Cloud Guard Concepts
Understand Cloud Guard components and terminology.
Cloud Guard examines your Oracle Cloud Infrastructure resources for security weakness related to configuration, and your operators and users for risky activities. Upon detection, Cloud Guard can suggest, assist, or take corrective actions, based on your configuration.
The following diagram provides a high-level overview of Cloud Guard system flow. You can refer to this diagram as you review the Cloud Guard concepts whose definitions follow.
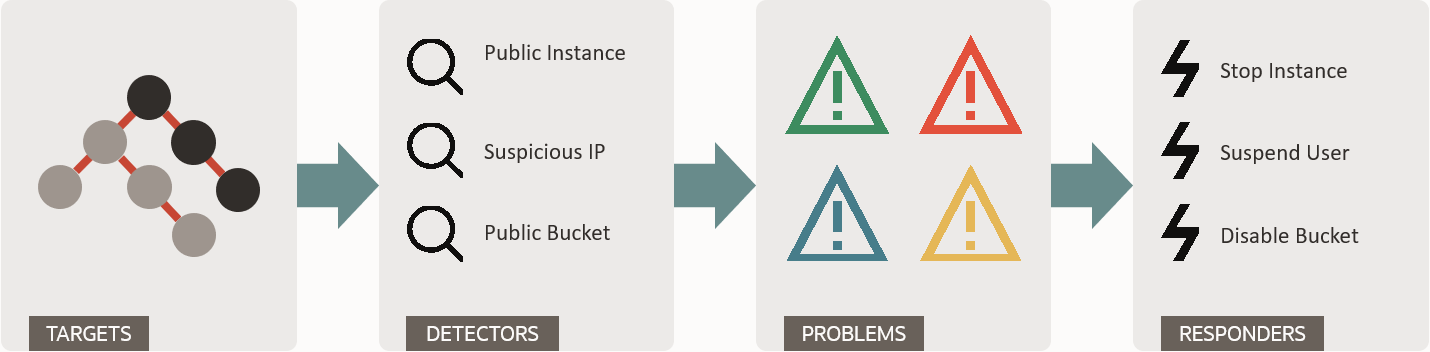
These terms are important for you to understand as you work with Cloud Guard:
- Target
- Defines the scope of what Cloud Guard is to check. For Oracle Cloud Infrastructure, this scope is tied to the compartment where the
target is defined and all the child compartments from that point until another target is
encountered. The other target that's encountered takes over from that point into any
descending compartments.
- A target can consist of your entire OCI tenancy (target at the root compartment).
- To monitor IAM policies, the root compartment must be a target.
- You must specify at least one target when you enable Cloud Guard. You can modify that target and define more targets later.
- Targets can't overlap, and only a single target at a time is applied to a compartment and its resources.
- A compartment (and its children) can be exempted from checks by being declared a target, but not having detector recipes applied to that target.
- Detector
- Performs checks and identifies potential security problems based on their type and
configuration.
- Detector recipe
- Provides the baselines for examining the resources and activities in the target.
- Oracle-managed detector recipe
-
- Provided by Cloud Guard.
- Allows setting only the scope of resources for which a rule triggers a problem.
- Doesn't allow you to disable rules or change a rule's risk level.
- May be updated to include new defaults and settings at any time.
Monitor Cloud Guard Release Notes for these updates.
- User-managed detector recipe
-
- Created by cloning an Oracle-managed recipe.
- Allows setting the scope of resources for which a rule triggers a problem.
- Also allows you to disable individual rules and change a rule's risk level.
- OCI Activity Detector recipe
- Set of rules designed specifically to detect actions on resources that could pose a security problem.
- OCI Configuration Detector recipe
- Set of rules designed specifically to detect resource configuration settings that could pose a security problem.
- OCI Container Security Config recipe
- Set of rules designed specifically to help an organization define how it intends to operate its containerized workloads, and then enforce those intentions.
- OCI Instance Security Detector recipe
- Set of rules designed specifically to provide runtime security for workloads in Compute virtual and bare metal hosts.
- OCI Threat Detector recipe
- Set of rules designed specifically to detect subtle patterns of activity in your environment that could be building up to pose a security problem.
- Detector rule
- Provides a specific definition of a class of resources, with specific actions or configurations, that cause a detector to report a problem. A detector recipe consists of multiple detector rules. If any one rule is triggered, it causes the detector to report a problem. Each rule in a detector recipe can be configured individually.
- Problem
- Any action or setting on a resource that could potentially cause a security problem. Cloud Guard monitors your Oracle Cloud Infrastructure tenancy's network activity to identify and resolve problems. Problems:
- Are created when Cloud Guard discovers a deviation from a detector rule.
- Are defined by the type of detector that creates them: activity or configuration.
- Contain data about the specific type of issue that was found.
- Can be resolved, dismissed, or remediated.
- Responder
- An action that Cloud Guard can take when a detector has identified a problem. The available actions are resource-specific. Responders are structured similar to detectors:
- Responder recipe
- Defines the action or set of actions to take in response to a problem that a detector has identified.
- Oracle-managed responder recipe
-
- Provided by Cloud Guard.
- Doesn't allow you to disable rules.
- May be updated to include new defaults and settings at any time.
Monitor Cloud Guard Release Notes for these updates.
- User-managed responder recipe
-
- Created by cloning the Oracle-managed recipe.
- Allows you to disable individual rules and change a rule's risk level.
- Responder rule
- Defines the specific actions to take. If any one responder rule is triggered, it triggers the responder. Each rule in a detector recipe can be configured individually.
- Managed list
- A reusable list of parameters that makes it easier to set the scope for detector and responder rules. For example, a predefined "Trusted Oracle IP address space" list contains all the Oracle IP addresses that you want to regard as trusted when you define rules for detectors and responders.
- Regions in Cloud Guard