Migrate Data into Autonomous Database on Dedicated Exadata Infrastructure
Data migration is moving data with or without its schema from one system, location, or application to another. One classic example of data migration is when you decide to adopt Autonomous Database for your organization and move the existing historical data from the current database to Autonomous Database.
Data migration is different from loading sample data or a small volume of data into your database. It usually involves large volumes of data and can be a one-time activity or periodic activity depending on the requirement. See Data Loading Options to explore the different options available for loading sample data into Autonomous Database.
- Data Migration Overview
- Migration Prerequisites
- Migration Options
There are multiple options available to move your data into an Autonomous Database on Dedicated Infrastructure in the public cloud as well as Cloud@Customer. - Migration Use Cases
Parent topic: Move Data Into Autonomous Database
Data Migration Overview
- On-premise database, system, or data source
- SaaS applications
- Third-party data source
- Data lakes (Hadoop)
- Other Oracle Database Cloud Services
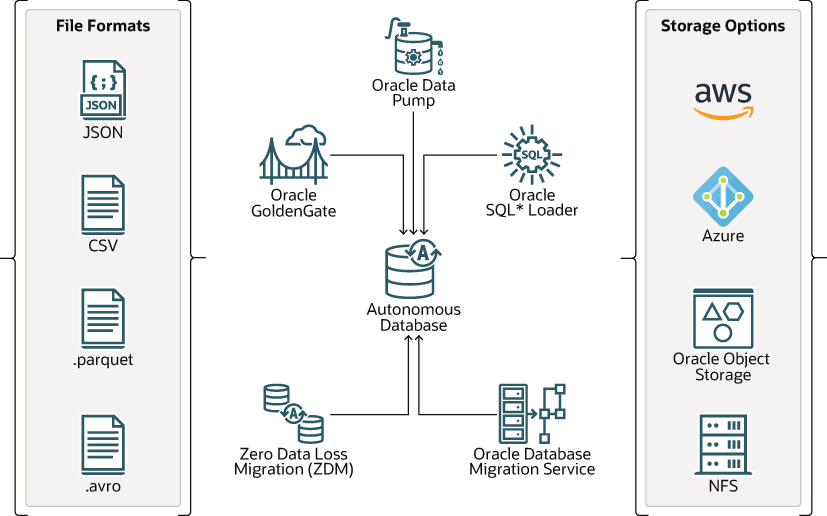
- Use traditional tools such as Oracle SQL*Loader and Oracle Data Pump to migrate your source databases into Autonomous Database.
- Use Data Migration Service (DMS) for simple data migration of large databases that require low migration downtime.
- Use Zero Downtime Migration (ZDM) tool for secure migration to Autonomous Database on Public Cloud and Exadata Cloud@Customer.
- Use Oracle Object Storage to manage, load, and upload large volumes of data.
- Provide the source data in various formats such as SQL Loader text files, export-import dump files, CSV, JSON, Parquet files.
- Load data into Autonomous Database by attaching external Network File System (NFS) devices provided by the customer or Oracle Cloud Infrastructure File System Service (OCI FSS) using
DBMS_CLOUD_ADMIN.
Migration Prerequisites
As a prerequisite, it is recommended that you run the Cloud Premigration Advisor Tool (CPAT) to help you evaluate the compatibility of the source database with the Autonomous Database. CPAT identifies potential actions you may need to take before or during the migration, prioritizing their importance and suggesting resolutions. Some migration tools and services automatically run this advisor. Refer to Cloud Premigration Advisor Tool for more information.
Migration Options
There are multiple options available to move your data into an Autonomous Database on Dedicated Infrastructure in the public cloud as well as Cloud@Customer.
- Oracle Database Migration Service: A fully managed cloud service that simplifies moving established databases from on-premise, third-party, or on Oracle Cloud to Autonomous Database.
- Oracle GoldenGate: Oracle's data replication tool for one time data migration as well as data replication with change data capture.
- Zero Downtime Migration (ZDM): A service with a command line interface that you install and run on a host that you provision. The server where the Zero Downtime Migration software is installed is called the Zero Downtime Migration service host. You can run one or more database migration jobs from the Zero Downtime Migration service host.
- Network File Storage (NFS): Use your local Network File System (NFS) storage to move data in and out of Exadata Cloud@Customer deployments by attaching your Network File Storage (NFS) share to your Autonomous Database.
- Oracle Data Pump: Database utility supporting high-speed bulk data and metadata movement between Oracle databases and Autonomous Database.
- Oracle SQL*Loader: Database utility to load data from external files into Oracle Database.
Migration Use Cases
| Migration Use Case | Migration Option(s) | Further Reference |
|---|---|---|
|
Non-Oracle Database → ADB-D on Public Cloud or Exadata Cloud@Customer. 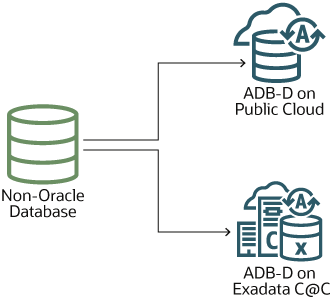 |
|
|
|
Oracle Database version 11.2.0.4 and above → ADB-D on Public Cloud 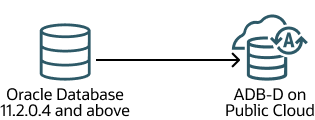 |
|
|
|
Oracle Database version 11.2.0.4 and above → ADB-D on Exadata Cloud@Customer 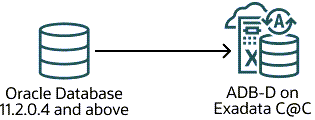 |
|
|
|
Oracle Database version below 11.2.0.4 → ADB-D on Public Cloud or Exadata Cloud@Customer  |
|
|
|
OCI Database (VMDB, BMDB, ExaCS) → ADB-D on Public Cloud  |
|
|
|
OCI Database (VMDB, BMDB, ExaCS) → ADB-D on Exadata Cloud@Customer  |
|
|
|
Autonomous Database Serverless → ADB-D on Public Cloud or Exadata Cloud@Customer  |
|
|
|
3rd Party Cloud Vendors (AWS, Azure) → ADB-D on Public Cloud or Exadata Cloud@Customer  |
|
|
|
Autonomous Database on Dedicated Exadata Infrastructure → Autonomous Database on Dedicated Exadata Infrastructure  |
|
Deciding the migration tool or utility to use depends on multiple factors such as your source database, source data format, data volume and complexity. To help you identify the most optimal solution for migrating your data to Autonomous Database, Oracle provides an advisory utility called Oracle Cloud Migration Advisor. See www.oracle.com/goto/move for more information about this utility.