For All US Government Cloud Customers
This topic contains information common to both the Oracle US Government Cloud and to the Oracle US Defense Cloud.
Shared Responsibilities
Oracle Cloud Infrastructure for government offers best-in-class security technology and operational processes to secure its enterprise cloud services. However, for you to securely run workloads , you must be aware of your security and compliance responsibilities. By design, Oracle provides security of cloud infrastructure and operations (cloud operator access controls, infrastructure security patching, and so on), and you're responsible for securely configuring cloud resources. Security in the cloud is a shared responsibility between you and Oracle.
For more information about shared responsibilities in the Oracle Cloud, see Shared Security Model.
Setting Up an Identity Provider for Your Tenancy
As a Government Cloud customer, you must bring your own identity provider that meets your agency's compliance requirements and supports common access card/personal identity verification card (CAC/PIV) authentication. You can federate Oracle Cloud Infrastructure with SAML 2.0 compliant identity providers that also support CAC/PIV authentication. For instructions on setting up a federation, see Federating with Identity Providers.
Remove the Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Default Administrator User and Any Other Non-Federated Users
When your organization signs up for an Oracle account and Identity Domain, Oracle sets up a default administrator for the account. This person is be the first IAM user for your company and has full administrator access to your tenancy. This user can set up your federation.
After you have successfully set up the federation with the chosen identity provider, you can delete the default administrator user and any other IAM service local users you might have added to help with setting up your tenancy. Deleting the local, non-federated users ensures that only users in the chosen identity provider can access Oracle Cloud Infrastructure.
To delete the default administrator:
-
Sign in to the Console through your identity provider.
More details-
Open a supported browser and go to the Government Cloud Console URL.
- Enter your Cloud Tenant and click Continue.
-
On the Single Sign-On pane, select your identity provider and click Continue. You're redirected to the identity provider to sign in.
- Enter your username and password.
-
- Open the navigation menu and select Identity & Security. Under Identity, select Users. The list of users is displayed.
- On the User Type filter, select only Local Users.
- For each local user, go to the the and click Delete.
Password Requirements
Password requirements for US Government Cloud and US Defense Cloud tenancies and services must meet or exceed requirements outlined in NIST Special Publication 800-63.
Using a Common Access Card/Personal Identity Verification Card to Sign in to the Console
After you set up CAC/PIV authentication with the identity provider and successfully federate with Oracle Cloud Infrastructure, you can use your CAC/PIV credentials to sign in to the Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Console. See the identity provider's documentation for the specific details for your implementation.
In general, the sign in steps are:
- Insert your CAC/PIV card into the card reader.
- Navigate to the Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Console sign in page.
- If prompted, enter your Cloud Tenant name and click Continue.
- Select the Single Sign-On provider and click Continue.
- On the identity provider's sign-on page, select the appropriate card, for example, PIV Card.
- If presented with a certificate picker, choose the appropriate certificate or other attributes set up by your organization.
- When prompted, enter the PIN.
IPv6 Support for Virtual Cloud Networks
IPv6 addressing is supported for all commercial and government regions. Government customers have the option to enable IPv6 addressing for their VCNs. For more information, see IPv6 Addresses.
Setting Up Secure Access for Compute Hosts
You can set up CAC/PIV authentication using third-party tools to enable multi-factor authentication for securely connecting to compute hosts. Example tools include PuTTY-CAC for Windows and Open SC for macOS. For more information see the US Government website, PIV Usage Guidelines.
Enabling FIPS Mode for Your Operating System
US Government Cloud and US Defense Cloud customers are responsible for enabling FIPS mode for the operating systems (OS) on their Compute hosts. To make the OS compliant with Federal Information Processing Standard (FIPS) Publication 140-2, follow the guidelines for the OS:
Oracle Linux
Follow the guidance provided at FIPS 140-2 Compliance in Oracle Linux 8.
Ubuntu
Follow the guidance provided at Ubuntu Security Certifications - Enabling FIPS 140.
Windows Server 2012
Follow the guidance provided at Data Encryption for Web console and Reporting server Connections.
Windows Server 2016 and Windows Server 2019
First, follow the guidance provided at How to Use FIPS Compliant Algorithms.
Next, go to the Microsoft document, FIPS 140 Validation and navigate to the topic Information for System Integrators. Follow the instructions under "Step 2 – Setting FIPS Local/Group Security Policy Flag" to complete the FIPS enablement.
CentOS
The following guidance is for enabling FIPS on CentOS 7.5 and CentOS Stream 8. These procedures are valid for both VM and bare metal instances, and only in NATIVE mode. These procedures can be modified for both Emulated and PV modes as needed. Note that this procedure provides an instance that contains the exact FIPS cryptographic modules EXCEPT kernel. The kernel module is the same major/minor version, however, but is accelerated in revision, so can be considered compliant under most FIPS-compliant models.
After you complete this procedure, we recommend that you don't run system-wide yum updates. The system-wide update will remove the FIPS modules contained herein.
Verify that the version of the kernel, FIPS modules, and FIPS software are at the minimum version:
-
Validate the current version of the kernel package meets the requirement:
- Current version:
kernel-3.10.0-693.el7 -
Run
rpm -qa | grep kernel-3
- Current version:
-
Run the following and validate the major or minor version is the same as the requirements.
-
Run
yum list <package_name> -
Verify that the major/minor version matches the required ones.
Required packages and versions are:
- fipscheck - fipscheck-1.4.1-6.el7
-
hmaccalc - hmaccalc-0.9.13-4.el7
-
dracut-fips - dracut-fips-033-502.el7
-
dracut-fips-aesni - dracut-fips-aesni-033-502.el7
-
For each version of package that's not installed, run
yum install <package_name>
-
- Download and install the following packages:
- Packages already installed as part of the image:
Create a directory called
preinstall.Download the following packages into this directory:
openssl, openssl-libs – 1.0.2k-8.el7
nss, nss-tools, nss-sysinit – 3.28.4-15.el7_4
nss-util – 3.28.4-3.el7
nss-softokn, nss-softokn-freebl – 3.28.3-8.el7_4
openssh, openssh-clients, openssh-server – 7.4p1-11.el7
In the preinstall directory, run
yum - -nogpgcheck downgrade *.rpm
- Packages to be added to the image:
- Create a directory called
newpackages. Download the following packages into this directory:
libreswan – 3.20-3.el7
libgcrypt – 1.5.3-14.el7
gnutls – 3.3.26-9.el7
gmp – 6.0.0-15.el7
nettle – 2.7.1-8.el7
In the
newpackagesdirectory, runyum - -nogpgcheck localinstall *.rpm
- Create a directory called
- Packages already installed as part of the image:
The URLs for the packages used for this installation are:
Preinstall:
http://linuxsoft.cern.ch/cern/centos/7/updates/x86_64/Packages/nss-3.28.4-15.el7_4.x86_64.rpm
http://linuxsoft.cern.ch/cern/centos/7/updates/x86_64/Packages/nss-util-3.28.4-3.el7.x86_64.rpm
http://linuxsoft.cern.ch/cern/centos/7/updates/x86_64/Packages/nss-tools-3.28.4-15.el7_4.x86_64.rpm
http://linuxsoft.cern.ch/cern/centos/7/updates/x86_64/Packages/nss-sysinit-3.28.4-15.el7_4.x86_64.rpm
http://linuxsoft.cern.ch/cern/centos/7/updates/x86_64/Packages/nss-softokn-freebl-3.28.3-8.el7_4.x86_64.rpm
http://linuxsoft.cern.ch/cern/centos/7/updates/x86_64/Packages/nss-softokn-3.28.3-8.el7_4.x86_64.rpm
http://linuxsoft.cern.ch/cern/centos/7/updates/x86_64/Packages/openssl-1.0.2k-8.el7.x86_64.rpm
http://linuxsoft.cern.ch/cern/centos/7/updates/x86_64/Packages/openssl-libs-1.0.2k-8.el7.x86_64.rpm
http://linuxsoft.cern.ch/cern/centos/7/updates/x86_64/Packages/openssh-7.4p1-11.el7.x86_64.rpm
http://linuxsoft.cern.ch/cern/centos/7/updates/x86_64/Packages/openssh-clients-7.4p1-11.el7.x86_64.rpm
http://linuxsoft.cern.ch/cern/centos/7/updates/x86_64/Packages/openssh-server-7.4p1-11.el7.x86_64.rpm
Newpackages:
http://linuxsoft.cern.ch/cern/centos/7/updates/x86_64/Packages/libreswan-3.20-3.el7.x86_64.rpm
http://linuxsoft.cern.ch/cern/centos/7/updates/x86_64/Packages/libgcrypt-1.5.3-14.el7.x86_64.rpm
http://linuxsoft.cern.ch/cern/centos/7/updates/x86_64/Packages/gnutls-3.3.26-9.el7.x86_64.rpm
http://linuxsoft.cern.ch/cern/centos/7/updates/x86_64/Packages/gmp-6.0.0-15.el7.x86_64.rpm
http://linuxsoft.cern.ch/cern/centos/7/updates/x86_64/Packages/nettle-2.7.1-8.el7.x86_64.rpm
Kernel FIPS module and initramfs validation installation
Perform this procedure as root:
-
Regenerate dracut:
dracut -f -v -
Add the fips argument to the end of the default kernel boot command line:
-
Edit
/etc/default/grub -
At the end of the line starting with "GRUB_CMDLINE_LINUX," add
fips=1inside the double quotes of the command.
-
Save the result.
-
-
Generate a new
grub.cfg:grub2-mkconfig -o /etc/grub2-efi.cfg
Configure SSH to limit the encryption algorithms
-
Sudo to root.
-
Edit
/etc/ssh/sshd_config. -
Add the following lines to the bottom of the file:
Protocol 2 Ciphers aes128-ctr,aes192-ctr,aes256-ctr,aes128-cbc,3des-cbc,aes192-cbc,aes256-cbc Macs hmac-sha1 - Reboot the instance.
- After instance has rebooted, validate that FIPS mode has been enabled in the kernel:
Sudo to root.
Run the following command:
cat /proc/sys/crypto/fips-enabledThe result should be '1'.
To further secure CentOS7/RHEL 7.x systems as required by individual agency guidance, follow the checklist contained in the OpenSCAP guide. This guide can be found here: https://static.open-scap.org/ssg-guides/ssg-centos7-guide-index.html
The STIG for evaluating compliance under multiple profiles can be found here: https://iase.disa.mil/stigs/os/unix-linux/Pages/index.aspx . Use the Red Hat Linux 7.x STIG for CentOS 7.5 releases.
Required Site-to-Site VPN Parameters for Government Cloud
If you use Site-to-Site VPN with the US Government Cloud or the US Defense Cloud, you must configure the IPSec connection with the following FIPS-compliant IPSec parameters.
For some parameters, Oracle supports multiple values, and the recommended one is highlighted in bold text.
Oracle supports the following parameters for IKEv1 or IKEv2. Check the documentation for your particular CPE to confirm which parameters the CPE supports for IKEv1 or IKEv2.
Phase 1 (ISAKMP)
| Parameter | Options |
|---|---|
| ISAKMP protocol |
Version 1 |
| Exchange type |
Main mode |
| Authentication method |
Pre-shared keys * |
| Encryption algorithm |
AES-256-CBC (recommended) AES-192-CBC AES-128-CBC |
| Authentication algorithm |
SHA-2 384 (recommended) SHA-2 256 SHA-1 (also called SHA or SHA1-96) |
| Diffie-Hellman group |
group 14 (MODP 2048) group 19 (ECP 256) group 20 (ECP 384) (recommended) |
| IKE session key lifetime |
28800 seconds (8 hours) |
|
* Only numbers, letters, and spaces are allowed characters in pre-shared keys. |
|
Phase 2 (IPSec)
| Parameter | Options |
|---|---|
| IPSec protocol |
ESP, tunnel mode |
| Encryption algorithm |
AES-256-GCM (recommended) AES-192-GCM AES-128-GCM AES-256-CBC AES-192-CBC AES-128-CBC |
| Authentication algorithm |
If using GCM (Galois/Counter Mode), no authentication algorithm is required because authentication is included with GCM encryption. If not using GCM, use HMAC-SHA-256-128. |
| IPSec session key lifetime |
3600 seconds (1 hour) |
| Perfect Forward Secrecy (PFS) |
Enabled, group 14 (default, recommended) Supports disabled as well as enabled for group 2, 5, 14, 19, 20, 24. |
Oracle's BGP ASN
This section is for network engineers who configure an edge device for FastConnect or Site-to-Site VPN.
Oracle's BGP ASN for the Government Cloud depends on the authorization level:
- US Government Cloud: 6142
- US Defense Cloud (Impact Level 5 authorization): 20054
FIPS Compatible Terraform Provider
To use Terraform in US Government Cloud or US Defense Cloud regions, see Enabling FIPS Compatibility for installation and configuration information.
Kubernetes Engine
The components installed by Kubernetes Engine are compliant with FIPs. When using Kubernetes Engine in US Government Cloud or US Defense Cloud regions, ensure that the underlying hosts are FIPs-compliant.
Exadata Database Service on Dedicated Infrastructure – Patch Management Rescheduling
You can reschedule monthly and quarterly patching events in the Console for Exadata Database Service on Dedicated Infrastructure in US Government Cloud and US Defense Cloud regions. Specifying a maintenance schedule for Exadata patch management isn't supported in US Government Cloud and US Defense Cloud regions.
To meet and maintain FedRAMP and DISA certifications, Oracle Cloud Infrastructure must patch Exadata Infrastructure on a regular and consistent basis. These patching events include but aren't limited to the following types:
- Exadata Database Node Security patches (monthly)
- Exadata Storage Cell patches (monthly)
- Exadata Infrastructure Full Patches (quarterly)
An OCI Change Notification (CN) message is sent to you when a patching event is planned for each patch type. You can request to reschedule a patching event through the Console. To reschedule a patching event using the Console, you need to request the reschedule within the defined 21 day patching window. Patching schedule requests outside of the defined 21 day patching window must still be made through an Oracle Support Service Request (SR). For more information, see Cloud Infrastructure Maintenance Updates in the Exadata Database on Dedicated Infrastructure How-To Guides.
TLS Certificates for API Gateway
If you use API Gateway in US Government Cloud or US Defense Cloud regions, you must:
- Obtain a custom TLS certificate from an approved Certificate Authority.
- Record the mapping between an API gateway's custom domain name and its public IP address with an approved DNS provider.
For more information, see Setting Up Custom Domains and TLS Certificates for installation and configuration information.
VN Encryption
Virtual network (VN) encryption provides instance-to-instance encryption for in-transit traffic within a region (in the same VCN or between VCNs peered with a local peering gateway) between any of the following compute shapes:
- E3
- E4
- A1
- X9
VN encryption is enabled by default at the region level and is available in US Government Cloud and US Defense Cloud regions only. To disable VN encryption, you must create a service request.
The encryption keys are fully managed by Oracle Cloud Infrastructure. The mechanism for encryption is based on RFC3948. Specifications for key settings and encryption ciphers comply with FIPS 140-2 requirements.
When enabled, the VN encryption feature increases latency and decreases throughput because of the encryption/decryption overhead. This might or might not be noticeable at the application layer. For more details around the latency numbers contact customer support.
Requesting a Service Limit Increase for US Government Cloud and US Defense Cloud Tenancies
If you need to request a service limit increase, use the following instructions to create a service request in My Oracle Support.
- Before you can create a service request, you must have an
oracle.comaccount and you must register your Oracle Cloud Infrastructure CSI with My Oracle Support. See Requesting a Service Limit Increase for US Government Cloud and US Defense Cloud Tenancies for details. - Be aware that the support engineer that reviews the information in the service limit request might not be a US citizen.
Creating a Service Request
To create a service request for US Government Cloud and US Defense Cloud:
-
Go to My Oracle Support and sign in.
If you're not signed in to Oracle Cloud Support, click Switch to Cloud Support at the top of the page.
- At the top of the page, click Service Requests.
- Click Create Technical SR.
- Select the following from the displayed menus:
- Service Type: Select Oracle Cloud Infrastructure from the list.
- Service Name: Select the appropriate option for your organization.
- Problem Type: Select Account Provisioning, Billing and Termination, and then select Limit Increase from the submenu.
- Enter your contact information.
- Enter a Description, and then enter the required fields specific to the issue. If a field doesn't apply, you can enter n/a.
For help with any of the general fields in the service request or for information on managing service requests, click Help at the top of the Oracle Cloud Support page.
Find Oracle Cloud Infrastructure IDs
Use the following tips to help you find identifiers you might be asked to provide:
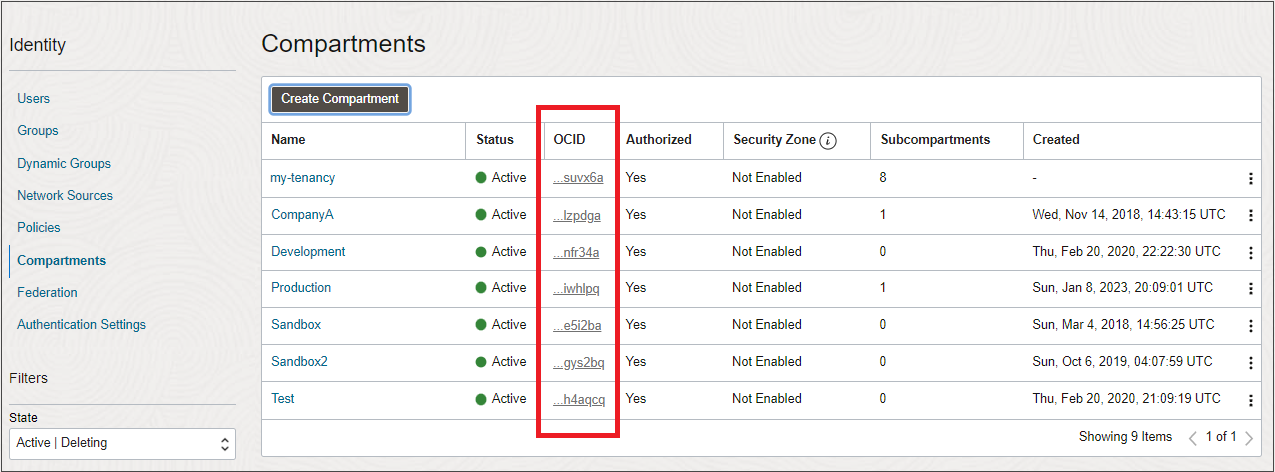
To find the OCID (Oracle Cloud Identifier) of a compartment:
- Open the navigation menu and select Identity & Security. Under Identity, select Compartments.
A list of the compartments in the tenancy is displayed.
A shortened version of the OCID is displayed next to each compartment.
- Click Copy to copy the OCID to the clipboard. You can then paste it into the service request form field.
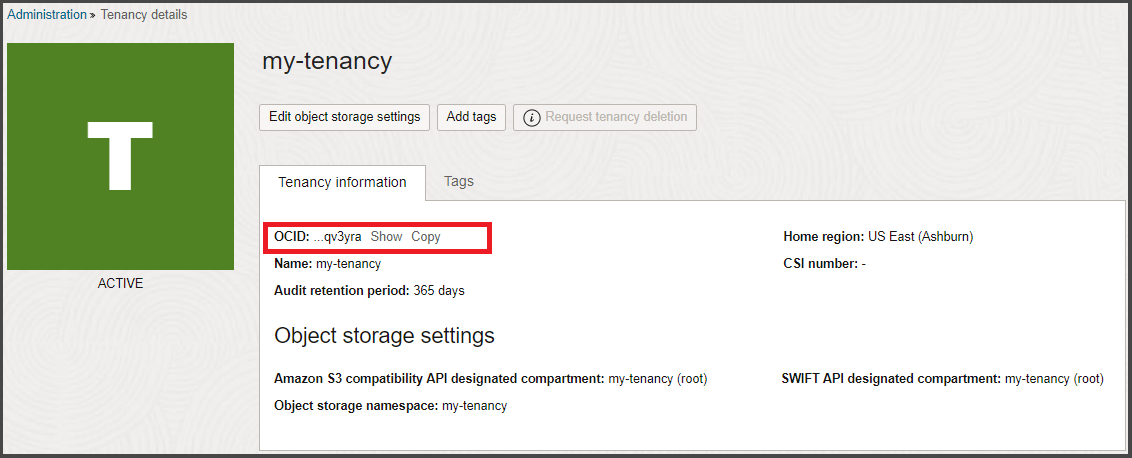
The OCID (Oracle Cloud Identifier) of a resource is displayed when you view the resource in the Console, both in the list view and on the details page.
For example, to get the OCID for a compute instance:
- Open the Console.
-
Select the Compartment to which the instance belongs from the list on the left side of the page.
Note that you must have appropriate permissions in a compartment to view resources.
- Open the navigation menu and select Compute. Under Compute, select Instances. A list of instances in the selected compartment is displayed.
-
A shortened version of the OCID is displayed on the instance details page.
- Click Copy to copy the OCID to the clipboard. You can then paste it into the service request form field.
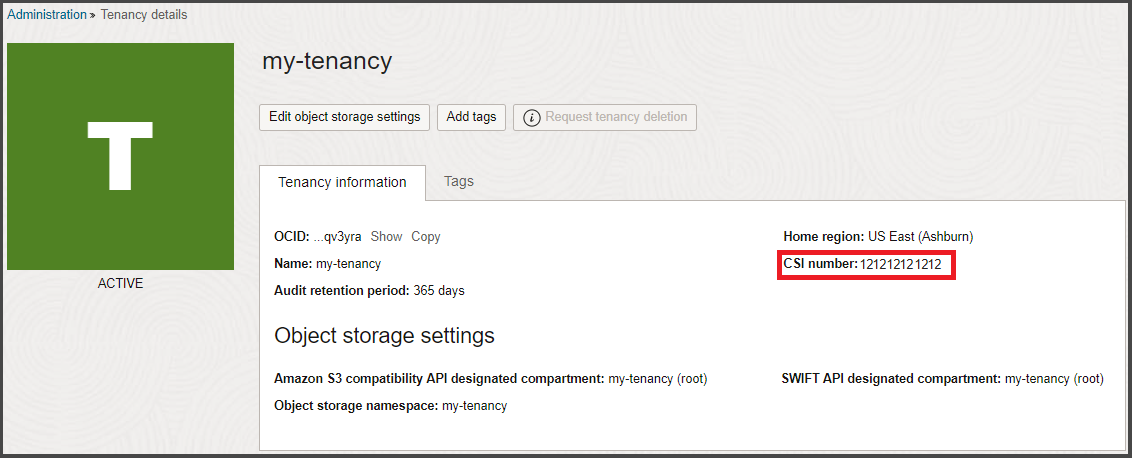
The Customer Support Identifier (CSI) number is generated after you buy Oracle Cloud services. This number can be found in several places, including in your contract document and also on the tenancy details page. You'll need the CSI number to register and log support requests in My Oracle Support (MOS).
The CSI number isn't available for US Government Cloud and US Defense Cloud regions.
To find your CSI number:
- In the navigation bar, select the Profile menu and then select Tenancy: <your_tenancy_name>.
-
The CSI number is shown under Tenancy Information.
Using My Oracle Support for the First Time
Before you can create service requests with My Oracle Support, you need to have an Oracle Single Sign-On (SSO) account and you need to register your Customer Support Identifier (CSI) with My Oracle Support.
Before you begin this procedure, have your CSI handy (see Requesting a Service Limit Increase for US Government Cloud and US Defense Cloud Tenancies).
- Go to https://support.oracle.com.
-
Click New user? Register here to create your Oracle Single Sign On (SSO) account.
-
Enter your company e-mail address in the Email address field, complete the rest of the form, and then click Create Account. A verification email is generated.
-
Check your email account for an email from Oracle asking you to verify your email address.
- Open the email and click Verify Email Address.
- Sign in with the credentials you set up.
- At sign in, you're prompted to enter a Note to the Approver and the Support Identifier (your CSI).
-
Click Request Access.
- Enter the first five characters of the name of the organization that owns the Customer Support Identifier (listed in the Welcome letter and on My Services), and then click Validate. The support identifier appears in the table.
- Click Next.
- Enter your contact information and click Next.
- Accept the terms and click Next.
The status of the request is pending until you receive approval from the Customer User Administrator (CUA) or from Oracle Support if you're the first person requesting this support identifier.
- Go to https://support.oracle.com and sign in.
- Navigate to the My Account page: Go to your username at the of the page, open the menu, and then click My Account.
- The Support Identifiers region displays the accounts that your username is currently associated with.
- Click Request Access.
- Enter a Note to the Approver and then enter the Support Identifier (your CSI).
- Click Request Access.
- Enter the first five characters of the name of the organization that owns the Customer Support Identifier (listed in the Welcome letter and on My Services), and then click Validate. The support identifier appears in the table.
- Click Validate.
- The entry is validated. Close the dialog.
The status of the request is pending until you receive approval from the Customer User Administrator (CUA).
For more information about signing in and using My Oracle Support, see Registration, Sign In, and Accessibility Options in My Oracle Support Help.
 )
)