpu3dvm". <-- namespaceObject Storage YAML
The following are sections of the pipeline configuration YAML to be aware of:
- OCI Secrets: You can create a secret in Vault with your OpenSearch cluster credentials and use it in the pipeline YAML for connecting to the OpenSearch cluster.
- OpenSearch Sink: The sink contains OpenSearch cluster OCIDs with index names for ingestion.
-
oci-object source: The Data Prepper supports scan-based ingestion using Object Storage which has many configurations supported. You can configure the source to ingest objects within you Object Storage bucket based on scheduled frequency or not based on any schedule. You have the following scan options
- One or more time scan: This option allows you to configure pipeline which reads objects in Object Storage buckets one or more times based on last modified time of objects.
- Scheduling based scan: This option allows you to schedule a scan on a regular interval after pipeline is created.
The following table lists the options you can use to configure the Object Storage source.
| Options | Required | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
acknowledgments
|
No | Boolean | When true, enables Object Storage object sources to receive end-to-end acknowledgments when events are received by OpenSearch sinks. |
buffer_timeout
|
No | Duration | The amount of time allowed for writing events to the Data Prepper buffer before timeout occurs. Any events that the OCI source can't write to the buffer during the specified amount of time are discarded. Default is 10s. |
codec
|
Yes | Codec | The codec from data-prepper to apply. |
compression
|
No | String | The compression algorithm to apply: none, gzip, snappy, or automatic. Default is none. |
delete_oci_objects_on_read
|
No | Boolean | When true, the Object Storage source scan attempts to delete Object Storage objects after all events from the Object Storage object are successfully acknowledged by all sinks. acknowledgments should be enabled when deleting Object Storage objects. Default is false. Delete doesn't work if end-to-end acknowledgments isn't enabled. |
oci
|
No | OCI | The OCI configuration. See the following OCI section for more information. |
records_to_accumulate
|
No | Integer | The number of messages that accumulate before being written to the buffer. Default is 100. |
workers
|
No | Integer | Configures the number of worker threads that the source uses to read data from OCI bucket. Leaving this value at the default unless your Object Storage objects are less than 1 MB. Performance may decrease for larger Object Storage objects. Default is 1. |
Object Storage Pipeline Configuration YAML
The following is an example of the Object Storage pipeline configuration YAML:
version: 2
pipeline_configurations:
oci:
secrets:
opensearch-username:
secret_id: <secret-ocid>
opensearch-password:
secret_id: <secret-ocid>
simple-sample-pipeline:
source:
oci-object:
codec:
newline:
compression: none
scan:
start_time: 2024-11-18T08:01:59.363Z
buckets:
- bucket:
namespace: <namespace>
name: <bucket-name>
sink:
- opensearch:
hosts: [ <cluster-ocid> ]
username: ${{oci_secrets:opensearch-username}}
password: ${{oci_secrets:opensearch-password}}
insecure: false
index: <index-name>
Sample Configurations
The following are one time scan options you can apply on individual Object Storage bucket level or at scan level
oci-object:
codec:
newline:
scan:
buckets:
- bucket:
namespace: "<namespace>"
name: "data-prepper-object-storage-testing"
start_time: 2023-01-01T00:00:00Z
compression: "none"End Time
The following is an example of end time:
simple-sample-pipeline:
source:
oci-object:
codec:
newline:
scan:
buckets:
- bucket:
namespace: "idee4xpu3dvm"
name: "data-prepper-object-storage-testing"
end_time: 2024-12-01T00:00:00Z
compression: "none"Start Time and End Time
The following is an example of start time and end time:
simple-sample-pipeline:
source:
oci-object:
codec:
newline:
scan:
buckets:
- bucket:
namespace: "idee4xpu3dvm"
name: "data-prepper-object-storage-testing"
start_time: 2023-12-01T00:00:00Z
end_time: 2024-12-01T00:00:00Z
compression: "none"Range
The following is an example of range:
simple-sample-pipeline:
source:
oci-object:
codec:
newline:
scan:
buckets:
- bucket:
namespace: "idee4xpu3dvm"
name: "data-prepper-object-storage-testing"
start_time: 2023-12-01T00:00:00Z
range: "PT12H"
compression: "none"Start Time, End Time, and Range
The following is an example of start time, end time, and range:
oci-object:
codec:
newline:
scan:
start_time: 2023-01-01T00:00:00Z
end_time: 2024-12-01T00:00:00Z
range: "PT12H"
buckets:
- bucket:
namespace: "idee4xpu3dvm"
name: "data-prepper-object-storage-testing"
include_prefix Filter
The following is an example of the include_prefix filter:
simple-sample-pipeline:
source:
oci-object:
codec:
newline:
scan:
buckets:
- bucket:
namespace: "idee4xpu3dvm"
name: "data-prepper-object-storage-testing"
start_time: 2023-12-01T00:00:00Z
filter:
include_prefix: ["newtest1", "10-05-2024"]
compression: "none"Filter Files from Folder
The following is an example of filter files from folder. To read files only from specific folders, use filter to specify folders. Here is an example of including files from folder2 within folder1 using include_prefix.
simple-sample-pipeline:
source:
oci-object:
codec:
newline:
scan:
buckets:
- bucket:
namespace: "idee4xpu3dvm"
name: "data-prepper-object-storage-testing"
start_time: 2023-12-01T00:00:00Z
filter:
include_prefix: ["folder1/folder2"]
compression: "none"
exclude_prefix Filter
The following is an example of the exclude_prefix filter:
simple-sample-pipeline:
source:
oci-object:
codec:
newline:
scan:
buckets:
- bucket:
namespace: "idee4xpu3dvm"
name: "data-prepper-object-storage-testing"
start_time: 2023-12-01T00:00:00Z
filter:
include_prefix: ["newtest", "10-05-2024"]
exclude_suffix: [".png"]
compression: "none"Codec Support for JSON
The following is an example of codec support for JSON:
source:
oci-object:
acknowledgments: true
codec:
json: null
scan:
start_time: 2024-06-10T00:00:00Z
end_time: 2024-06-10T23:00:00Z
buckets:
- bucket:
namespace: "idee4xpu3dvm"
name: "data-prepper-object-storage-testing"
start_time: 2024-06-13T00:00:00Z
end_time: 2024-06-13T23:00:00Z
- bucket:
namespace: "idee4xpu3dvm"
name: "object-storage-testing"
start_time: 2024-06-13T00:00:00Z
end_time: 2024-06-13T23:00:00Z
compression: "none"Codec Support for CSV
The following is an example of codec support for CSV:
source:
oci-object:
acknowledgments: true
codec:
csv: null
scan:
start_time: 2024-06-10T00:00:00Z
end_time: 2024-06-10T23:00:00Z
buckets:
- bucket:
namespace: "idee4xpu3dvm"
name: "data-prepper-object-storage-testing"
start_time: 2024-06-13T00:00:00Z
end_time: 2024-06-13T23:00:00Z
- bucket:
namespace: "idee4xpu3dvm"
name: "object-storage-testing"
start_time: 2024-06-13T00:00:00Z
end_time: 2024-06-13T23:00:00Z
compression: "none"Codec Support for Newline
The following is an example of codec support for newline:
source:
oci-object:
acknowledgments: true
codec:
newline: null
scan:
start_time: 2024-06-10T00:00:00Z
end_time: 2024-06-10T23:00:00Z
buckets:
- bucket:
namespace: "idee4xpu3dvm"
name: "data-prepper-object-storage-testing"
start_time: 2024-06-13T00:00:00Z
end_time: 2024-06-13T23:00:00Z
- bucket:
namespace: "idee4xpu3dvm"
name: "object-storage-testing"
start_time: 2024-06-13T00:00:00Z
end_time: 2024-06-13T23:00:00Z
compression: "none"Scheduling Ingestion Options without Count
The following is an example of scheduling ingestion options without count:
simple-sample-pipeline:
source:
oci-object:
codec:
newline: null
scan:
scheduling:
interval: PT40S
buckets:
- bucket:
namespace: idee4xpu3dvm
name: data-prepper-object-storage-testing
compression: noneScheduling Ingestion Options with Count
The following is an example of scheduling ingestion options with count:
simple-sample-pipeline:
source:
oci-object:
codec:
newline: null
scan:
scheduling:
interval: PT40S
count: 10
buckets:
- bucket:
namespace: idee4xpu3dvm
name: data-prepper-object-storage-testing
compression: noneScheduling Ingestion Options with Start Time
The following is an example of scheduling ingestion options with start time:
oci-object:
codec:
newline:
scan:
scheduling:
interval: "PT40S"
count: 10
start_time: 2023-01-01T00:00:00Z
buckets:
- bucket:
namespace: "idee4xpu3dvm"
name: "data-prepper-object-storage-testing"
compression: "none"Scheduling Ingestion Options with End Time
The following is an example of scheduling ingestion options with end time:
oci-object:
codec:
newline:
scan:
scheduling:
interval: "PT40S"
count: 10
end_time: 2023-01-01T00:00:00Z
buckets:
- bucket:
namespace: "idee4xpu3dvm"
name: "data-prepper-object-storage-testing"
compression: "none"Kafka YAML
The Kafka source doesn't require any source coordination.
For information on all the available configurations for the Kafka Source, access the following link:
https://opensearch.org/docs/latest/data-prepper/pipelines/configuration/sources/kafka/
You can use the OCI Streaming Service as the Kafka source to ingest into the OpenSearch cluster. For information on how to do this, see Using Kafka APIs.
The number of nodes can't exceed the maximum number of partitions defined for the topic.
OCI Streaming Public Access YAML
version: 2
pipeline_configurations:
oci:
secrets:
opensearch-username:
secret_id: <secret-ocid>
opensearch-password:
secret_id: <secret-ocid>
kafka-pipeline:
source:
kafka:
bootstrap_servers:
- <bootstrap_servers>
topics:
- name: <topic_name>
group_id: <group_id>
acknowledgments: true
encryption:
type: ssl
insecure: false
authentication:
sasl:
oci:
stream_pool_id: <target-stream-pool-ocid>
sink:
- opensearch:
hosts: [ <opensearch-cluster-ocid> ]
username: ${{oci_secrets:opensearch-username}}
password: ${{oci_secrets:opensearch-password}}
insecure: false
index: <index-name>Pipelines OCI Streaming Service Private Access YAML
The following is an example of the YAML for the OpenSearch pipelines in the OCI Streaming service:
version: 2
pipeline_configurations:
oci:
secrets:
opensearch-username:
secret_id: <secret-ocid>
opensearch-password:
secret_id: <secret-ocid>
kafka-pipeline:
source:
kafka:
bootstrap_servers:
- <bootstrap_servers>
topics:
- name: <topic_name>
group_id: <group_id>
acknowledgments: true
encryption:
type: ssl
insecure: false
authentication:
sasl:
oci:
stream_pool_id: <target-stream-pool-ocid>
sink:
- opensearch:
hosts: [ <opensearch-cluster-ocid> ]
username: ${{oci_secrets:opensearch-username}}
password: ${{oci_secrets:opensearch-password}}
insecure: false
index: <index-name>
Self-Managed Kafka YAML
The following is an example of the self-managed Kafka YAML for the OpenSearch:
version: 2
pipeline_configurations:
oci:
secrets:
opensearch-username:
secret_id: <secret-ocid>
opensearch-password:
secret_id: <secret-ocid>
kafka-credentials:
secret_id: <secret-ocid>
simple-sample-pipeline:
source:
kafka:
bootstrap_servers:
- "https://<bootstrap_server_fqdn>:9092"
topics:
- name: <topic_name>
group_id: <group_id>
acknowledgments: true
encryption:
type: ssl
insecure: false
certificate: <certificate-in-pem-format>
authentication:
sasl:
plaintext:
username: ${{oci_secrets:kafka-credentials:username}}
password: ${{oci_secrets:kafka-credentials:password}}
sink:
- opensearch:
hosts: [ <opensearch-cluster-ocid> ]
username: ${{oci_secrets:opensearch-username}}
password: ${{oci_secrets:opensearch-password}}
insecure: false
index: <index-name>
PUSH Pipeline
Common Network Policies
Policies to be added to allow OpenSearch service to create, read, update the delete the private endpoints in the customer subnet.
Allow group SearchOpenSearchAdmins to manage vnics in compartment <network_resources_compartment>
Allow group SearchOpenSearchAdmins to manage vcns in compartment <network_resources_compartment>
Allow group SearchOpenSearchAdmins to manage subnets in compartment <network_resources_compartment>
Allow group SearchOpenSearchAdmins to use network-security-groups in compartment <network_resources_compartment>
Persistent Buffer
OpenSearch pipelines with Data Prepper push connectors require persistent buffer to store the disk-based buffer to add durability to your data. This is mandatory in push connectors to prevent data loss in an event of any node malfunction. OCI Streaming Service is the only supported persistent buffer.
Each data ingestion pipeline must have a dedicated buffer. Sharing the same buffer across several pipelines can lead to data corruption because of overlapping or mixed data.
The following table lists the data ingestion pipeline source components and whether it requires buffering.
| Source | Persistent Buffering Required |
|---|---|
| Object Storage | No |
| Self Managed Kafka | No |
| OCI Streaming Service (Public) | No |
| OCI Streaming Service (Private) | No |
| OpenTelemetry (Logs, Metrics or Trace) | Yes |
| HTTP | Yes |
The number of nodes can't exceed the maximum number of partitions defined for the topic.
Policies
Use the following policies for applying permissions related to persistent buffering for OCI Streaming Service with public endpoints:
- To allow OpenSearch pipelines to consume and produce the records in the OCI Streaming Service:
Allow any-user to {STREAM_INSPECT, STREAM_READ, STREAM_CONSUME, STREAM_PRODUCE} in compartment '<compartment_name>' where ALL {request.principal.type='opensearchpipeline', target.streampool.id = '<target_stream_pool_ocid>'} - To allow OpenSearch pipelines to read stream pools from the OCI Streaming Service:
Allow any-user to read stream-pools in compartment '<compartment_name>' where ALL {request.principal.type='opensearchpipeline', target.streampool.id = '<target_stream_pool_ocid>'}
For more information, see Details for the Streaming Service.
Network Security Rules
This configuration is only required for Private OCI Streaming service and Self-managed Kafka. In case of Public OCI Streaming service, select none.
Add an ingress security rule in the Security List of the subnet or the Network Security Group to all OpenSearch pipelines to communicate to the private OCI Streaming service running in your subnet.
To add the security rule, see Security Rules and Access and Security.
To find the CIDR of your subnet, see Getting a Subnet's Details.
The following image shows the ingress rules for the Network Security Group.

OpenTelemetry Logs
OpenTelemetry Logs require persistent buffering.
The port for OpenTelemetry Logs is 21892, which can't be changed.
For configuration information, see OTel logs source.
You can use the OCI Streaming Service as the persistent buffer. For more information, see Using Kafka APIs.
OpenTelemetry Logs Pipeline Configuration
The following example shows a pipeline configuration for OpenTelemetry Logs:
version: 2
pipeline_configurations:
oci:
secrets:
opensearch-username:
secret_id: <secret_ocid>
opensearch-password:
secret_id: <secret_ocid>
pipeline-username:
secret_id: <secret_ocid>
pipeline-password:
secret_id: <secret_ocid>
sample-log-pipeline:
source:
otel_logs_source:
authentication:
http_basic:
username: '${{oci_secrets:pipeline-username}}'
password: '${{oci_secrets:pipeline-password}}'
buffer:
kafka:
# Idempotence should be 'false' for OCI Streaming Service
producer_properties:
enable_idempotence: false
bootstrap_servers:
- <bootstrap_servers>
topics:
- name: <topic_name>
group_id: <group_id>
encryption:
type: ssl
insecure: false
authentication:
sasl:
oci:
stream_pool_id: <target_stream_pool_ocid>
sink:
- opensearch:
hosts: [ <cluster-ocid> ]
username: ${{oci_secrets:opensearch-username}}
password: ${{oci_secrets:opensearch-password}}
insecure: false
index: 'otel-logs-%{yyyy.MM.dd}'OpenTelemetry Metrics
OpenTelemetry Metrics requires persistent buffering.
The port for OpenTelemetry Metrics is 21891 which can't be changed.
For configuration information, see OTel metrics source.
You can use the OCI Streaming Service as the persistent buffer. For more information, see Using Kafka APIs.
OpenTelemetry Metrics Pipeline Configuration
The following example shows a pipeline configuration for OpenTelemetry Metrics:
version: 2
pipeline_configurations:
oci:
secrets:
opensearch-username:
secret_id: <secret_ocid>
opensearch-password:
secret_id: <secret_ocid>
pipeline-username:
secret_id: <secret_ocid>
pipeline-password:
secret_id: <secret_ocid>
sample-metrics-pipeline:
source:
otel_metrics_source:
authentication:
http_basic:
username: '${{oci_secrets:pipeline-username}}'
password: '${{oci_secrets:pipeline-password}}'
buffer:
kafka:
# Idempotence should be 'false' for OCI Streaming Service
producer_properties:
enable_idempotence: false
bootstrap_servers:
- <bootstrap_servers>
topics:
- name: <topic_name>
group_id: <group_id>
encryption:
type: ssl
insecure: false
authentication:
sasl:
oci:
stream_pool_id: <target_stream_pool_ocid>
sink:
- opensearch:
hosts: [ <cluster_ocid> ]
username: ${{oci_secrets:opensearch-username}}
password: ${{oci_secrets:opensearch-password}}
insecure: false
index: 'otel-metrics-%{yyyy.MM.dd}'OpenTelemetry Trace
OpenTelemetry Trace requires persistent buffering.
The port for OpenTelemetry Trace is 21890, which can't be changed.
For configuration information, see OTel trace source.
You can use the OCI Streaming Service as the persistent buffer. For more information, see Using Kafka APIs.
OpenTelemetry Trace Pipeline Configuration
The following example shows a pipeline configuration for OpenTelemetry Trace:
version: 2
pipeline_configurations:
oci:
secrets:
opensearch-username:
secret_id: <secret_ocid>
opensearch-password:
secret_id: <secret_ocid>
pipeline-username:
secret_id: <secret_ocid>
pipeline-password:
secret_id: <secret_ocid>
traces-entry-shared-pipeline:
source:
otel_trace_source:
authentication:
http_basic:
username: '${{oci_secrets:pipeline-username}}'
password: '${{oci_secrets:pipeline-password}}'
buffer:
kafka:
# Idempotence should be 'false' for OCI Streaming Service
producer_properties:
enable_idempotence: false
bootstrap_servers:
- <bootstrap_servers>
topics:
- name: <topic_name>
group_id: <group_id>
encryption:
type: ssl
insecure: false
authentication:
sasl:
oci:
stream_pool_id: <target_stream_pool_ocid>
sink:
- pipeline:
name: traces-pipeline
- pipeline:
name: service-map-pipeline
traces-pipeline:
source:
pipeline:
name: traces-entry-shared-pipeline
processor:
- otel_traces:
sink:
- opensearch:
hosts: [ <cluster-ocid> ]
username: ${{oci_secrets:opensearch-username}}
password: ${{oci_secrets:opensearch-password}}
insecure: false
index_type: trace-analytics-raw
service-map-pipeline:
source:
pipeline:
name: traces-entry-shared-pipeline
processor:
- service_map:
sink:
- opensearch:
hosts: [ <cluster-ocid> ]
username: ${{oci_secrets:opensearch-username}}
password: ${{oci_secrets:opensearch-password}}
insecure: false
index_type: trace-analytics-service-mapHTTP Push Connector
HTTP Push Connector requires persistent buffering.
The port for HTTP Push Connector is 2021, which can't be changed.
For configuration information, see HTTP source.
You can use the OCI Streaming Service as the persistent buffer. For more information, see Using Kafka APIs.
HTTP Push Connector Pipeline Configuration
The following example shows a pipeline configuration for HTTP Push Connector:
version: 2
pipeline_configurations:
oci:
secrets:
opensearch-username:
secret_id: <secret_ocid>
opensearch-password:
secret_id: <secret_ocid>
http-username:
secret_id: <secret_ocid>
http-password:
secret_id: <secret_ocid>
simple-sample-pipeline:
source:
http:
authentication:
http_basic:
username: '${{oci_secrets:http-username}}'
password: '${{oci_secrets:http-password}}'
buffer:
kafka:
# Idempotence should be 'false' for OCI Streaming Service
producer_properties:
enable_idempotence: false
bootstrap_servers:
- <bootstrap_servers>
topics:
- name: <topic_name>
group_id: <group_id>
encryption:
type: ssl
insecure: false
authentication:
sasl:
oci:
stream_pool_id: <target_stream_pool_ocid>
sink:
- opensearch:
hosts: [ <cluster-ocid> ]
username: ${{oci_secrets:opensearch-username}}
password: ${{oci_secrets:opensearch-password}}
insecure: false
index: <index_name>HTTP Push Connector with Multiple Processors
The following example shows a pipeline configuration for HTTP Push Connector with multiple processors:
# Keep caution while adding percentage symbols
version: 2
pipeline_configurations:
oci:
secrets:
opensearch-username:
secret_id: <secret_ocid>
opensearch-password:
secret_id: <secret_ocid>
http-username:
secret_id: <secret_ocid>
http-password:
secret_id: <secret_ocid>
simple-sample-pipeline:
source:
http:
path: "/logs"
authentication:
http_basic:
username: '${{oci_secrets:http-username}}'
password: '${{oci_secrets:http-password}}'
buffer:
kafka:
# Idempotence should be 'false' for OCI Streaming Service
producer_properties:
enable_idempotence: false
bootstrap_servers:
- <bootstrap_servers>
topics:
- name: <topic_name>
group_id: <group_id>
encryption:
type: ssl
insecure: false
authentication:
sasl:
oci:
stream_pool_id: <target_stream_pool_ocid>
processor:
- grok:
match:
log: [ "%{COMMONAPACHELOG}" ]
- date:
from_time_received: true
destination: "@timestamp"
- substitute_string:
entries:
- source: "log"
from: '\.'
to: "-"
- uppercase_string:
with_keys:
- "log"
- trim_string:
with_keys:
- "log"
- split_string:
entries:
- source: "request"
delimiter: "?"
- key_value:
source: "/request/1"
field_split_characters: "&"
value_split_characters: "="
destination: "query_params"
- lowercase_string:
with_keys:
- "verb"
- add_entries:
entries:
- key: "entry1"
value: "entry1value"
- key: "entry2"
value: "entry2value"
- key: "entry3"
value: "entry3value"
- rename_keys:
entries:
- from_key: "entry1"
to_key: "renameEntry1"
- from_key: "entry2"
to_key: "renameEntry2"
- from_key: "entry3"
to_key: "renameEntry3"
- copy_values:
entries:
- from_key: "log"
to_key: "copy_key"
- delete_entries:
with_keys: [ "renameEntry1", "renameEntry2", "renameEntry3" ]
sink:
- opensearch:
hosts: [ <cluster_ocid> ]
username: '${{oci_secrets:opensearch-username}}'
password: '${{oci_secrets:opensearch-password}}'
insecure: false
index: <index_name>