Use Google Service Account to Access Google Cloud Platform Resources
You can use a Google service account to access Google Cloud Platform (GCP) resources from an Autonomous AI Database instance.
- About Using a Google Service Account to Access Google Cloud Resources
When you use Google service account based authentication with Autonomous AI Database, an application can securely access Google Cloud Platform (GCP) resources without creating and saving credentials based on long-term IAM access keys for the GCP resources. - Enable Google Service Account and Find the GCP Service Account Name
Prior to using a Google Cloud Platform (GCP) resource with a Google service account you need to enable GCP access for your Autonomous AI Database instance. - Assign Roles to the Google Service Account and Provide Access for GCP Resources
To use Google Cloud Platform (GCP) resources from an Autonomous AI Database instance, you or a Google Cloud Administrator must assign roles and privileges to the Google service account that your application accesses. In addition to assigning roles for the Google service account, for any GCP resources you want to use a Google Cloud administrator must add Google IAM principals. - Use Google Service Account with DBMS_CLOUD
When you makeDBMS_CLOUDcalls to access Google Cloud Platform (GCP) resources and specify the credential name asGCP$PA, the authentication on the Google Cloud Platform side happens using a Google service account. - Disable Google Service Account
To disable Google service account access to Google Cloud Platform (GCP) resources, useDBMS_CLOUD_ADMIN.DISABLE_PRINCIPAL_AUTH. - Google Service Account Notes
Notes for using Google service account.
Parent topic: Configure Policies and Roles to Access Resources
About Using a Google Service Account to Access Google Cloud Resources
When you use Google service account based authentication with Autonomous AI Database, an application can securely access Google Cloud Platform (GCP) resources without creating and saving credentials based on long-term IAM access keys for the GCP resources.
A Google service account is a special kind of GCP account used by an application. You can use a Google service account to make authorized GCP REST API calls from an application (after the service account is given access permissions through IAM role configuration). When an application makes calls with GCP service account based authentication, the initial call generates a temporary access token through OAuth2.0. The OAuth2.0 access token is valid for one hour. Subsequent requests within the hour use the OAuth2.0 access token to make authorized GCP REST API calls.
For example, you may want to load data from Google Cloud Storage into your Autonomous AI Database, perform some operation on the data, and then write the modified data back to Google Cloud Storage. You can do this without using a service account if you have GCP user credentials to access Google Cloud Storage. However, using a role-based Google service account to access GCP resources from Autonomous AI Database has the following benefits:
- You can create role-based access, with different policies for different users or schemas that need access to GCP resources from an Autonomous AI Database instance. This allows you to set a policy to limit access to resources by role. For example, setting a policy that is limited to read-only access, by role, to a Google Cloud Storage bucket.
-
Google service account based credentials provide better security, as you do not need to provide long-term user credentials in code when your application accesses GCP resources. Autonomous AI Database manages the temporary credentials for the Google service account and does not need to store GCP resource user credentials in the database.
See Service accounts for information on Google service accounts.
Enable Google Service Account and Find the GCP Service Account Name
Prior to using a Google Cloud Platform (GCP) resource with a Google service account you need to enable GCP access for your Autonomous AI Database instance.
See ENABLE_PRINCIPAL_AUTH Procedure for more information.
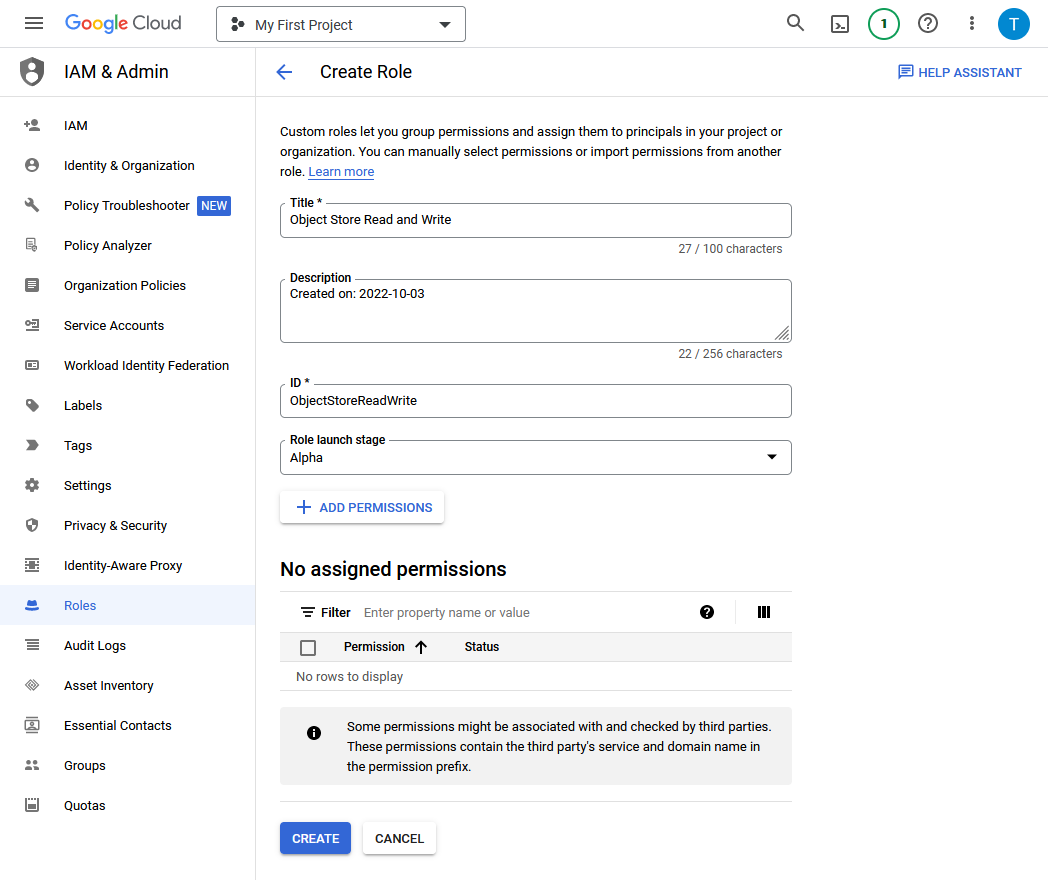
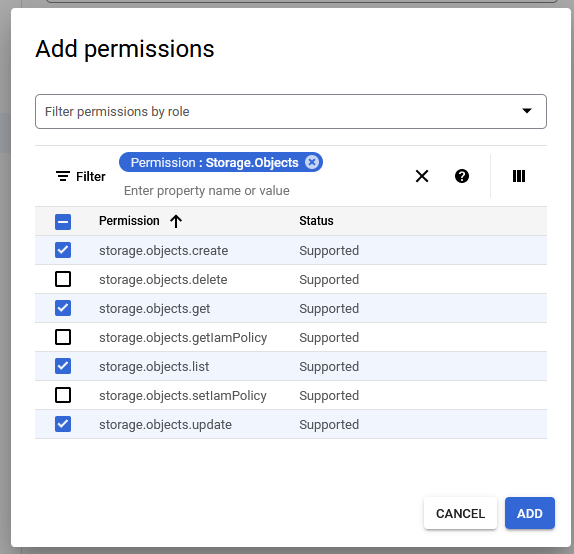
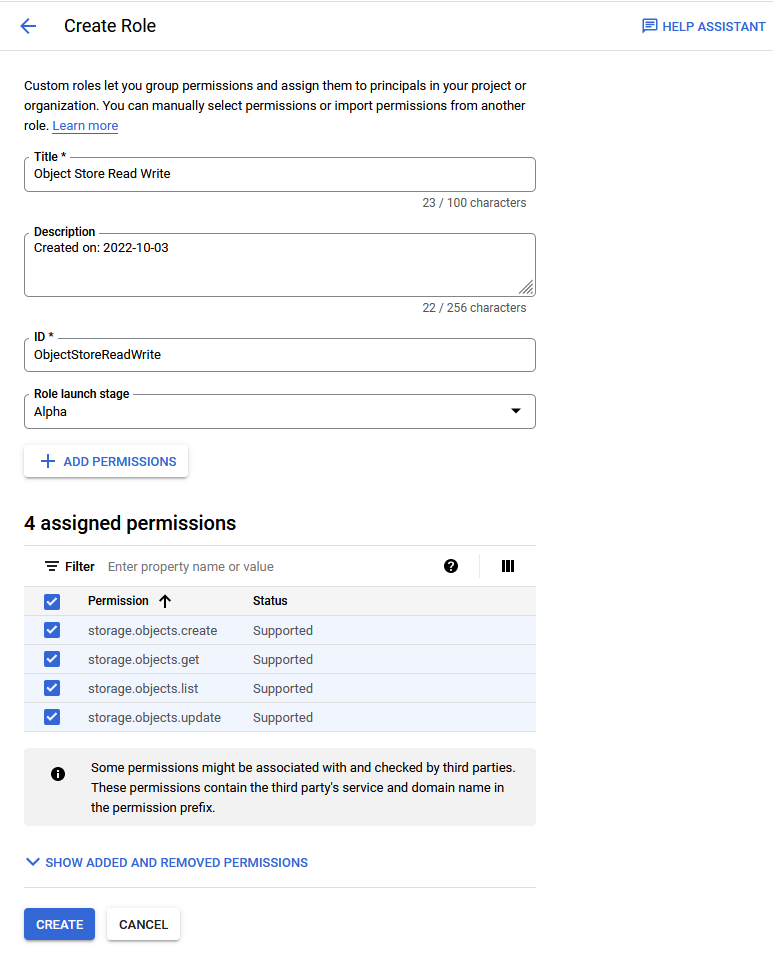
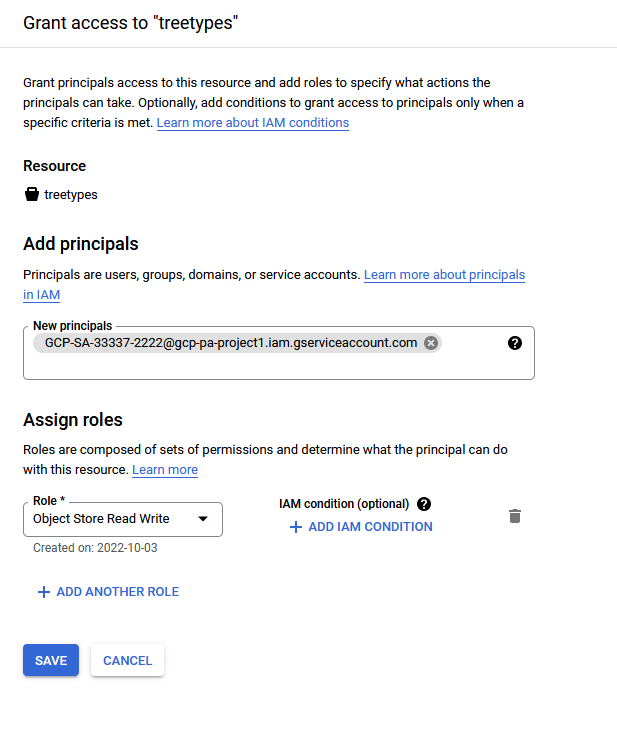
Assign Roles to the Google Service Account and Provide Access for GCP Resources
To use Google Cloud Platform (GCP) resources from an Autonomous AI Database instance, you or a Google Cloud Administrator must assign roles and privileges to the Google service account that your application accesses. In addition to assigning roles for the Google service account, for any GCP resources you want to use a Google Cloud administrator must add Google IAM principals.
As a prerequisite, first enable the Google service account on your Autonomous AI Database instance. See Enable Google Service Account and Find the GCP Service Account Name for more information.
After you complete these steps the roles and principals are assigned. This allows your application running on the Autonomous AI Database instance to access the GCP resource with a Google service account.
Use Google Service Account with DBMS_CLOUD
When you make DBMS_CLOUD calls to
access Google Cloud Platform (GCP) resources and specify the credential name as
GCP$PA, the authentication on the Google Cloud Platform
side happens using a Google service account.
If you have not already done so, perform the prerequisite steps:
-
Enable the ADMIN schema or another schema to use Google service account authentication. See Enable Google Service Account and Find the GCP Service Account Name for more information.
-
Perform the Google Cloud Platform role assignments for the resources you want to access. See Assign Roles to the Google Service Account and Provide Access for GCP Resources for more information.
To use a DBMS_CLOUD procedure or
function with Google service account authentication:
See the following for more information:
-
See Request endpoints for more information on GCP virtual hosted-style requests.
Disable Google Service Account
To disable Google service account access to Google
Cloud Platform (GCP) resources, use DBMS_CLOUD_ADMIN.DISABLE_PRINCIPAL_AUTH.
When the provider value is GCP and the
username is a user other than the ADMIN user,
the procedure revokes the privileges from the specified user. In this case, the
ADMIN user and other users can continue to use
GCP$PA.
For example, to revoke privileges for adb_user:
BEGIN
DBMS_CLOUD_ADMIN.DISABLE_PRINCIPAL_AUTH(
provider => 'GCP',
username => 'adb_user');
END;
/When the provider value is GCP and the
username is ADMIN, the procedure disables
Google service account access on the Autonomous AI Database instance. The default value for username is
ADMIN.
For example:
BEGIN
DBMS_CLOUD_ADMIN.DISABLE_PRINCIPAL_AUTH(
provider => 'GCP' );
END;
/See DISABLE_PRINCIPAL_AUTH Procedure for more information.
Google Service Account Notes
Notes for using Google service account.
-
Google Cloud Platform (GCP) character restriction:
DBMS_CLOUDdoes not support a URI containing an "_" to access a Google Cloud Storage bucket name. If your Google Cloud Storage bucket name contains an "_", you might see the following error:SELECT * FROM DBMS_CLOUD.LIST_OBJECTS('GCP$PA', 'https://app_bucket.storage.googleapis.com/'); ORA-20006: Unsupported object store URI - https://app_bucket.storage.googleapis.com/ ORA-06512: at "C##CLOUD$SERVICE.DBMS_CLOUD", line 1306 -
Cloning an Autonomous AI Database instance with a Google service account: When you clone an instance with a Google service account enabled, the Google service account configuration is not carried over to the clone. Perform the steps to enable the Google service account on the clone if you want to enable Google service account on a cloned instance.