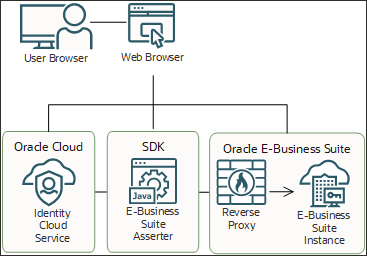
Architecture
The IAM E-Business Suite Asserter is deployed to a separate Oracle WebLogic Server instance. The E-Business Suite Asserter interacts with IAM through IAM REST API and redirects the user's web browser to IAM and to Oracle E-Business Suite.
This architectural diagram shows how the E-Business Suite Asserter, Oracle E-Business Suite, and IAM interact.
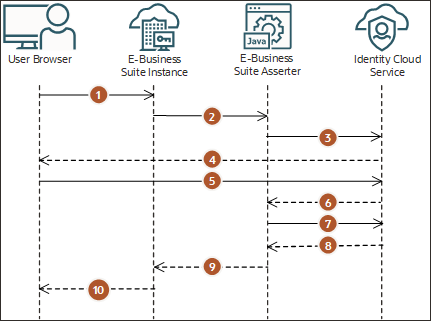
The following diagrams show the login and logout flow when using the E-Business Suite Asserter to integrate Oracle E-Business Suite with IAM. These flow diagrams show the login and logout process starting with Oracle E-Business Suite, but the E-Business Suite Asserter approach also supports E-Business Suite Asserter and IAM initiated flow.
- The user has access to an Oracle E-Business Suite protected resource.
- Oracle E-Business Suite redirects the user browser to the E-Business Suite Asserter application.
- The E-Business Suite Asserter uses an IAM SDK to generate the authorization URL and then redirects the browser to IAM.
- IAM presents its sign in page to the user.
- The user submits credentials to IAM.
- IAM issues an authorization code and redirects the user's browser to the E-Business Suite Asserter.
- The E-Business Suite Asserter uses an IAM SDK to communicate with IAM to exchange the authorization code for an access token.
- IAM issues an access token and an ID token to the E-Business Suite Asserter.
- The E-Business Suite Asserter creates an Oracle E-Business Suite session using Oracle E-Business Suite SDK and redirects the user's browser to Oracle E-Business Suite.
- Oracle E-Business Suite presents the user requested protected resource.
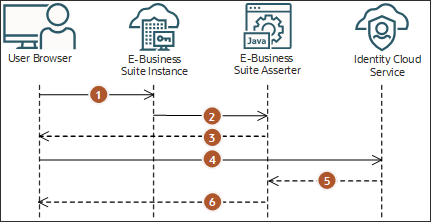
The following logout process refers to a user invoking logout from Oracle E-Business Suite. If the logout process is initiated in IAM, then only step 5 and 6 are run.
- The user selects to log out from Oracle E-Business Suite.
- Oracle E-Business Suite logs the user out and then redirects the user's browser to the E-Business Suite Asserter application.
- The E-Business Suite Asserter uses an IAM SDK to obtain the IAM logout URL, and then redirects the user's browser to this URL
- The user browser invokes the IAM logout URL.
- IAM removes the user session and then redirects the user's browser to the E-Business Suite Asserter logout URL, which is defined in the application configuration.
- The E-Business Suite Asserter logs out the user and redirects the user's browser to the Post Logout Redirect URL, which is defined in the application configuration.
Considerations for Using the E-Business Suite Asserter
To use the E-Business Suite Asserter, you must understand the following considerations for installation and configuration:
-
The host names for the EBS Asserter's WebLogic server and Oracle E-Business Suite's application server must have exactly same domain for SSO to work.
-
The E-Business Suite Asserter must be accessed over SSL, since IAM can only be accessed over SSL. Failure to do so might cause SSO between IAM and the E-Business Suite Asserter to fail.
-
Synchronize the server clock where the E-Business Suite Asserter runs, and the server clock where Oracle E-Business Suite runs.
-
You can deploy the asserter in Oracle WebLogic Server 12c by using secure communications such as Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) and Transport Layer Security (TLS).
How to Use the Asserter With Multiple Instances of Oracle E-Business Suite
You can use the same WebLogic Server installation with multiple managed servers or from a different WebLogic Server installation, each with one managed server. In both cases, each IAM E-Business Suite Asserter URL has its own domain name and port number pair.
For each Oracle E-Business Suite (EBS) instance, the associated database name must be unique. For example, if there are three EBS instances - test, dev and prod, the database names could be
ebstest, ebsdev, ebsprod respectively.For each Oracle E-Business Suite (EBS) instance, you configure and deploy one instance of the E-Business Suite Asserter (EBS Asserter) Java application. Usually you deploy each EBS Asserter Java application to a specific WebLogic managed server.
Starting from EBS Asserter version 19.2.1-1.5.0, if you don't want to create multiple managed servers and deploy one EBS Asserter Java application to each of them, you can deploy multiple EBS Asserter Java applications to the same WebLogic managed server.
To accomplish this scenario, you need to perform the following tasks:
-
Rename each EBS Asserter Java application's Web Application Resource (WAR) file before you deploy the file to the same WebLogic managed server. In this case, the domain name and port number of all EBS Asserter's URLs are same, but the URL's context changes.
-
Extract the contents of each
ebs.warfile to a folder, find theweblogic.xmlfile, edit this file, update the value of the<cookie-path>tag to match the EBS Asserter's URL, and then rebuild theebs.war.For example, if you want EBS Asserter to respond to URL context
/app/ebs, then the update the tag withinweblogic.xmlwith the value<cookie-path>/app/ebs</cookie-path>.
For example: If you have two EBS instances named Development 1 and Development 2, you want to integrate these EBS instances with IAM using the EBS Asserter, but you only have one WebLogic managed server for the two EBS Asserter Java applications, you need to run the procedures in this tutorial for each EBS instance. You configure the WebLogic Server only once, and configure and deploy the EBS Asserter Java Application for each EBS instance:
-
For EBS instance Development 1:
- Make a copy of the
ebs.warfile and name the new fileebsdev1.war. - Update the
weblogic.xmlfile contained in theebsdev1.warfile, by replacing thecookie-pathtag with the following:<cookie-path>/ebsdev1</cookie-path>. - Update the
bridge.propertiesfile contained in theebsdev1.warfile. - Deploy the
ebsdev1.warfile to the WebLogic managed server.
- Make a copy of the
-
For EBS instance Development 2:
- Make a copy of the
ebs.warfile and name the new fileebsdev2.war. - Update the
weblogic.xmlfile contained in theebsdev2.warfile, by replacing thecookie-pathtag with the following:<cookie-path>/ebsdev2</cookie-path>. - Update the
bridge.propertiesfile contained in theebsdev2.warfile. - Deploy the
ebsdev2.warfile to the WebLogic managed server.
- Make a copy of the
You deploy both ebsdev1.war and ebsdev2.war files in to the same WebLogic managed server. The EBS Asserter's URL for EBS instance Development 1 is similar to the following example: https://ebsasserter.example.com:7002/ebsdev1.
The EBS Asserter's URL for EBS instance Development 2 is similar to the following example: https://ebsasserter.example.com:7002/ebsdev2.