Metric Extensions
Introduction
Metric Extensions allow you to create full-fledged metrics on any resource type that is monitored by Stack Monitoring. Metric Extensions allow you to create custom metrics to monitor conditions specific to your IT environment. This provides you with a comprehensive view of your environment.
Creating Metric Extensions lets you simplify your IT organization's operational processes by leveraging Stack Monitoring as the single central monitoring tool for your entire environment instead of relying on other monitoring tools to provide this supplementary monitoring.
Metric Extension Lifecycle
Developing a Metric Extension follows the same phases you would expect from any programmatic customization.
Creating a Metric Extension involves the following phases:
-
- Create
- Test
- Edit
- Clone
- Export and Import
In this phase, after you create your Metric Extension, the Metric Extension is in draft status, which allows you to test it against resources and edit it accordingly.
-
Publishing a Metric Extension makes it available for general use, while edits are no longer possible.
-
Enabling Metric Extensions on Resources:
With your Metric Extension published, it can be deployed and enabled on your resources.
Working with Metric Extensions
Prerequisites
Certain policies are required to use Metric Extensions. For more information, see Create Policies for Metric Extension Operators.
Developing Metric Extensions
- Create Metric Extensions
- Test and Edit Metric Extensions
- Clone Metric Extensions
- Export and Import Metric Extensions
Create Metric Extensions
- From the Stack Monitoring menu, select Metric Extensions.
- Click Create Metric Extension. The Create Metric Extension UI panel displays.
-
Metric Extensions properties:
- Enter a Name for the Metric Extension. The Metric Extension name will always have an ME_ prefix.
Note
The Metric Extension name must be unique across a resource type. - Enter a Display name for the Metric Extension.
- Enter a Description of the Metric Extension.
- Enter a Name for the Metric Extension. The Metric Extension name will always have an ME_ prefix.
-
Collection method properties specify the resource type for the Metric Extension being created and other collection properties:
- Resource type: the resource type (e.g. Host, Container DB) for which you are creating the Metric Extension. For more information regarding resource types supported and their supported instance properties, see Resource Types supported and their supported instance properties.
- Collection frequency: specify how often the Metric Extension should be collected.
- Collection method: Specify the type of collection method needed to collect the Metric Extension. Following collection methods are supported. For details of each collection method and examples, see Collection Method Properties
- OS Command: This method executes the specified OS command or script and parses each command output line (delimited by a user-specified character) into multiple values. The metric result is a multi-row, multi-column table.
- SQL: This method executes custom SQL queries or function or SQL scripts against databases, returning results in a metric table.
- JMX: (Java Management Extensions) : This method retrieves JMX attributes from JMX-enabled servers and returns these attributes as a metric table.
- HTTP: This method invokes the specific HTTP(S) endpoint i.e. URL and uses the specified JavaScript file to transform the response as a metric table.
-
Metrics/dimensions:
For each of the values returned by running a Metric Extension, identify if the value is a metric or dimension along with its associated properties.
Note
- Values returned by custom scripts are expected to result in a multi-row, multi-column table.
- The output from each column should be identified as either a metric or dimension along with its associated attributes.
- A metric data point must be a number.
Metric dimensions should contain the following attributes:
- Name: specify the name of the metric or dimension having only english alphabets in PascalCase i.e. Every first letter of the word should be a capital letter with no spaces or numbers in between as per OCI monitoring requirements. Examples of a good metric name are CpuUtilization, TotalDatabaseSize , FileSystemUsage etc.
Note
Draft metrics can have the same names for the same resource type, but not in the case of published metrics . If a particular metric name for a resource type is already taken and is used in a published Metric Extension, then the same cannot be used by another metric which is part of any other published Metric Extension's name for the same resource type.
For example, if there is a published Metric Extension ME_FirstMetricExtension for resource type
host_linuxand it has a metric namedMetricFirst, then it is not allowed to publish another Metric Extension, ME_SecondMetricExtension for the same resource type,host_linuxwhich has a metric with nameMetricFirst.This constraint is not applicable to hidden metrics and dimensions.
- Display name (optional):specify the display name, if different from the name. Display name can carry spaces and numbers as well.
- Is dimension?: Choose No if you are defining a metric; choose Yes if you are defining a metric dimension.
A dimension is a qualifier for a metric and it should be a unique value for each row in the metric collection results. For example, a metric could be the Filesystem Usage percentage, and the dimension is the Filesystem Name.
- Is hidden? (Advanced): Choose Yes if the metric will only be used in Compute expressions, i.e. if the metric is used only as a value to compute another metric or it is not required to be sent to OCI Monitoring. Otherwise, choose No.
- Value type: All non-hidden metrics must be numeric; A hidden metric or dimension can be
StringorNumber. - Unit : The unit associated with the metric. Possible units could be, depending on the metric, latency in seconds, milliseconds, microseconds, minutes, or frequency in Hertz or percentage.
- Category: Identify the type of metric data the metric is collecting: Availability, Capacity, Load, Utilization
-
Compute expression: Use Compute expressions to calculate the value of a metric based on mathematical or logical operations performed on other metrics or dimensions within the same Metric Extension. Compute expressions require at least one other metric to be defined first, and can only include those other metrics that have already been defined in the Metric Extension. For additional details, see Compute Expressions.
-
Create and test or Create the Metric Extension
-
Create and test allows you to test your Metric Extension against one or more resources and verify the values returned are correct. Based on the values returned, you can continue to edit and test in an iterative manner.
Note
When testing a Metric Extension the Management Agent will be restarted. As a result it is recommended to test Metric Extensions on non-production resources.Note
If you find that a column is out of place, use to Reorder metrics/dimensions button to fix it. -
Create allows you to save the Metric Extension definition and test against resources at a later time.
-
Test and Edit Metric Extensions
- After creating the Metric Extension, it is in Draft status. While it is in Draft status, you can continue to edit the Metric Extension definition and test the Metric Extension against resources.
- Testing involves selecting a resource on which the metric can be tested. This process may take a few minutes as it involves deploying the Metric Extension to the resource's agents and running the metric collection against the resource.
Note
The resources on which you can test and later enable Metric Extensions need to be enabled with Stack Monitoring Enterprise Edition. For details, see Configuring Licensing.Note
When testing a Metric Extension, follow these guidelines:- Do not test on production environments.
- Allocate a test resource instance with its own Management Agent dedicated to testing. A query/script that is being tested in the Metric Extension could perform poorly and thus impact other Management Agent functionality.
- If testing results in a failure, repeat the steps to create the Metric Extensions.
- If testing is successful, verify that the metric values returned are correct.
If you find that a column is out of place, use to Reorder metrics/dimensions button to fix it.
Clone Metric Extensions
Cloning a Metric Extension allows the development of a new Metric Extension from an existing one.
For a Metric Extension in Draft or Published status, from the row-level menu select Clone, which opens the Create Metric Extensions UI panel. All information from the original Metric Extension is filled in but the Name, which is the name of the original Metric Extension followed by Clone. Edit the parameters as needed and finalize by following the rest of the process for Create Metric Extensions.
Export and Import Metric Extensions
Importing and exporting Metric Extensions allows more flexibility in working with Metric Extensions such as sharing them between compartments and storing Metric Extensions locally.
-
To export Metric Extensions:
- For a Metric Extension in Draft or Published status, from the row-level menu select Export to locally save the Metric Extension.
- The default name of the file includes a time stamp and
MetricExtensions-Exportprefix. Edit the name of the export file as needed and click Save.
- To import Metric Extensions, click the Import Metric Extension and select the Metric Extension file to be imported.
Note
When importing a Metric Extension, ensure that the file is usingschemeVersiongreater than or equal to1.0.0.
Publishing Metric Extensions
Metric Extensions are not available for general use until they are published. After testing and verifying the results of your Metric Extension, you may now publish it. Once a Metric Extension is published, it can be enabled on your resources.
Once a Metric Extension is published, it CANNOT be edited nor tested any longer.
Enabling Metric Extensions on Resources
Once your Metric Extension has been published, it can be enabled and deployed to intended resources. When enabling the Metric Extension, it is deployed to the agent that is monitoring the resource, which starts metric collection on the resource.
To enable Metric Extensions on resources:
- Choose the published Metric Extension from the list of Metric Extensions.
- From the row-level action menu select Enable.
- Choose the resources on which you want to start the metric collection.
Note
The resources on which you can enable Metric Extensions must have the Enterprise Edition license set on it. For details, see Configuring Licensing. - The process of enabling a Metric Extension on a resource may take a few minutes as it involves deploying the Metric Extension to the agent, and starting the metric collection on the chosen resources. Make sure you stay on the page to track the status of the enable request.
Note
When deploying Metric Extension to agent for the first time (as part of enabling a Metric Extension on a resource), the deployment can take up to two minutes, this may result in the agent restarting, and hence you may see agent not reporting status for all of the resources monitored by that agent for the duration of the two minutes.
Viewing Metric Extensions
After the Metric Extension has been enabled on a resource, it will automatically show up in the performance charts of its homepage. You can identify the Metric Extension by locating the * symbol next to the metric name.
Metric data from the Metric Extension is stored in the same compartment as the resource on which it is enabled under the namespace oracle_metric_extensions_appmgmt.
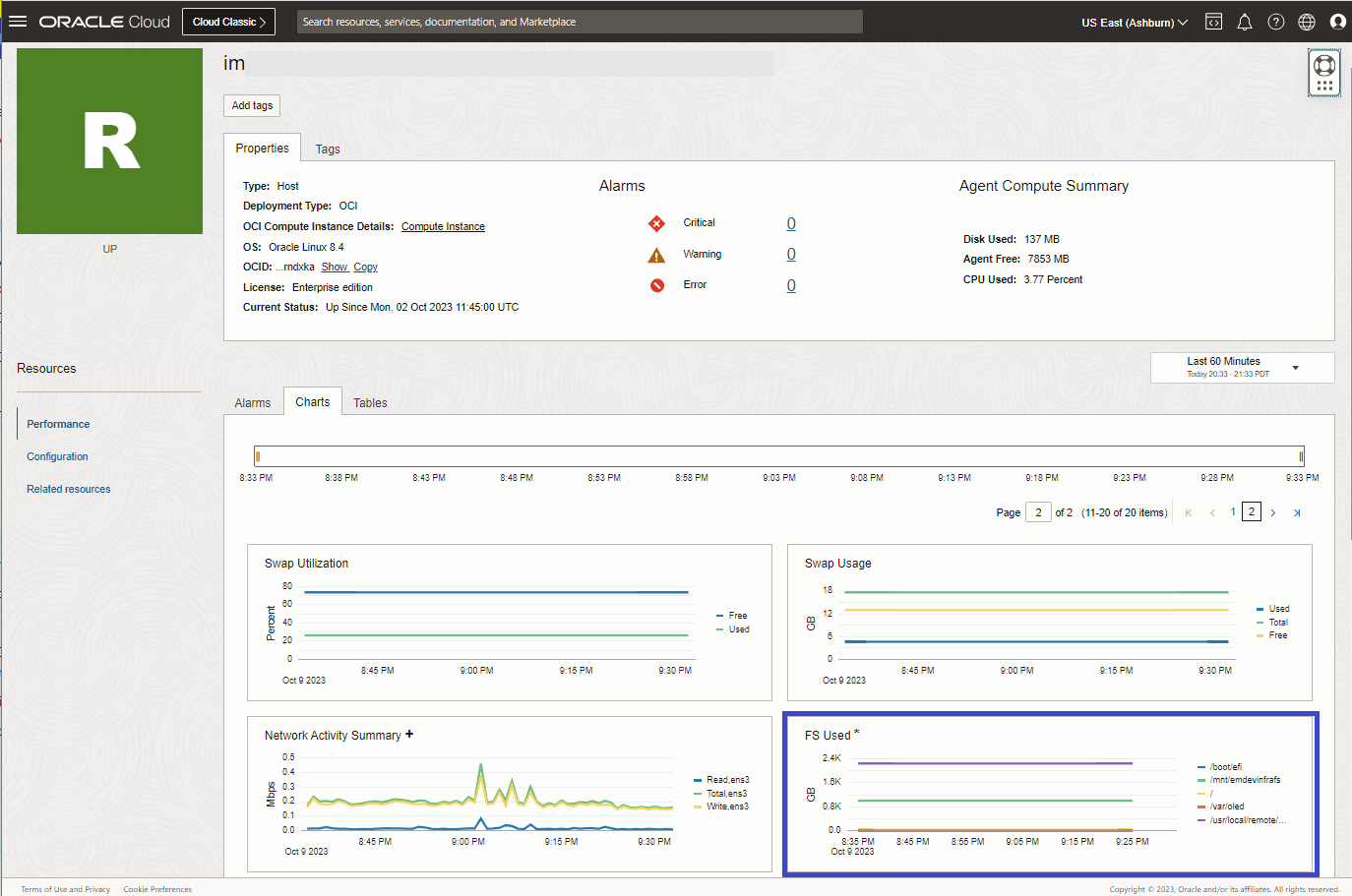
In Enterprise Health and Alarms, to show the Metric Extension in any of the charts:
- Customize the chart by clicking on the pencil icon.
- In the edit dialog that comes up, choose:
- Namespace:
oracle_metric_extensions_appmgmt - Resource type: the type of the resource on which the Metric Extension was created.
- Metric name: the metric from your Metric Extension.
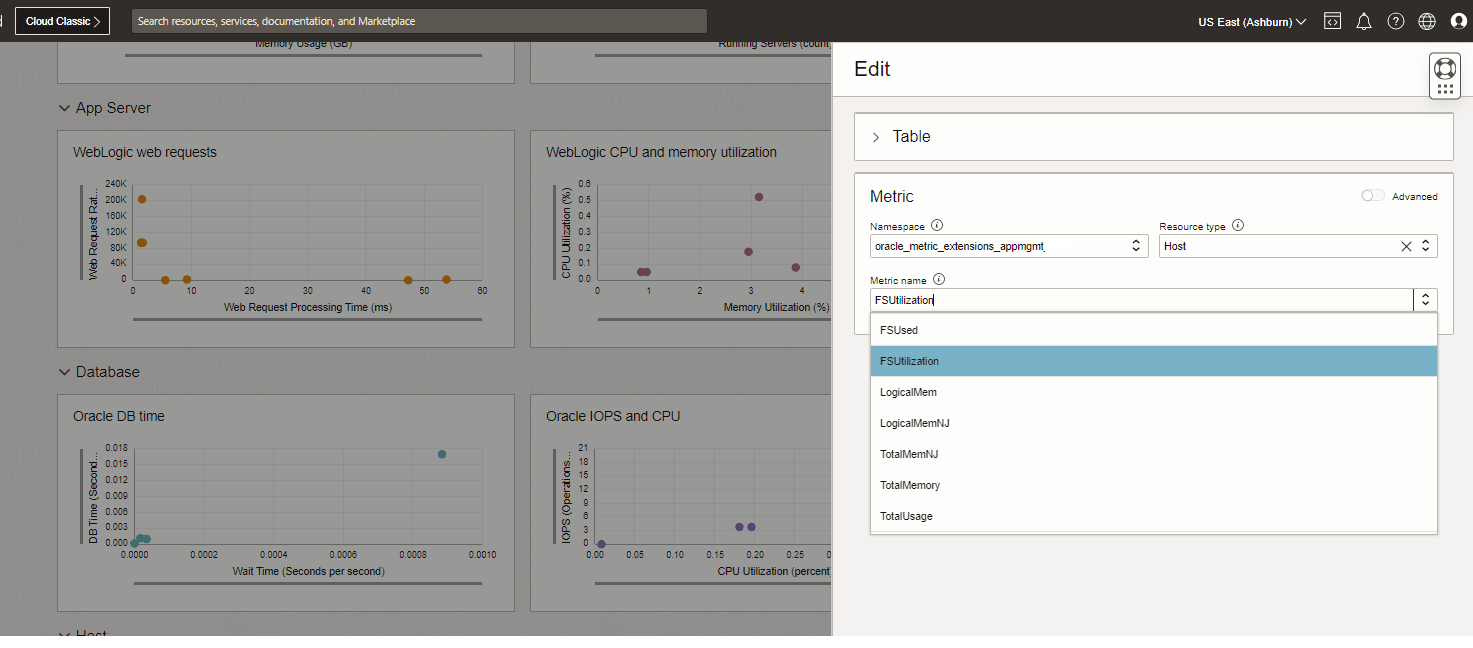
- Namespace:
Metric Extension Parameters
- Resource Types supported and their supported instance properties
- Collection Method Properties
- Compute Expressions
Resource Types supported and their supported instance properties
| Resource Type Display Name | Resource Type | Plugin Belongs to | Collection Methods Supported | Instance Properties List |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Apache HTTP Server | apache_http_server | appmgmt | OS_COMMAND, HTTP | compartmentId,metric_endpoint,httpd_conf_path,httpd_bin_path,httpd_pid_path,protocol,listen_port,os_type |
| Apache Tomcat | apache_tomcat | appmgmt | OS_COMMAND, JMX | compartmentId,service_url |
| ASM | oci_oracle_asm | dbaas | OS_COMMAND, SQL | |
| Cluster Instance | oci_oracle_cluster_instance | dbaas | OS_COMMAND | oracleHome |
| Container DB | oci_oracle_cdb | dbaas | OS_COMMAND, SQL | |
| EBS | ebs_instance | appmgmt | OS_COMMAND, SQL | hostname,db_port,db_sid,db_host,db_service,allowed_logon_version,app_schema,long_running_request_threshold_in_minutes |
| EBS Application Listener | oracle_ebs_app_lsnr | appmgmt | OS_COMMAND | listener_ora_directory,oracle_home,tns_control |
| EBS Concurrent Processing | oracle_ebs_conc_mgmt_service | appmgmt | OS_COMMAND, SQL | db_host,db_port,db_sid,app_schema,service_name,allowed_logon_version,long_running_request_threshold_in_minutes |
| EBS Concurrent Processing - Specialized | oracle_ebs_conc_mgmt_service_specialized | appmgmt | OS_COMMAND, SQL | db_host,db_port,db_sid,app_schema,service_name,allowed_logon_version |
| EBS Forms System | oracle_ebs_forms_system | appmgmt | OS_COMMAND, SQL | db_host,db_port,db_sid,app_schema,service_name,allowed_logon_version |
| EBS Workflow Agent Listener | oracle_ebs_wf_agent_lsnr | appmgmt | OS_COMMAND, SQL | db_host,db_port,db_sid,app_schema,service_name,allowed_logon_version |
| EBS Workflow Background Engine | oracle_ebs_wf_bkgd_engine | appmgmt | OS_COMMAND, SQL | db_host,db_port,db_sid,app_schema,service_name,allowed_logon_version |
| EBS Workflow Notification Mailer | oracle_ebs_wf_notification_mailer | appmgmt | OS_COMMAND, SQL | db_host,db_port,db_sid,app_schema,service_name,allowed_logon_version |
| Elasticsearch | elastic_search | appmgmt | OS_COMMAND, HTTP | es_base_url |
| GoldenGate | oracle_goldengate | appmgmt | OS_COMMAND, HTTP | ogg_url,compartmentId |
| GoldenGate Admin Service | oracle_goldengate_admin_server | appmgmt | OS_COMMAND, HTTP | compartmentId,process_name,api_process_name,pm_server_url,deployment_path |
| GoldenGate Deployment | oracle_goldengate_deployment | appmgmt | OS_COMMAND, HTTP | compartmentId,ogg_url,ogg_hostname,ogg_port |
| GoldenGate Distribution Path | oracle_goldengate_distribution_path | appmgmt | OS_COMMAND, HTTP | compartmentId,distribution_server_url,path_name,deployment_path |
| GoldenGate Distribution Service | oracle_goldengate_distribution_server | appmgmt | OS_COMMAND, HTTP | compartmentId,process_name,api_process_name,pm_server_url,deployment_path |
| GoldenGate Extract | oracle_goldengate_extract | appmgmt | OS_COMMAND, HTTP | pm_server_url,process_name,api_process_name,compartmentId,deployment_path |
| GoldenGate Performance Metric Service | oracle_goldengate_pm_server | appmgmt | OS_COMMAND, HTTP | compartmentId,pm_server_url,process_name,api_process_name,deployment_path |
| GoldenGate Receiver Path | oracle_goldengate_receiver_path | appmgmt | OS_COMMAND, HTTP | receiver_server_url,path_name,compartmentId,deployment_path |
| GoldenGate Receiver Service | oracle_goldengate_receiver_server | appmgmt | OS_COMMAND, HTTP | compartmentId,process_name,api_process_name,version,pm_server_url,deployment_path |
| GoldenGate Replicat | oracle_goldengate_replicat | appmgmt | OS_COMMAND, HTTP | compartmentId,pm_server_url,api_process_name,process_name,deployment_path |
| GoldenGate Service Manager | oracle_goldengate_service_manager | appmgmt | OS_COMMAND, HTTP | ogg_url,ogg_hostname,ogg_port,compartmentId,service_manager_url |
| GPU | gpu | appmgmt | OS_COMMAND | pciId |
| Host - Linux | host_linux | appmgmt | OS_COMMAND | compartmentId,hostType,osType |
| Host - Solaris | host_solaris | appmgmt | OS_COMMAND | compartmentId,hostType,osType |
| Host - Windows | host_windows | appmgmt | OS_COMMAND | compartmentId,hostType,osType |
| Listener | oci_oracle_lsnr | dbaas | OS_COMMAND | oracleHome,lsnrType,alias |
| Microsoft Internet Information Services | microsoft_iis | appmgmt | OS_COMMAND | compartmentId,hostname,total_cpus,total_memory |
| Microsoft Internet Information Services Website | microsoft_iis_website | appmgmt | OS_COMMAND | compartmentId,hostname,id,website_name |
| Microsoft SQL Server | sql_server | appmgmt | OS_COMMAND, SQL | compartmentId,inst_name,hostname,port,root_dir,os_platform,os_distro,os_release,time_zone,version |
| Non-Container DB | oci_oracle_db | dbaas | OS_COMMAND, SQL | |
| OpenSearch | open_search | appmgmt | OS Command, HTTP | os_base_url |
| Oracle Access Management Cluster** | oracle_oam_cluster | appmgmt | OS_COMMAND, JMX | app_name,server_names,service_url |
| Oracle Access Management** | oracle_oam | appmgmt | OS_COMMAND, JMX | app_name,server_names,service_url,weblogic_home |
| Oracle HTTP Server | oracle_http_server | appmgmt | OS_COMMAND | compartmentId,service_url,name,version,domain_name,node_manager_hostname,node_manager_port,ohs_home_path,type,owner_credentials |
| Oracle Identity Manager Cluster** | oracle_oim_cluster | appmgmt | OS_COMMAND, JMX | service_url,app_name,server_names,version |
| Oracle Identity Manager** | oracle_oim | appmgmt | OS_COMMAND, JMX | hostname,service_url,app_name,server_names,version,weblogic_home |
| Oracle JVM Runtime | oracle_jvm | appmgmt | OS_COMMAND, JMX | compartmentId,service_url |
| Oracle Managed File Transfer** | oracle_mft | appmgmt | OS_COMMAND, SQL | server_name,service_url,db_schema_name,db_port,db_sid,db_host,db_service_name |
| Oracle Service Bus (OSB)** | oracle_servicebus | appmgmt | OS_COMMAND, JMX | compartmentId,name,server_name,oracle_home,version,service_url |
| Oracle WebLogic Cluster** | weblogic_cluster | appmgmt | OS_COMMAND, JMX | compartmentId,service_url,server_names,name,version,dms_spy |
| Oracle WebLogic Domain** | weblogic_domain | appmgmt | OS_COMMAND, JMX | admin_server_host,admin_server_port,admin_server_protocol,admin_service,admin_service_url |
| Oracle WebLogic Server** | weblogic_j2eeserver | appmgmt | OS_COMMAND, JMX | compartmentId,service_url,name,version,dms_spy |
| Pluggable DB | oci_oracle_pdb | dbaas | OS_COMMAND, SQL | |
| PSFT Application | oracle_psft | appmgmt | OS_COMMAND, SQL | hostname,db_port,db_sid,db_host,db_service_name,peoplesoft_json_file,allowed_logon_version |
| PSFT Application Server Domain | oracle_psft_appserv | appmgmt | OS_COMMAND, JMX | hostname,jmx_url,ps_cfg_home,app_server_domain |
| PSFT Application Server Group | oracle_psft_appserv_group | appmgmt | OS_COMMAND | hostname,db_port,db_host,db_service |
| PSFT PIA | oracle_psft_pia | appmgmt | OS_COMMAND, JMX | ostname,jmx_url,ps_cfg_home,pia_domain |
| PSFT PIA Group | oracle_psft_pia_group | appmgmt | OS_COMMAND | hostname,db_port,db_host,db_service |
| PSFT Process Monitor | oracle_psft_prcm | appmgmt | OS_COMMAND, SQL | db_host,db_port,db_service_name |
| PSFT Process Scheduler Domain | oracle_psft_prcs | appmgmt | OS_COMMAND, JMX | hostname,jmx_url,ps_cfg_home,prcs_domain |
| PSFT Process Scheduler Group | oracle_psft_prcs_group | appmgmt | OS_COMMAND | hostname,db_port,db_host,db_service |
| SOA Infrastructure** | oracle_soainfra | appmgmt | OS_COMMAND, JMX | compartmentId,name,server_name,version,service_url |
** Some resource types also support remote monitoring. However, they support local monitoring as well, hence OS Command is available only for those resource instances that are being monitored locally by their respective management agent.
Collection Method Properties
OS Command collection method- Command: The command to execute. For example:
/bin/bash- for Linuxcmd.exe- for Windows
The complete command line will be constructed as:
Command + Script + Arguments.Before using any script, ensure the command/script being invoked is not destructive.
Note
Use shell commands inside the script content, as they cannot be directly used as part of command value. - Delimiter for output: The string used to delimit the command output. An example delimiter could be
|. - Arguments: Arguments to the script or command separated by a space.
Note
Instance property of a resource type can be passed as argument by placing it inside two%symbols. For example in case ofhost_linuxresource type,osTypeis an applicable instance property. In case, you are required to pass value of this instance property as argument to the script then argument property can be set to%osType%. List of available instance properties is given in the Resource Types supported and their supported instance properties table. - Prefix for output: The starting string of metric result lines.
For example, if the command output is:
sm_result= 3454 | abc | defsetting thePrefix for output = sm_resultspecifies that only lines starting withsm_resultwill be used to gather metric data. - Script file: Custom script executed to generate the metric data .
The creation parameters of a Metric Extension for a listener resource type which captures the handler load, maxload, established, refused, handler ids and connection rate for every service using an OS Command collection method is described bellow:
-
Metric Extension properties:
Property Name Property Value Name ME_GetListenerDetails Display name Get Listener Details Description A Metric Extension for listener resource type which captures the handler load, maxload, established, refused, handler ids and connection rate for every service
-
Collection method properties:
oracleHome , alias and lsnrType are instance properties of Listener resource type used in the Arguments property inside
%symbols. Here%symbols are used to hold the instance property referencesProperty Name Property Value on UI Property Value on API (ONLY if different from UI) Resource type Listener oci_oracle_lsnr Collection method OS Command OS_COMMAND Collection frequency 15 Minutes FREQ=MINUTELY;INTERVAL=15 Command /bin/bash Delimiter | Arguments %oracleHome% %alias% %lsnrType% Prefix for output result= Script file services.sh
-
"content" - Should carry base64 encoded content of services.sh
- "name" : services.sh
-
-
Metrics/dimensions:
Metric/dimension Metric/dimension Properties TotalRefusedConnections -
Value type: Number
-
Is dimension?: No
-
Is hidden?: No
TotalEstablishedConnections -
Value type: Number
-
Is dimension?: No
-
Is hidden?: No
MaxConnections -
Value type: Number
-
Is dimension?: No
-
Is hidden?: No
-
Unit: Connections
HandlerId -
Value type: String
-
Is dimension?: Yes
-
Is hidden?: No
EstablishedConnectionsRate -
Value type: Number
-
Is dimension?: No
-
Is hidden?: No
- Compute Expression:
(TotalEstablishedConnections > _TotalEstablishedConnections) ? ((TotalEstablishedConnections - _TotalEstablishedConnections) / __interval) : 0 -
Unit: Connections per second
- __interval can be used to derive rate metrics. Please note __interval is always equal to "seconds" representation of the "Collection frequency" field. For example, if Collection frequency is 15 minutes then __interval is 15x60 i.e. 900 seconds.
- "_" when prefixed to a Metric name has a special meaning. Such representation in compute expressions can be used to refer to the value of a metric as calculated in the last collection of a Metric Extension. This can be used in compute expressions to derive change in a particular metric's value in comparison to its last collected value. This special prefix can be used to derive delta metrics.
ActiveConnections -
Value type: Number
-
Is dimension?: No
-
Is hidden?: No
-
Unit: Connections
-
SQL Collection Method
- SQL query: The sql query to execute. For example,
select a.ename, (select count(*) from emp p where p.mgr=a.empno) directs from emp a.PL/SQL statements are also supported, and if used, the Out parameter position and Out parameter type properties should be populated. Bind variables can be passed to sql query using In parameter properties.
- SQL Script: Upload the required sql script to execute and provide the relevant In parameter and Out parameter properties. You can use either of SQL query or SQL script.
- In parameter (optional) - These can be used provide the bind variable for SQL query case or in parameters for SQL script case.
Note
This property supports use of instance property place holder which can be used to replace the placeholder with actual value of instance property of the resource for which metric is being collected. For example fororacle_psft,db_service_nameis an instance property. It can be passed inside an In parameter value within a pair of%(percentage) symbols, such as%db_service_name%. - Out parameter position (optional) - This is the position number of out parameter
- Out parameter type (optional) - This is the type of out parameter.
The creation parameters of a Metric Extension for Non-container DB resource type which captures the Wait Time for different wait classes using a SQL collection method is described below:
-
Metric Extension properties:
Property Name Property Value Name ME_GetWaitTime Display name Get Wait Time Description A Metric Extension for Non-container DB resource type which captures the
Wait Time for different wait classes
-
Collection method properties:
Property Name Property Value on UI Property Value on API (ONLY if different from UI) Collection frequency 1 Hours FREQ=HOURLY;INTERVAL=1 Collection method SQL Resource type Non-Container DB oci_oracle_db SQL query WITH wait_stats AS ( SELECT inst_id, wait_class, time_waited_fg FROM TABLE ( gv$(CURSOR( SELECT to_number(userenv('INSTANCE')) AS inst_id, wait_class, time_waited_fg / 100 AS time_waited_fg FROM v$system_wait_class WHERE wait_class <> 'Idle' )) ) ), inst_list AS ( SELECT instance_number, instance_name, host_name FROM TABLE ( gv$(CURSOR( SELECT instance_number, instance_name, host_name FROM v$instance )) ) ) SELECT inst.instance_number instance_number, inst.instance_name instance_name, inst.host_name host_name, ws.wait_class wait_class, ws.time_waited_fg time_waited_fg FROM wait_stats ws, inst_list inst WHERE inst.instance_number = ws.inst_id-
"content" - Should carry base64 encoded SQL statement
- sqlType : STATMENT
-
-
Metric/dimensions:
Metric/dimension Metric/dimension Properties InstanceNumber -
Value type: Number
-
Is dimension?: Yes
-
Is hidden?: No
InstanceName -
Value type: String
-
Is dimension?: Yes
-
Is hidden?: No
HostName -
Value type: String
-
Is dimension?: Yes
-
Is hidden?: No
WaitClass -
Value type: String
-
Is dimension?: Yes
-
Is hidden?: No
TimeWaitedSeconds -
Value type: Number
-
Is dimension?: No
-
Is hidden?: No
-
Unit: Seconds
-
JMX collection method
- MBean name - JMX MBean ObjectName or Metric Service table name.
Note
This property supports use of instance property place holder which can be used to replace the placeholder with actual value of instance property of the resource for which metric is being collected. For example for
weblogic_j2eeserver,service_urlis an instance property. It can be passed inside MBean name value string within%symbols, such as%service_url%.JMX attributes and Identity column also support use of instance property placeholder.
- JMX attributes - Java Management Extensions (JMX) attributes. List of JMX attributes or Metric Service columns, separated by semi-colon.
- Identity column (Optional) - Semi-colon separated list of key properties from Managed Bean ObjectName to be used as key metrics.
- Auto row prefix (Optional) - This is prefix used for an automatically generated row as key metrics. For example : if it is set to ShipItem-, then values will be set as ShipItem-0, ShipItem-1 and so on.
- Metric service Enabled on Server domain ? (Optional) - Indicates whether Metric Service is enabled on server domain. If set to true, then the basic property
MBean nameshould represent theMetric Servicetable name and the basic propertyJMX attributeswill represent a semi colon separated list of column names forMetricServicetable.Note
Check this option only when you have Metric Service applicable to the resource type and enabled on the server domains.
The creation parameters of a Metric Extension for an oracle weblogic server resource type which captures the collection time of the Garbage Collector using JMX collection method.
-
Metric Extension properties:
Property Name Property Value Name* ME_TotalGcExecutionTime Display name* Get Total Garbage Collection Time Description A Metric Extension for oracle weblogic server resource type which captures the
total garbage collection execution time
-
Collection method properties:
Here name is an instance property of Oracle Weblogic Server and is being used inside
%instance property placeholder insideMbean nameattribute of JMX type Metric Extension definition.Property Name Property Value on UI Property Value on API (ONLY if different from UI) Resource type Oracle WebLogic Server weblogic_j2eeserver Collection method JMX Collection frequency 1 Days FREQ=DAILY;INTERVAL=1 Mbean name java.lang:Location=%name%,type=GarbageCollector,* JMX attributes CollectionTime Identity column name;Location -
Metrics/dimensions:
Metric/dimension Metric/dimension Properties ServerName -
Value type: String
-
Is dimension?: Yes
-
Is hidden?: No
ServerRuntime -
Value type: String
-
Is dimension?: Yes
-
Is hidden?: No
TotalGCExecTime -
Value type: Number
-
Is dimension?: No
-
Is hidden?: No
-
Unit: milliseconds
-
HTTP collection method
- URL: The http(s) endpoint which needs to be invoked to get raw metric data. For example:
%metric_endpoint%?auto=dummyNote
This property supports use of instance property place holder which can be used to replace the placeholder with actual value of instance property of the resource for which metric is being collected. In above example,metric_endpointis an instance property of Apache HTTP Server resource type and is mentioned within a pair of%(percentage) symbols. When Metric Extension runs, then actual value of%metric_endpoint%is replaced with the instance property value of respective resource. - Response Type: Type of response returned by the http(s) endpoint. Following types of responses are supported :
text/plaintext/htmlapplication/jsonapplication/xml
- Protocol (optional) : This is applicable only in case of Apache HTTP Server and needs to be set according to the protocol used while discovering an Apache HTTP Server resource.
httporhttpsare the two possible values. For all other resource types, this property can only be set tohttps, which is the default value as well.Note
An HTTP Metric Extension defined with protocol valuehttpcan be enabled only for those Apache HTTP Server resources that were discovered with a matching protocol value,httporhttps, respectively. - Script File : A JavaScript file that converts URL response into meaningful metric data. This file must have a function called
runMethodwith a pre-defined signature. This function must always return a two dimensional array, which is carrying the transformed data that exactly maps to the metrics and dimensions defined in the Metric Extension.Parameters of
runMethod(metricObservation, sourceProps):Parameter Description metricObservationResponse from the URL which is needed to generate metric data. sourcePropsList of key-value pair and carries instance properties of the resource for which Metric Extension is getting executed. Functional requirement of
runMethod:- Parse response from the URL which is contained in parameter
metricObservation. - Generate required metric/dimension data and return it in a two dimensional array.
- Use
sourceProps, if required, to implement the functional logic.
- Parse response from the URL which is contained in parameter
Example:
The creation parameters of a Metric Extension for Apache HTTP Server resource type which captures the CacheRetrievesCount for Hit and Miss cases using a HTTP collection method is described below:
- Metric Extension properties:
Property Name Property Value Name ME_GetCacheRetrievesCount Display name Get Cache Retrieves Count Description A Metric Extension for Apache HTTP Server resource type which captures the CacheRetrievesCount for Hit and Miss cases
- Collection method properties:
Property Name Property Value on UI Property Value on API (ONLY if different from UI) Collection frequency 1 Hours FREQ=HOURLY;INTERVAL=1 Collection method HTTP Resource type Apache HTTP Server apache_http_server URL %metric_endpoint%?auto=dummy Response Type text/plain TEXT_PLAIN Protocol Type http Script File const METRIC_NAMES = ["CacheRetrieveMissCount", "CacheRetrieveHitCount"];
function runMethod(metricObservation, sourceProps)
{
const metrics = {};
const metricOutput = metricObservation;
/*
Parse URL response available in metricObservation
Following is a portion of sample response:
************************
TLSSessionCacheStatus
CacheType: SHMCB
CacheSharedMemory: 512000
CacheCurrentEntries: 0
CacheSubcaches: 32
CacheIndexesPerSubcaches: 88
CacheIndexUsage: 0%
CacheUsage: 0%
CacheStoreCount: 5
CacheReplaceCount: 0
CacheExpireCount: 5
CacheDiscardCount: 0
CacheRetrieveHitCount: 0
CacheRetrieveMissCount: 104
CacheRemoveHitCount: 0
CacheRemoveMissCount: 0
************************
*/
const lines = metricOutput.trim().split("\n");
for (const line of lines) {
const lineParts = line.trim().split(": ");
if (lineParts.length === 2 && METRIC_NAMES.includes(lineParts[0])) {
metrics[lineParts[0]] = parseFloat(lineParts[1]);
}
}
/*
Generate two dimensional array having values for dimension CacheRetrievesType and metric CacheRetrievesCount
*/
return [['Hit', metrics["CacheRetrieveHitCount"]],
['Miss', metrics["CacheRetrieveMissCount"]]];
}
- "content" - Should carry base64 encoded content of JavaScript file
- "name" : ahs_cacheRetrieves.js
- Metric/dimensions:
Metric/dimension Metric/dimension Properties CacheRetrievesType - Value type: String
- Is dimension?: Yes
- Is hidden?: No
CacheRetrievesCount - Value type: Number
- Is dimension?: No
- Is hidden?: No
Compute Expressions
To create valid compute expressions, you must give space between operators and operands/metric names.
Example:
((MetricA * MetricB) / MetricC)
Please note the use of space between MetricA and the * symbol. Similarly, a space is important between * and MetricB, between closing parenthesis and / symbol and / symbol and MetricC.
The following table shows operators which can be used while defining compute expression:
| Operator | Example | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| != | MetricA != 1 | Returns false if the value of MetricA is 1, else returns true. |
| % | MetricA % MetricB | Returns the remainder when value of MetricA is divided by MetricB |
| () ? : | (MetricA == 'UP') ? 1: 0 | This operator is equivalent to if then else statement. This expression will return 1 if MetricA value is 'UP' otherwise it will return 0. |
| * | (MetricA * MetricB) + MetricC | First multiply MetricA and MetricB values, then add MetricC value and return the result. |
| + | MetricA + MetricB | Returns the sum of the values of MetricA and MetricB. |
| - | (MetricA + MetricB) - MetricC | First add MetricA and MetricB values, then subtract MetricC value and return the result. |
| / | (MetricA + MetricB) / 2 | Returns the average of MetricA and MetricB values. |
| < | MetricA < MetricB | Returns true if the value of MetricA is less than MetricB, else returns false. |
| <= | MetricA <= MetricB | Returns true if the value of MetricA is less than or equal to MetricB, else returns false. |
| == | MetricA == 1 | Returns true if the value of MetricA is 1, else returns false. |
| > | MetricA > MetricB | Returns true if the value of MetricA is greater than MetricB, else returns false. |
| >= | MetricA >= MetricB | Returns true if the value of MetricA is greater than or equal to MetricB, else returns false. |
| __beginswith | MetricA __beginswith 'ORA-' | Returns true if the value of MetricA starts with the string 'ORA-', else returns false. |
| __ceil | __ceil MetricA | Returns the value of MetricA rounded off to the largest integer. |
| __contains | MetricA __contains 'ORA-' | Returns true if the value of MetricA contains the string 'ORA-', else returns false. |
| __delta | __delta MetricA | Returns the difference between the current value and the previous value of MetricA. |
| __floor | __floor MetricA | Returns the value of MetricA rounded off to the lowest integer. |
| __interval | MetricA / __interval | Returns the MetricA value divided by the collection interval. |
| __is_null | __is_null MetricA | Returns true if the value of MetricA is NULL, else returns false. |
| __length | __length MetricA | Returns the length of string value of MetricA. |
| __matches | MetricA __matches 'UP' | Returns true if the value of MetricA is equal to 'UP', else returns false. |
| __round | __round MetricA | This expression will round the value of MetricA to the nearest integer, away from zero. |
| __to_lower | __to_lower MetricA | Returns the lower case of string value of MetricA. |
| __to_upper | __to_upper MetricA | Returns the upper case of string value of MetricA |
Usage of Operators:
This attribute specifies the formula for calculating the value of the metric. Metrics previously defined in the Metric Extension can participate in the calculation.
Refer to the examples for details about the expression grammar and usage.
Predefined special values:
For string expression inputs required for certain operators, provide the input value inside single quotes ( ' ).
- __interval: collect interval. Its collection frequency is represented in seconds.
- __sysdate: current system time.
- _metricName : Refers to value of metric during its previous collection. While
metricNameneeds to be replaced with actual metric's name. - __GMTdate: current GMT time.
- __contains: tests a given string expression for presence of a string expression. .
- __beginswith: tests whether a given string expression begins with a specified string expression.
- __endswith: tests whether a given string expression ends with the specified string expression.
- __matches: tests whether a given string expression matches a specified string expression.
- __delta: computes the difference between the current value and the previous value.
- __leadingchars: returns the leading characters in the specified string.
- __trailingchars: returns the trailing characters in the specified string.
- __substringpos: returns the position of the occurrence of the pattern within a specified string.
- __is_null: tests whether the expression is NULL
- __is_notnull : tests whether the expression is NOT NULL
- __length: returns the length of the string expression.
- __to_upper: converts the string to upper case.
- __to_lower: converts the string to lowercase.
- __ceil: returns the smallest integral value not less than identifier.
- __floor: returns the largest integral value not greater than the identifier.
- __round: rounds to nearest integer, away from zero.
Examples:
NAME="Average" COMPUTE_EXPR="(MetricA + MetricB )/ 2"The value of the metric is the average of the other two metrics MetricA and MetricB.
-
NAME="Version" COMPUTE_EXPR="(MetricA __contains 'NetApp Release 7.') ? 7.0 : 6.0"The value of the metric Version is computed as 7.0 if metric MetricA contains the String NetApp Release 7.
-
NAME="MetricA" COMPUTE_EXPR="(MetricB - MetricC)"The value of the metric MetricA is the difference of the columns MetricB and MetricC.
-
NAME="Status" COMPUTE_EXPR="State __matches 'STARTED'"The value of the metric Status is 1 if the value of column State matches the String STARTED and 0 otherwise.
-
NAME="MetricA" COMPUTE_EXPR="(__is_null MetricB)?'yes':'no'"The value of the column MetricA is yes if the value of Metric2 is null and no otherwise.
-
NAME="Source" COMPUTE_EXPR="((__length result) == 0) ? 'empty' : result"The value of the metric Source is string empty if the length of string value of metric result is 0, else it is the value of the metric result itself.
-
NAME="Rate" COMPUTE_EXPR="(__ceil (MetricA/__interval))"The value of the metric Rate is the value of metric MetricA divided by the collection interval, rounded up to the largest integer.
-
NAME="MetricA" COMPUTE_EXPR="((MetricB == 0) ? 0 : ((MetricC / (MetricB / 8)) * 100.0))"The value of the MetricA is 0 if MetricB is equal to 0 , else value of MetricA is 100* MetricC divided by 1/8th of MetricB the computed based on MetricB and MetricC are using above formula when MetricB is not equal to 0, otherwise it is 0.
-
NAME="PERCENTAGE_VALUE" COMPUTE_EXPR="(Metric1 != 0) ? 100.0*(Metric2/Metric1) : 0"The value of the column is the total percentage of disk available where Metric1 and Metric2 are existing metrics in the Metric Extension.
-
NAME="RATE_OF_CHANGE" COMPUTE_EXPR="((MetricA - _MetricA) / __interval)"The delta and rate of a metric can be generated inside a compute expression by subtracting its previously collected value from current collected value to get the delta and dividing the delta by __interval to get the rate.
Creating Alarms on Metric Extensions
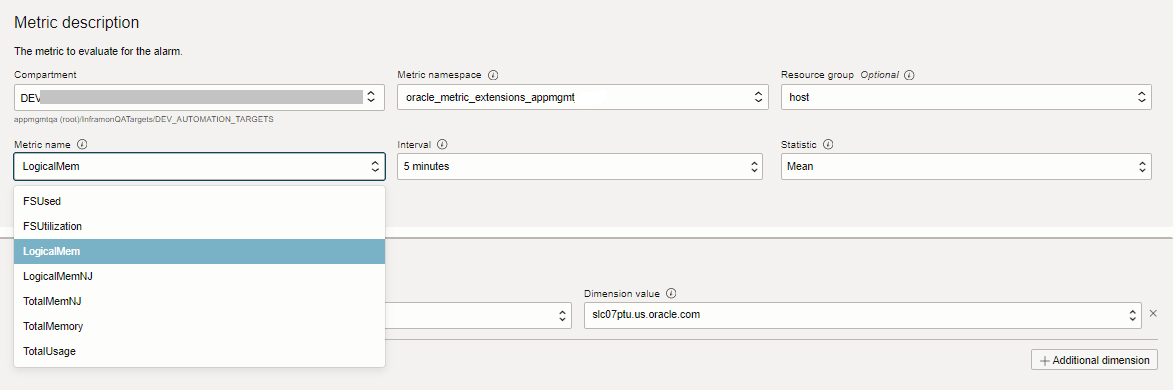
You can create alarm rules to trigger alarms when metric values from your Metric Extensions cross thresholds. Use the same general workflow that you would follow to create an alarm rule for built-in metrics for your resources. The main difference is in the Metric description section.
In the Metric description section of the Alarm rule:
- Compartment: choose the compartment of the resource on which the Metric Extension was enabled
- Metric namespace: select
oracle_metric_extensions_appmgmt - Resource group: the resource type of the resource on which the Metric Extension was enabled.
Creating an Alarm rule for a Metric Extension of a host is shown in the image below: