Setting Up RADIUS Proxy
Remote Authentication Dial In User Service (RADIUS) is a network protocol that defines rules and conventions for communication between network devices. RADIUS Proxy authenticates and authorizes users or devices and also tracks the usage of those services.
Required Policy or Role
- Be a member of the Administrators group
- Be granted the Identity Domain Administrator role or the Security Administrator role
- Be a member of a group granted
managedomains
To understand more about policies and roles, see The Administrators Group, Policy, and Administrator Roles, Understanding Administrator Roles, and Understanding Policies.
Setting up RADIUS Proxy
Install, setup, and test RADIUS Proxy.
- Ensure that your RADIUS Proxy is available for your identity domain. RADIUS Proxy is available only for Oracle Apps Premium and Premium Identity Domain Types. To learn about identity domain types and the features and limits associated with each, see IAM Identity Domain Types.
- Install the latest Postman client.
- Download the RADIUS Proxy Postman collection.
- Review the RADIUS Proxy mapping instructions. See RADIUS Proxy Mapping.
- Review these checkpoints. As you're setting up RADIUS Proxy, use the following checkpoints to verify that your configuration is correct at each step of the process.
- Check that the RADIUS Proxy and the RADIUS Proxy Client App are activated in the identity domain.
- Check the IP address of Database and port number of RADIUS Proxy are correctly configured in the RADIUS App.
- Check that the RADIUS Agent is up and running.
- Check that the proxy server is up and running.
- Check that the database is up.
-
Download the latest RADIUS Proxy Installer from the Downloads page in the Console.
- Open the navigation menu and click Identity & Security. Under Identity, click Domains.Click the name of the identity domain that you want to work in. You might need to change the compartment to find the domain that you want. Then, click Settings and then Downloads.
- Choose Oracle Identity Cloud Service RADIUS Proxy for Linux, and then click Download.
-
Create the RADIUS App from the RADIUS App Template. Note: For REST go to RADIUS Proxy, RADIUS App, Search, and then Search all apps (with search criteria).
-
Create a RADIUS Proxy in IAM.
-
Run the Installer.
-
Install RADIUS Proxy.
-
Check that the RADIUS Agent and RADIUS Proxy are running. The RADIUS Agent obtains configuration data from IAM at regular intervals. Then, it updates the configuration files used by RADIUS Proxy.
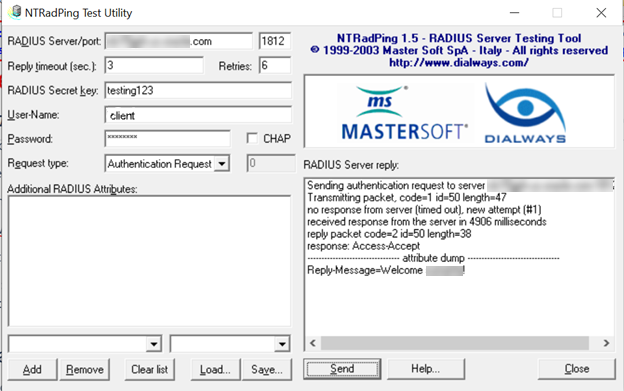
- (Optional)
Use the NTRadPing Test Utility to validate that RADIUS proxy is working.
- Set up and Configure Oracle Database 12c. Follow the instructions at Configuring Authentication and then use the following commands to create a user/role in the database.
- Set up and Configure Oracle Database 12c. For more information, see Configuring RADIUS Authentication. Follow the instructions in the Configuring RADIUS Authentication section to create a user and role in the database.
- You can't add an IP address in CIDR format using the IAM user interface. If the IP address of the Oracle Database is in CIDR format, use the following request from the Postman collection. See Change an IP Address from CIDR Format.
- Set up MFA. To set up MFA follow these instructions, see Managing Multifactor Authentication.
RADIUS Proxy Log Files and Configuration Information
Note the following RADIUS Proxy file locations for log and configuration information. This information can be useful for troubleshooting.
| Installer Logs | <radius_proxy_installer_location>/oracle_radius_proxy/_Oracle/ Identity/ Cloud/ Service/ RADIUS/ Proxy_installation/Logs/ |
| Agent Logs | <radius_proxy_installer_location>/oracle_radius_proxy/radius_agent/logs/agent.log |
| Proxy logs | <radius_proxy_installer_location>/oracle_radius_proxy/radius_proxy/log/radius_proxy.log |
| Proxy Configuration | <radius_proxy_installer_location>/radius_proxy/conf/radius_proxy.conf |
| Agent Configuration | <radius_proxy_installer_location>/radius_agent/conf/radius_agent.conf |
| Client Configuration | <radius_proxy_installer_location>/radius_proxy/conf/radius_clients.conf |
RADIUS Proxy Mapping
RADIUS Proxy and RADIUS Proxy Listener has a 1-1 mapping, for example for each RADIUS Proxy there is one RADIUS Proxy Listener. Multiple Oracle DB RADIUS clients can be mapped to one RADIUS Proxy, that is, a RADIUS Proxy has a 1-n mapping with Oracle DB RADIUS clients.
If an administrator configures multiple Oracle DB RADIUS clients, then that many Oracle Database RADIUS apps need to be created in IAM identity domains-one for each Oracle DB RADIUS client. For example, if an administrator has configured four Oracle DB RADIUS clients to one RADIUS Proxy, then in IAM identity domains there must be four Oracle Database RADIUS apps configured-one for each Oracle DB client.