Scopes
Using the scope parameter, the access token can grant different levels of access to multiple IAM identity domain APIs.
Scopes provide a way to more specifically define a set of resources and operations that an access token allows. Scopes represent intent. When a client requests an access token, the scopes asked for indicate the kind of functionality a client wants to use when presenting the access token.
Additionally, different types of applications use different access token grants. Trusted applications (such as backend services) may request access tokens directly on behalf of users. Web applications typically need to first validate the user's identity and optionally obtain the user's consent.
Use the urn:opc:idm:__myscopes__ scope when you need to obtain an access token that contains all the permitted identity domain scopes. Access tokens are returned that contain all applicable identity domain scopes based on the privileges represented by the identity domain application roles granted to the requesting client and the user being specified by the client's request (if present). This scope isn't granted directly to any identity domain administrator role.
Use the urn:opc:idm:role.<r_name> scope (for example, urn:opc:idm:role.User%20Administrator) when you need to obtain an access token that contains the applicable scopes of a specific role, provided that both the client and the user are granted the specific role. For example, to request an access token with a role-based scope of user administrator and application administrator:
Request Example
curl -i
-H 'Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded;charset=UTF-8'
--request POST https://<domainURL>/oauth2/v1/token
-d 'grant_type=password&username=<user-name>&password=<example-password>&client_id=<client-id>&client_assertion_type=urn%3Aietf%3Aparams%3Aoauth%3Aclient-assertion-type%3Ajwt-bearer&client_assertion=<client-assertion>&scope=urn:opc:idm:role.User%2520Administrator urn:opc:idm:role.Application%2520Administrator'The access token generated would contain the applicable scopes for the user administrator and the application administrator as long as both the client and the user are granted these roles. For example, a client has Role1, Role2, and Role3. A User has Role1, Role2, and Role 4. The scopes included in the request for the access token are Role1 and Role3. The access token generated would contain only scopes for Role1.
Scope claims can have multiple space separated scopes. If a scope name contains a space,
the server can't determine the correct scope boundary. This can happen when a role name
is used in the scope. In the request example, the roles "user administrator" and
"application administrator" have spaces that have been URL encoded:
scope=urn:opc:idm:role.User%2520Administrator
urn:opc:idm:role.Application%2520Administrator.
To avoid space issues in role names, you must encode the role names twice using URL encoding:
Example Java Code
String scope = "scope=urn:opc:idm:role." + URLEncoder.encode(URLEncoder.encode("User Administrator", "UTF-8"), "UTF-8");
scope = scope + " urn:opc:idm:role." + URLEncoder.encode(URLEncoder.encode("Application Administrator", "UTF-8"), "UTF-8");No Scopes Defined for an App
/oauth2/v1/authorize
endpoint:scope=openid: The resulting access token can be used with/oauth2/c1/userinfo, which provides the bare minimum user information.scope=openid approles groups: The resulting access token can be used with/oauth2/v1/userinfoto get the user's roles and groups.
Using Trust Scopes
Trust scopes define how an OAuth client accesses resources. Trust scopes allow a trusted or confidential client application to acquire an access token that gives access to any of the resources within an identity domain (Account), to other resources based on defined tags (Tags), or to only those services where an explicit association between the client and the service (Explicit) exists.
The option to define the
trustScope parameter is available to only
trusted and confidential client applications. The option isn't available to public
client applications.The
trustScope attributes of Account,
Tags, and Explicit are named All (for Account), Tagged (for Tags), and Specific (for Explicit) in the identity domain Console.-
Use only the
urn:opc:resource:consumer::allscope in the request. An invalid scope error is returned if you attempt to include both theurn:opc:resource:consumer::allscope and another scope in the same request, such asurn:opc:idm:__myscopes__. -
Requesting an access token using the
urn:opc:resource:consumer::allscope doesn't return an access token that provides access to the identity domains admin APIs. You must continue to use the scope:urn:opc:idm:__myscopes__to access the admin APIs. See Scopes. -
The scope requested by the Client app should always exist and match, either directly or hierarchically, the client's defined allowed scopes to allow the client access to the resource.
-
The
trustScopevalue ofExplicitis assigned by default to trusted and confidential client applications and allows your client application to acquire an access token with permissions based on an explicit association between the client and target services. To use theAllorTaggedoption, you must update the client application with either thetrustScopevalue ofAllorTags. - For identity propagation token requests using the
urn:opc:resource:consumer::allscope, the resulting access token doesn't include theurn:opc:resource:consumer::allscope.
The following links provide more information on each trustScope
available:
Using the Account Trust Scope
The Account trust scope allows a trusted or confidential client application to get an access token that gives access to any of the services that are in the same identity domain without requiring explicit association with the target services.
The option to define the
trustScope parameter is available to only trusted and confidential client applications. The option isn't available to public client applications.To use the Account trust scope:
-
Assign the value of
Accountto thetrustScopeparameter for the appropriate trusted client application.Note
ThetrustScopeattribute ofAccountis named All in the identity domain Console.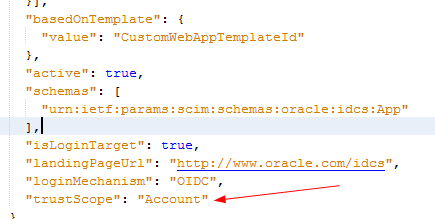
-
Request an access token using the trusted or confidential client and request the scope
urn:opc:resource:consumer::all.The access token in the response contains the audienceurn:opc:resource:scope:accountand the scopeurn:opc:resource:consumer::all, which gives access to any of the services that are in the same domain without requiring explicit association with the target services.
The requested scope should always exist and match, either directly or hierarchically, the client's defined allowed scopes to allow the client access to the resource.
Using Fine-Grained Scopes
urn:opc:resource:consumer::all scope, you can
also specify the following fine-grained
scopes:urn:opc:resource:consumer:paas::readurn:opc:resource:consumer:paas:stack::allurn:opc:resource:consumer:paas:analytics::read
urn:opc:resource:consumer:paas:analytics::read scope in its request
for access to a resource. If the scope directly matches an allowed scope defined, in the
returned access token, the audience is urn:opc:resource:scope:account
and the scope is urn:opc:resource:consumer:paas:analytics::read.If the allowed scope defined by the client is urn:opc:resource:consumer:paas::read, then the client app is allowed to access the resource hierarchically if the client requests one of the following scopes: urn:opc:resource:consumer:paas::read or urn:opc:resource:consumer:paas:analytics::read. However, if the requested scope is urn:opc:resource:consumer:paas:analytics::write, then the client isn't allowed access to the resource, because that isn't one of the allowed scopes defined by the client app.
Request and Response Examples
The following examples show request and response examples for the client credentials and resource owner grant flows.
Client Credentials Flow Request Example
curl -i
-H 'Authorization: Basic TXlUZXN0U2VydmljZV9BUFBJRDoxMGE2ODAwMC03YTYzLTQxNDItODE0Ny03MGNmMGJhMDFkYjg='
-H 'Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded; charset=utf-8'
--request POST 'https://<domainURL>/oauth2/v1/token'
-d 'grant_type=client_credentials&scope=urn:opc:resource:consumer::all' -kResponse Example
{
"access_token":"eyJ4NX....Zh3ieBlQ",
"token_type":"Bearer",
"expires_in":3600
}The access token contains the audience
urn:opc:resource:scope:account
and the scope urn:opc:resource:consumer::all.Resource Owner Flow Request Example
curl -i
-H 'Authorization: Basic TXlUZXN0U2VydmljZV9BUFBJRDoxMGE2ODAwMC03YTYzLTQxNDItODE0Ny03MGNmMGJhMDFkYjg='
-H 'Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded; charset=utf-8'
--request POST https://<domainURL>/oauth2/v1/token'
-d 'grant_type=password&scope=urn:opc:resource:consumer::all&username=admin@example.com&password=PasswordExample1'-kResponse Example
{
"access_token":"eyJ4NX...71aImeBsU",
"token_type":"Bearer",
"expires_in":3600
}Request and Response Examples Using a Fully Qualified Scope
The following examples show request and response examples using a fully qualified scope.
Request Example
curl -i
-H 'Authorization: Basic TXlUZXN0U2VydmljZV9BUFBJRDoxMGE2ODAwMC03YTYzLTQxNDItODE0Ny03MGNmMGJhMDFkYjg='
-H 'Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded; charset=utf-8'
--request POST 'https://<domainURL>/oauth2/v1/token'
-d 'grant_type=client_credentials&scope=http://abccorp1.com/scope1'Response Example
{
"access_token":"eyJ4NXzF.....rT5SH7sUw",
"token_type":"Bearer",
"expires_in":3600
} Resource Owner Flow Request Example Including the Request for a Refresh Token
To generate a refresh token in addition to the access token, use the scope
urn:opc:resource:consumer::all offline_access in the request.
curl -i
-H 'Authorization: Basic TXlUZXN0U2VydmljZV9BUFBJRDoxMGE2ODAwMC03YTYzLTQxNDItODE0Ny03MGNmMGJhMDFkYjg='
-H 'Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded; charset=utf-8'
--request POST https://<domainURL>/oauth2/v1/token'
-d 'grant_type=password&scope=urn:opc:resource:consumer::all offline_access&username=admin@example.com&password=PasswordExample1'-kResponse Example
{
"access_token":"eyJ4...pNYM0M",
"token_type":"Bearer",
"expires_in":3600,
"refresh_token":"AQIDBAUi....djF9NCA="
}Using the Tags Trust Scope
The Tags trust scope allows a trusted or confidential client application to get an access token that gives access to other resources based on the defined tags.
The option to define the
trustScope parameter is available to only trusted and confidential client applications. The option isn't available to public client applications.To use the Tags trust scope:
-
Assign the value of
Tagsto thetrustScopeparameter to enable the client application to access tags from other applications.Note
ThetrustScopeattribute ofTagsis named Tagged in the identity domain Console. -
Define the
key:valuepair for theAllowedTagsparameter.Note
These steps assume that the appropriate Resource App has definedkey:valuepairs for theTagsattribute and that at least onekey:valuepair from the list of theallowedTagsattribute of the Client App match onekey:valuepair of theTagsattribute of the Resource App.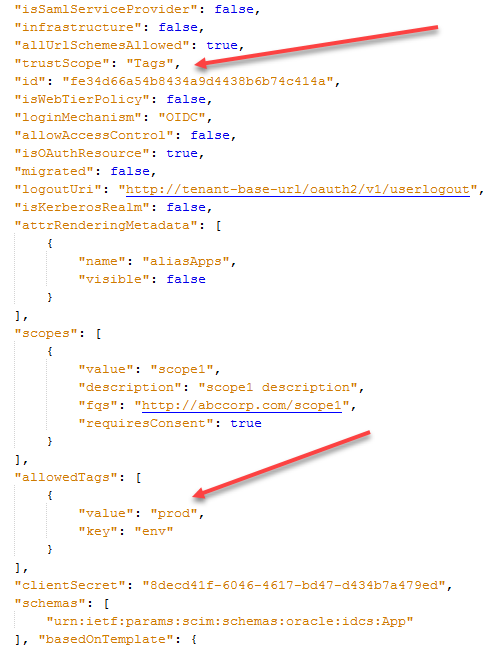
-
Request an access token using the trusted or confidential client and request the scope
urn:opc:resource:consumer::all.The access token in the response contains the audienceurn:opc:resource:scope:tag=<base64 encoded JSON>and the scopeurn:opc:resource:consumer::all, which gives access to Resource Apps that have tags that match the allowed tags specified in the Client App.
The requested scope must always exist and match, either directly or hierarchically, the client's defined allowed scopes to allow the client access to the resource.
Using Fine-Grained Scopes
urn:opc:resource:consumer::all scope, you can
also specify the following fine-grained
scopes:urn:opc:resource:consumer:paas::readurn:opc:resource:consumer:paas:stack::allurn:opc:resource:consumer:paas:analytics::read
urn:opc:resource:consumer:paas:analytics::read scope in its request
for access to a resource. If the scope directly matches an allowed scope defined, then
in the returned access token the audience is
urn:opc:resource:scope:tag=<base64 encoded JSON> and the scope
is urn:opc:resource:consumer:paas:analytics::read.If the allowed scope defined by the client is urn:opc:resource:consumer:paas::read, then the client app is allowed to access the resource hierarchically if the client requests one of the following scopes: urn:opc:resource:consumer:paas::read or urn:opc:resource:consumer:paas:analytics::read. However, if the requested scope is urn:opc:resource:consumer:paas:analytics::write, then the client isn't allowed access to the resource, because that isn't one of the allowed scopes defined by the client app.
Request and Response Examples
The following examples show request and response examples for the client credentials flow
using the urn:opc:resource:consumer::all scope.
Request Example
curl -i
-H 'Authorization: Basic MjA3Mz....zllNjI2'
-H 'Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded; charset=utf-8'
--request POST 'https://tenant101.idcs.internal.oracle.com:8943/oauth2/v1/token'
-d 'grant_type=client_credentials&scope=urn:opc:resource:consumer::all'Response Example
{
"access_token""eyJ4NX....ZbDtAw",
"token_type":"Bearer", "expires_in":3600
}The access token contains the audience
urn:opc:resource:scope:tag=<base64 encoded JSON> and the scope urn:opc:resource:consumer::all. The following is an example of a decoded audience: aud:["urn:opc:resource:scope:tag=eyAidGFncyI6WyB7ICJrZXkiOiJjb2xvciIsInZhbHVlIjoiZ3JlZW4ifSAsICB7ICJrZXkiOiJjb2xvciIsInZhbHVlIjoiYmx1ZSJ9IF19"]The following examples show request and response examples for the client credentials flow using a fully qualified scope.
Request Example
curl -i
-H 'Authorization: Basic MzRjYz....Q3OWVk'
-H 'Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded; charset=utf-8'
--request POST 'https://<domainURL>/oauth2/v1/token'
-d 'grant_type=client_credentials&scope=http://abccorp1.com/scope1'Response Example
{
"access_token""eyJ4NXzF.....rT5SH7sUw",
"token_type":"Bearer",
"expires_in":3600
} Using the Explicit Trust Scope
The Explicit trust scope defines trust scope for only those services
where an explicit association between the client and the target service exists.
The option to define the
trustScope parameter is available to only trusted and confidential client applications. The option isn't available to public client applications.You don't have to do anything to use the Explicit trust scope because this is the default assigned to trusted and confidential client application. To use the Account or Tags option, you must update the client application with the trustScope value of either Account or Tags.
The
trustScope attribute of Explicit is named Specific in the identity domain.See Using the Account Trust Scope and Using the Tags Trust Scope.
Request and Response Examples
The request and response examples show the client credentials flow using a fully qualified scope.
Request Example
curl -i
-H 'Authorization: Basic MzRjYz....Q3OWVk'
-H 'Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded; charset=utf-8'
--request POST 'https://<domainURL>/oauth2/v1/token'
-d 'grant_type=client_credentials&scope=http://abccorp1.com/scope1'Response Example
{
"access_token""eyJ4NXzF.....rT5SH7sUw",
"token_type":"Bearer",
"expires_in":3600
}Using the Explicit Trust Scopes from Multiple Resources
The Explicit trust scope defines trust scope for only those services where an explicit association between the client and the target service exists. You can specify multiple scopes belonging to different resources in a single Authorization request or token request and obtain multiple access tokens in return with each of them containing the scopes for each resource.
- You must specify the newly defined scope,
urn:opc:resource:multiresourcescopein the Authorization request or token request. Token requests will fail if multiple scopes belonging to different resources are specified without this scope. - The OAuth Client must be able to parse the token response that includes multiple access tokens and use each token to access each resource service.
You can use this feature with all the grant types except for the Implicit flow. See Implicit Grant Type.
See Using the Explicit (Specific) Trust Scope for more information about the explicit trust scopes.
Request and Response Examples
The request and response examples show the client credentials flow using a fully qualified scope.
Request Example
https://<domainURL>/oauth2/v1/authorize?
client_id=<client-id>&
response_type=code&
redirect_uri=<redirect-url>&
scope=http://abccorp.com/scope1 http://123corp.com/scope1 openid urn:opc:resource:multiresourcescope
curl -i
-H 'Authorization: Basic MzgzZTU4Z….NTM3YjFm' \
--request POST 'https://<domainURL>/oauth2/v1/token' \
-d 'grant_type=authorization_code' \
-d 'code=AgAgYjc1MzgzNWM2NGQxNDA5…YcxU_XdtfLWXUp1Vn4a5uIHiOn4='
curl -i
-H 'Authorization: Basic MzgzZTU4Z….NTM3YjFm' \
--request POST 'https://<domainURL>/oauth2/v1/token' \
-d 'grant_type=client_credentials' \
-d 'scope=http://abccorp.com/scope1 http://123corp.com/scope1 urn:opc:resource:multiresourcescope
Response Example
{
"tokenResponses":[
{
"access_token": "eyJ4NXQjUzI1NiI6InZBV3RzNEo1clE1Z.....1iZDc2NjFjMWJiZjA0OGNhOTkyMWNlN2Q4MThkNDY0YSIsImp0aSI6Ijg53ZFOT2FxyZYjocCnm1b1w",
"token_type": "Bearer",
"expires_in": 3600
},
{
"access_token": "eyJ4NXQjUzI1NiI6InZBV3RzNEo1clE1Z.....HplcmtUNjdsU19SjZlYjc5ZDgzMTVhYjQ0ODBiNDlkMjU3NzdkZWMzMDE2In0.k4QShMbO5aPGmYyKo",
"token_type": "Bearer",
"expires_in": 3000
}
],
"id_token": "eyJ4NXQjUzI1NiI6InZBV3RzNEo1clE1ZHplc.....mtUNjdsU19SYjhQTWoYDSVhTUmDl8zK3a9vk7cowIW2hr3smwtcsvfsbrewwtbnCrGerp7v4CUcVYlSw"
}