eval
Use the eval command to calculate the value of an expression and display the value in a new field.
-
While the
statscommand calculates statistics based on existing fields, theevalcommand creates new fields by using existing fields and arbitrary expressions. -
String processing functions like
indexofandsubstrare resource intensive. Due to this, running theevalcommand with these functions against large number of log records, or large field values is not recommended. Instead, extract these values using the Extended Field Definitions (EFD) or Labels in your Log Source. See Use Extended Fields in Sources and Use Labels in Sources. -
Ensure that the field name used in the
evalcommand does not contain the characters[and].
Syntax
*|eval <new_field_name>=<expression>Operators and Functions Available with the Command:
The following table lists the operators available with the
eval command.
| Category | Example |
|---|---|
|
Arithmetic Operators |
+, -,
*, /,
% |
|
Comparison Operators |
=, !=,
<, >,
<=, >= |
|
Logical Operators |
and, or,
not |
|
Conditional Operators |
if(<expression>,<expression>,<expression>) |
|
Multiple Comparison Operators |
in, not in |
The following table lists the functions available with the
eval command.
| Category | Example |
|---|---|
|
String Functions |
|
|
Numeric Functions |
|
|
Date Functions |
Similar to
|
|
Conditional Functions |
|
|
Hash Functions |
Note: |
|
Trigonometric Functions |
|
Parameters
The following table lists the parameters used in this command, along with their descriptions.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
Specify the name of the field where the calculated value of the expression is to be displayed. |
|
|
Specify the expression for which the value needs to be calculated. |
For examples of using this command in typical scenarios, see:
- Rename the Fields by Editing the Query
- Mark the Unit for a Field at Query Time
- Histogram Chart
- Visualize Time Series Data Using the Link Trend Feature
- Generate Charts with Virtual Fields
- Link by Using SQL Statement as the Field of Analysis
- Analyze the Time Taken Between Steps in a Transaction
- Use Link Navigation Functions to Identify Events in a Database
- Add URLs to Link Table
- Use URL Short-Cut with Custom Name
- Use the Currency Symbols in Your Log Analysis
Following are some examples of the eval command.
*|eval newField = 'foo'*|eval newField = 123*|eval newField = upper(Target)*|eval newField = length('hello world')*|eval s =capitalize(severity)*|eval newField = concat(host, concat (':', port))*|eval n = contains(uri, '.com')*|eval n =endsWith(uri, '.com')*|eval n =startsWith(uri, 'http://oracle')*|eval s = decode64(value)*|eval s = encode64(uri)*|eval s = reverse(Command)*|eval newField = host || ':'|| port*|eval newField = round(123.4)*|eval newField = floor(4096/1024)+Length*|eval newField = if (max(Length)(Target), length(Severity)) <= 20, 'OK', 'ERROR')*|eval newField = urlDecode('http%3A%2F%2Fexample.com%3A893%2Fsolr%2FCORE_0_0%2Fquery')*|eval s = urlEncode(uri)*|eval newField = 'Host Name (Destination)' in (host1, host2)*|eval value = arccos(angle)*|eval value = arcsin(angle)*|eval value = arctan(angle)*|eval value = atan2(x, y)*|eval value = cos(angle)*|eval value = e()*|eval value = pi()*|eval value = sin(angle)*|eval value = tan(angle)*|eval value =toDegrees(angle)*|eval value =toRadians(angle)The following example compares the IP addresses in the field srvrhostip to a subnet range.
*|eval newField = if (cidrmatch(srvrhostip, '192.0.2.254/25') = 1, 'local', 'not local')The following example returns the string “Target”.
*|eval newField = literal(Target)The following example removes the spaces and tabs from both the ends.
*|eval newField = trim(Label)The following example removes the matching character from both the ends.
*|eval newField = trim('User Name',h)The following example removes the matching character from the left end.
*|eval newField = ltrim('Error ID',0)The following example removes the matching character from the right end.
*|eval newField = rtrim('OS Process ID',2)The following example sets the field date to Start Date and defines the format of the date as MM/dd/yyyy HH:mm.
*|eval date = toDate('Start Date', 'MM/dd/yyyy HH:mm')The function toDate can also be used to handle epoch as follows:
... | where 'Start Time' > toDate(1405544998000)The following example sets the value of the field duration to 1.30.
*|eval duration = toduration("1.30")The following example sets the value of the field duration to a numerical value which is the difference of End Time and Start Time.
*|eval duration = formatDuration('End Time' - 'Start Time')The following examples illustrate the use of date functions.
*| eval lastHour = dateAdd(now(), hour, -1)
*| eval midnight = dateSet(now(), hour, 0, minute, 0, sec, 0, msec, 0)
*| eval timeOnly = formatDate(now(), 'HH:mm:ss')
*| eval now = now()You can use the md5, sha1, sha256, and sha512 hash functions with the eval command to filter log data. The following example sets the value of the field user with the value sha1("jane").
*|eval user = sha1("jane")The following example converts a hex to a decimal and n evaluates to 255:
* | eval n = toNumber('0xFF')The following example converts an octal number to a decimal and n evaluates to 10:
* | eval n = toNumber('012')The following command calculates the distance (in miles) between two pairs of lat-long coordinates specified in degrees, when the input values are numbers:
* | eval n = distance(lat1, long1, lat2, long2) The following command calculates the distance (in miles) between two pairs of lat-long coordinates (in degrees), when the input values are two strings:
* | eval n = distance('lat1,long1', 'lat2,long2')Examples for unit
Function
Some simple examples:
* | eval newField = unit('Content Size', KB)* | eval 'File Size (bytes)' = unit('File Size', 'byte')* | eval 'File Size (KB)' = unit('File Size'/1024, 'kb')* | eval 'File Size (MB)' = unit('File Size'/(1024*1024), 'mb')* | eval 'Time Taken (Sec)' = unit(Time/1000, 'SEC')Examples for common units like bytes, currency, and duration:
* | eval Vol = unit('Content Size Out', byte) | stats sum(Vol) as 'Total Volume'* | eval Sales = unit('Sales Amount', currency_usd) | stats sum('Sales') as 'Total Sales'* | eval 'Disk Read Time' = unit('Disk Read Time (millis)', ms) | stats avg('Disk Read Time') as 'Avg Disk Read Time'Run the above three queries on Tile visualization with the option Format Number checked, for the best results.
A field with a size or duration type unit would be used to format the values in the Link Analyze chart, addfields histograms, Link Table, and Tile visualization:
'Log Source' = 'FMW WebLogic Server Access Logs'
| link span = 5minute Time, Server
| stats avg('Duration') as 'Raw Avg. Duration'
avg('Content Size') as 'Raw Avg. Transfer Size'
| eval 'Average Duration' = unit('Raw Avg. Duration', ms)
| eval 'Average Transfer Size' = unit('Raw Avg. Transfer Size', byte)
| classify 'Start Time', 'Average Duration',
'Average Transfer Size' as 'Response Time vs. Download Sizes'Mark a field as containing US Dollars, thousands of US Dollars, millions of US Dollars, or billions of US Dollars, respectively:
| eval 'Amount in USD' = unit('Sales Price', currency_usd)
| eval 'Amount in Thousands (USD)' = usd('Quarterly Sales', currency_usd_thousand)
| eval 'Amount in Millions (USD)' = usd('Annual Profit', currency_usd_million)
| eval 'Amount in Billions (USD)' = usd('Annual Sales', currency_usd_billion)Supported Types for the
unit Function
Unit Names:
PERCENT | PCT- Data size:
BYTEKILOBYTE | KBMEGABYTE | MBGIGABYTE | GBTERABYTE | TBPETABYTE | PBEXABYTE | EB
- Time:
MILLISECOND | MSS | SEC | SECS | SECOND | SECONDSM | MIN | MINS | MINUTE | MINUTESH | HR | HRS | HOUR | HOURSD | DAY | DAYSW | WEEK | WEEKSMON | MONTH | MONTHSY | YR | YRS | YEAR | YEARSMICRO | µs
- Power:
WATTKILOWATT | kWMEGAWATT | MWGIGAWATT | GWTERAWATT | TWPETAWATT | PWEXAWATT | EW
- Temperature:
KELVIN | KCELSIUS | CFAHRENHEIT | F
- Frequency:
HERTZ | HzKILOHERTZ | kHzMEGAHERTZ | MHzGIGAHERTZ | GHzTERAHERTZ | THzPETAHERTZ | PHzEXAHERTZ | EHz
Supported Currency Types in the
unit Function
You can use this function for eval command only under the
link command. See eval command example links for using
the function in typical scenarios.
Specify the currency unit using the following format:
eval <New Field> = unit(<Field>, currency_<ISO-4217 Code>)
eval <New Field> = unit(<Field>, currency_<ISO-4217 Code>_k)
eval <New Field> = unit(<Field>, currency_<ISO-4217 Code>_m)
eval <New Field> = unit(<Field>, currency_<ISO-4217 Code>_b)The suffixes _k, _m and
_b are used to indicate the currency in thousands, millions or
billions, respectively. For a full list of currency codes, see ISO Standards.
NLS_Territory |
Currency |
|---|---|
| AFGHANISTAN | AFN |
| ALBANIA | ALL |
| ALGERIA | DZD |
| AMERICA | USD |
| ANGOLA | AOA |
| ANTIGUA AND BARBUDA | XCD |
| ARGENTINA | ARS |
| ARMENIA | AMD |
| ARUBA | AWG |
| AUSTRALIA | AUD |
| AUSTRIA | EUR |
| AZERBAIJAN | AZN |
| BAHAMAS | BSD |
| BAHRAIN | BHD |
| BANGLADESH | BDT |
| BARBADOS | BBD |
| BELARUS | BYN |
| BELGIUM | EUR |
| BELIZE | BZD |
| BERMUDA | BMD |
| BOLIVIA | BOB |
| BOSNIA AND HERZEGOVINA | BAM |
| BOTSWANA | BWP |
| BRAZIL | BRL |
| BULGARIA | BGN |
| CAMBODIA | KHR |
| CAMEROON | XAF |
| CANADA | CAD |
| CAYMAN ISLANDS | KYD |
| CHILE | CLP |
| CHINA | CNY |
| COLOMBIA | COP |
| CONGO BRAZZAVILLE | XAF |
| CONGO KINSHASA | CDF |
| COSTA RICA | CRC |
| CROATIA | HRK |
| CURACAO | ANG |
| CYPRUS | EUR |
| CZECH REPUBLIC | CZK |
| DENMARK | DKK |
| DJIBOUTI | DJF |
| DOMINICA | XCD |
| DOMINICAN REPUBLIC | DOP |
| ECUADOR | USD |
| EGYPT | EGP |
| EL SALVADOR | SVC |
| ESTONIA | EUR |
| ETHIOPIA | ETB |
| FINLAND | EUR |
| FRANCE | EUR |
| FYR MACEDONIA | MKD |
| GABON | XAF |
| GEORGIA | GEL |
| GERMANY | EUR |
| GHANA | GHS |
| GREECE | EUR |
| GRENADA | XCD |
| GUATEMALA | GTQ |
| GUYANA | GYD |
| HAITI | HTG |
| HONDURAS | HNL |
| HONG KONG | HKD |
| HUNGARY | HUF |
| ICELAND | ISK |
| INDIA | INR |
| INDONESIA | IDR |
| IRAN | IRR |
| IRAQ | IQD |
| IRELAND | EUR |
| ISRAEL | ILS |
| ITALY | EUR |
| IVORY COAST | XOF |
| JAMAICA | JMD |
| JAPAN | JPY |
| JORDAN | JOD |
| KAZAKHSTAN | KZT |
| KENYA | KES |
| KOREA | KRW |
| KUWAIT | KWD |
| KYRGYZSTAN | KGS |
| LAOS | LAK |
| LATVIA | EUR |
| LEBANON | LBP |
| LIBYA | LYD |
| LIECHTENSTEIN | CHF |
| LITHUANIA | EUR |
| LUXEMBOURG | EUR |
| MACAO | MOP |
| MALAWI | MWK |
| MALAYSIA | MYR |
| MALDIVES | MVR |
| MALTA | EUR |
| MAURITANIA | MRU |
| MAURITIUS | MUR |
| MEXICO | MXN |
| MOLDOVA | MDL |
| MONTENEGRO | EUR |
| MOROCCO | MAD |
| MOZAMBIQUE | MZN |
| MYANMAR | MMK |
| NAMIBIA | NAD |
| NEPAL | NPR |
| NEW ZEALAND | NZD |
| NICARAGUA | NIO |
| NIGERIA | NGN |
| NORWAY | NOK |
| OMAN | OMR |
| PAKISTAN | PKR |
| PANAMA | PAB |
| PARAGUAY | PYG |
| PERU | PEN |
| PHILIPPINES | PHP |
| POLAND | PLN |
| PORTUGAL | EUR |
| PUERTO RICO | USD |
| QATAR | QAR |
| ROMANIA | RON |
| RUSSIA | RUB |
| SAINT KITTS AND NEVIS | XCD |
| SAINT LUCIA | XCD |
| SAUDI ARABIA | SAR |
| SENEGAL | XOF |
| SERBIA | RSD |
| SIERRA LEONE | SLL |
| SINGAPORE | SGD |
| SLOVAKIA | EUR |
| SLOVENIA | EUR |
| SOMALIA | SOS |
| SOUTH AFRICA | ZAR |
| SOUTH SUDAN | SSP |
| SPAIN | EUR |
| SRI LANKA | LKR |
| SUDAN | SDG |
| SURINAME | SRD |
| SWAZILAND | SZL |
| SWEDEN | SEK |
| SWITZERLAND | CHF |
| SYRIA | SYP |
| TAIWAN | TWD |
| TANZANIA | TZS |
| THAILAND | THB |
| THE NETHERLANDS | EUR |
| TRINIDAD AND TOBAGO | TTD |
| TUNISIA | TND |
| TURKEY | TRY |
| TURKMENISTAN | TMT |
| UGANDA | UGX |
| UKRAINE | UAH |
| UNITED ARAB EMIRATES | AED |
| UNITED KINGDOM | GBP |
| URUGUAY | UYU |
| UZBEKISTAN | UZS |
| VENEZUELA | VES |
| VIETNAM | VND |
| YEMEN | YER |
| ZAMBIA | ZMW |
| ZIMBABWE | ZWL |
indexof Function
Details
The syntax for the index0f function:
indexof (String, String [,int])indexof (String, String [,start_pos]): Index count begins with 0, returns the index of match starting from the start_pos (if provided), and returns -1 if no match.
The following example sets the value of the field newField
with the position of .com in the uri string.
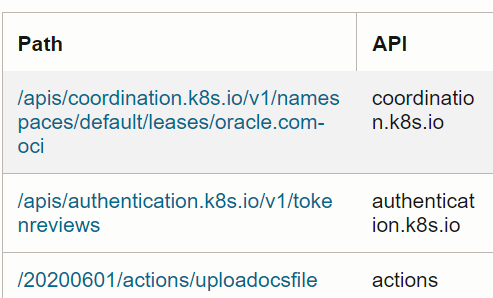
*|eval newField = indexOf(uri, '.com')Use Case: Extract the relevant portion of the API path from OCI Audit Logs, Path field
The Path field contains a value like
/apis/coordination.k8s.io/v1/namespaces/default/leases/oracle.com-oci.
You can extract the value coordination.k8s from the above field by
following these steps:
- Find the position of the first and second
/using theindexOf()function. - Find the position of the third
/. - Extract the values after the second
/, up to the third/, using thesubstr()function.
'Log Source' = 'OCI Audit Logs'
| eval firstPos = indexOf(Path, '/')
| eval secondPos = indexOf(Path, '/', firstPos + 1)
| eval API = substr(Path, secondPos + 1, indexOf(Path, '/', secondPos + 1))
| link Path, APIExample output:
lastindexof
Function Details
The syntax for the lastindexof function:
lastindexof(String, String, int)lastindexof (String, String [, end_pos]): Index count begins with 0, returns index of last occurrence of substring before the end_pos (if provided), and returns -1 if no match. The end_pos argument is optional.
Some examples for using lastindexof function:
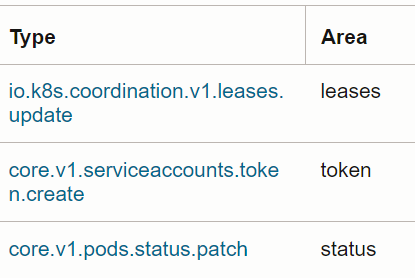
*|eval n = lastindexof(uri, '.com')Use Case: Extract the Area from the Type field in OCI Audit Logs
The Type field contains a value like
com.oraclecloud.computeApi.GetInstance.
To extract computeAPI from the above value, you could use the following
scheme:
- Identify the position of the last
.usinglastIndexOf(). - From this offset, identify the position of the previous
., using anotherlastIndexOf(), but by providing the offset from where to search back. - Extract the value between these two positions using
substr().
'Log Source' = 'OCI Audit Logs'
| eval lastDot = lastIndexOf(Type, '.')
| eval prevDot = lastIndexOf(Type, '.', lastDot - 1)
| eval Area = substr(Type, prevDot + 1, lastDot)
| link Type, AreaExample output:
replace Function
Details
The syntax for the replace function:
replace(String, String, String, String, String, ..)replace supports multiple replacements in a single
function. Some examples for using replace function:
-
*|eval newField = replace('aabbcc', 'bb', 'xx') -
*|eval newField = replace('aabbcc', 'bb', 'xx', 'cc', 'yy') -
Example of multiple replace actions in a single
replacefunction:* | eval CopiedURL = 'https://cloud.oracle.com/loganalytics/explorer?viz=<VIZ>&encodedQuery=<QUERY>&startTime=<START_TIME>&endTime=<END_TIME>®ion=us-phoenix-1&tenant=testtenant'| eval Query = encode64('* | stats count as "Log Records" by "Log Source"') | eval 'Start Epoch' = toString(toNumber(toDate(dateRelative(30day)))) | eval 'End Epoch' = toString(toNumber(now())) | eval Viz = pie | eval URL = replace(CopiedURL, '<VIZ>', Viz, '<QUERY>', Query, '<START_TIME>', 'Start Epoch', '<END_TIME>', 'End Epoch')
substr Function
Details
The syntax for the substr function:
substr(String, int [, int])substr(String, start_pos, end_pos - 1): index count begins with start_pos and ends with the end_pos - 1.
In the following example, newField is the substring of
aabbcc where the start index (inclusive) is 2 and
end index (exclusive) is 4. Note that for strings, the index count
begins with 0. So the resulting substring is bb.
*|eval newField = substr('aabbcc', 2, 4)For use cases where substr function is used, see indexof Function Details and lastindexof Function Details.
url Function
Details
The syntax for the url function:
url(String, Name, Parameter)Name and Parameter values are optional.
- String: This can be a URL or one of the predefined short names.
For example:
eval Link = url('https://www.oracle.com') - Name: Optional Name for the URL. For
example:
eval Link = url('https://www.oracle.com', 'Oracle Home Page') - Parameter: Optional parameter if a short-cut is used for
String. For
example:
eval Link = url('tech', 'Search Oracle', 'ORA-600')
Some examples for using url function:
-
* | stats latest(Status) as Status | eval ‘HTTP Status Code’ = url(‘https://www.google.com/search?q=http+code+’, Status, Status) -
Status != null | eval 'HTTP Status Code' = url('https://www.google.com/search?q=http+code+', Status, Status) | stats count by Status
Examples for using url function after the link command:
-
* | link status | eval ‘HTTP Status Code’ = url(‘https://www.google.com/search?q=http+code+’, Status, Status) -
* | link Type | stats latest(Status) as Status | eval ‘HTTP Status Code’ = url(‘[https://www.google.com/search?q=http+code+]’, Status, Status)
Oracle-Defined
url Short-Cuts
The following Oracle-defined short-cuts are available to use with the
url function for eval command.
| Short-Cut | URL and Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
|
ora search:oracle |
https://www.google.com/search?q=site:oracle.com%20Generate
a link to search all of |
|
|
tech oracle-tech |
https://community.oracle.com/tech/search?query=Generate a link to search Oracle technology forums |
|
|
mosc oracle-mosc |
https://community.oracle.com/mosc/search?query=Generate a link to search My Oracle Support forums |
|
https://www.google.com/search?q=Generate a link to search using Google |
|
|
| bing | https://www.bing.com/search?q=Generate a link to search using Bing |
|
|
ddg duckduckgo |
https://duckduckgo.com/?q=Generate a link to search using DuckDuckGo |
|
|
so stackoverflow |
https://stackoverflow.com/search?q=Generate a link to search at StackOverflow |
|
|
cve |
https://www.cve.org/CVERecord?id=Generate a link for the given CVE ID |
|