MySQL Database Use Cases
The Database Tools service allows you to create connections to MySQL database systems running in Oracle Cloud Infrastructure. Connections work with MySQL DB Systems (with or without Heatwave) and customer-managed MySQL databases running on OCI compute instances.
The following are some examples of using Database Tools connections with different MySQL Database configurations.
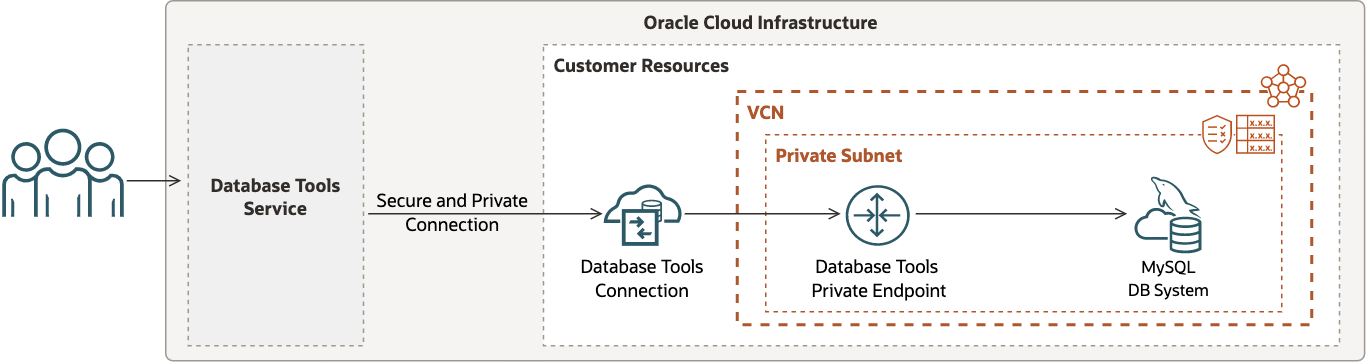
MySQL Database System
When a MySQL DB System is configured to restrict network access using a private subnet, then a Database Tools private endpoint should be setup in a subnet such that network traffic can be routed from the Database Tools service to the target database.
In this scenario:
- There is one Database Tools private endpoint for routing traffic through the VCN.
- The setup requires configuration of a route table and security list or network security group for the subnet.
- A Database Tools private endpoint can be setup in the same subnet or a different subnet (as the DB system). However, using isolated subnets may require additional VCN configuration to allow traffic to be routed accordingly.
- A secret stored in a vault must include the database password.
The following figure shows one possible way to configure your Database Tools connection for this use case.
See Overview of DB System for more information about MySQL DB systems.
See Creating a Connection for more information about creating database tools connections.
See Using Private Endpoints with Database Tools for more information about Database Tools private endpoints.
Familiarity with the following topics may also be useful when configuring a VCN.
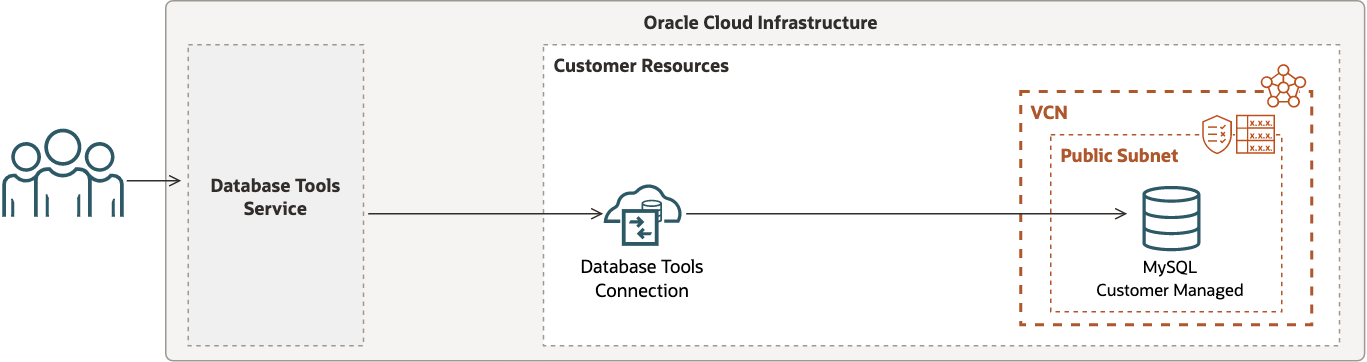
MySQL Database (Customer Managed)
When a customer-managed MySQL database is configured with a public IP address for access from everywhere, then a Database Tools private endpoint is not required to create a connection. This configuration is supported but is not considered best practice.
In this scenario:
- The setup requires configuration of a route table and security list or network security group for the subnet.
- Firewall rules of the database server should allow traffic to reach the database.
- A secret stored in a vault must include the database password.
The following figure shows one possible way to configure your Database Tools connection for this use case.
See Creating a Connection for more information about creating database tools connections.