Overview of the Network Firewall Service
Use the Network Firewall service to create a firewall with intrusion detection and prevention for your virtual cloud networks (VCNs).
Powered by Palo Alto Networks®, the Network Firewall service gives you visibility into network traffic entering cloud environments (north-south) and between subnets (east-west). You can use the Network Firewall service with other security services to create a layered network security solution.
A firewall is a highly available and scalable instance that you create in a subnet. The firewall applies business logic defined in a policy to network traffic. Use routing in the VCN to direct traffic to and from the firewall.
The Network Firewall service provides a throughput rate of 4 Gbps.
Security Features
- Stateful network filtering: Create stateful network filtering rules that allow or deny network traffic based on source IP (IPv4 and IPv6), destination IP (IPv4 and IPv6), port, and protocol.
- Custom URL and FQDN filtering: Restrict ingress and egress traffic to a specified list of fully qualified domain names (FQDNs), including wild cards and custom URLs.
- Intrusion Detection and Prevention (IDPS): Monitor networks for malicious activity. Log information, report, or block the activity.
- SSL inspection: Decrypt and inspect TLS-encrypted traffic with ESNI support for security vulnerabilities. Encrypted Server Name Indication (ESNI) is a TLSv1.3 extension that encrypts the Server Name Indication (SNI) in the TLS handshake.
- Intra VCN subnet traffic inspection: Route traffic between two VCN subnets through a firewall.
- Inter VCN traffic inspection: Route traffic between two VCNs through a firewall.
- VXLAN traffic inspection: Route traffic to a virtual test access point (VTAP) through a firewall. For more information on VTAPs, see Virtual Test Access Points.
- NAT rules: Use NAT rules to create a prioritized set of ingress and egress rules. These rules specify source and destination addresses, enabling you to perform source Network Address Translation (SNAT) on network traffic. With NAT rules, you can change source IP addresses, optimize IP address usage, and enhance security by concealing internal network details. See About NAT rules.
Common use cases for Network Firewall
Each scenario uses intra VCN routing to route traffic to the firewall. See Intra VCN Routing for more information.
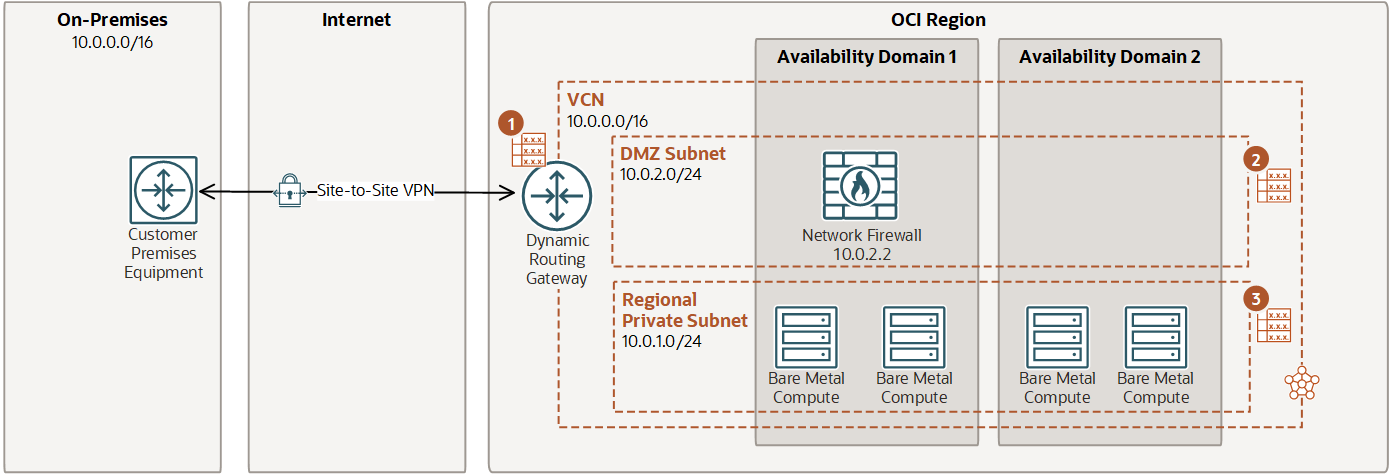
Securing traffic between an on-premises network and a VCN
| Destination CIDR | Route target |
|---|---|
| 0.0.0.0/0 | Network Firewall (10.0.2.2) |
| Destination CIDR | Route target |
|---|---|
| 0.0.0.0/0 | DRG |
| Destination CIDR | Route target |
|---|---|
| 0.0.0.0/0 | Network Firewall (10.0.2.2) |
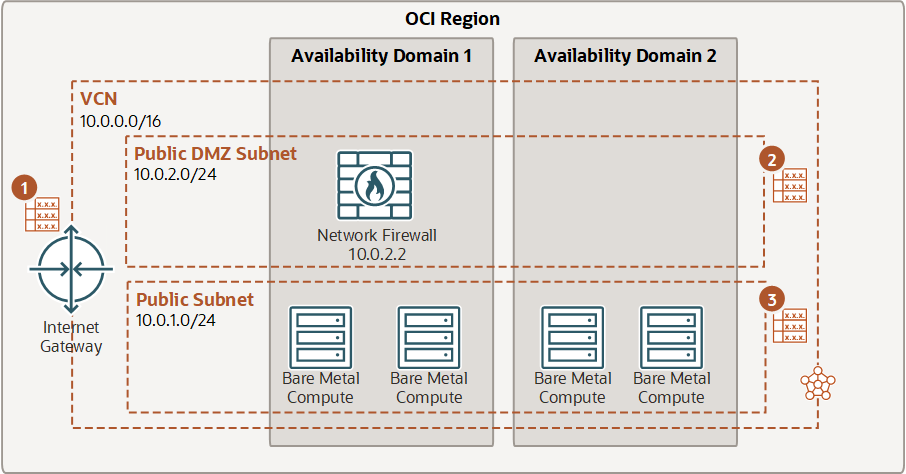
Securing traffic between the internet and a VCN
In this example, routing is configured from the internet to the firewall. Traffic is routed from the internet gateway (IGW), through the firewall, and then from the firewall subnet to a public subnet.
| Destination CIDR | Route target |
|---|---|
| VCN (10.0.0.0/16) | Network Firewall (10.0.2.2) |
| Destination CIDR | Route target |
|---|---|
| 0.0.0.0/0 | IGW |
| Destination CIDR | Route target |
|---|---|
| 0.0.0.0/0 | Network Firewall (10.0.2.2) |
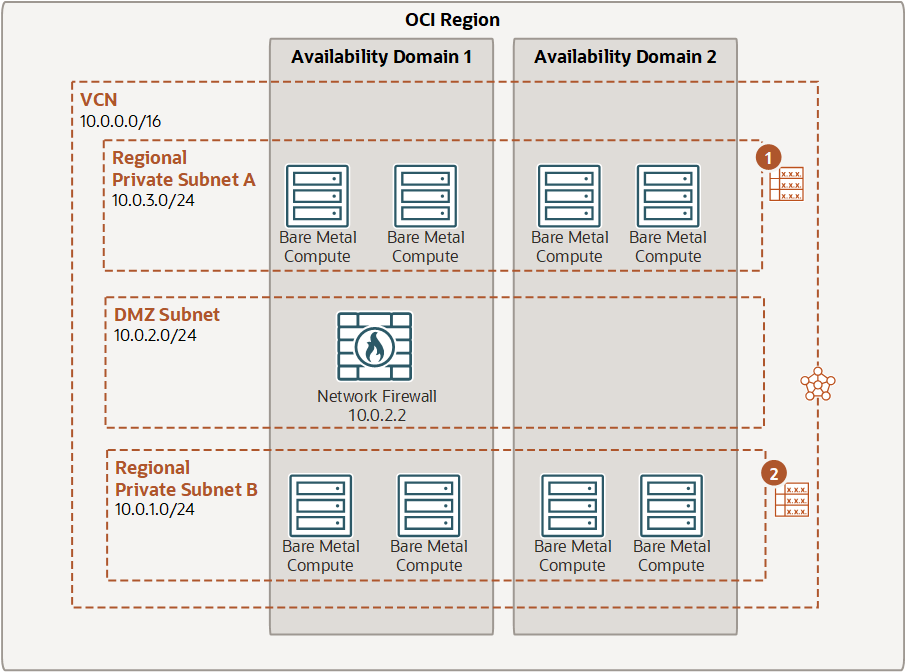
Securing traffic between subnets in a VCN
In this example, routing is configured from a subnet to the firewall. Traffic is routed from Subnet A, through the firewall, and then from the firewall subnet to Subnet B.
Regions and Availability Domains
You can use the Network Firewall service in all regions. For a list of supported regions and general information, see Regions and Availability Domains.
When you create a firewall, you can create it in a region or a specific availability domain within a region. The default when you create a firewall is regional.
- Regional firewall instances are distributed across all availability domains in the region, which reduces the risk of availability domain failure.
- Regional firewalls are high-availability, and have high fault tolerance.
- Using regional firewalls might add minor inter availability domain latencies. For example, if the client or server is in a different availability domain than the firewall instance, there can be latency in milliseconds. If the client or server is in the same availability domain as the firewall instance, then latency is in microseconds.
- Availability domain-specific firewall instances are distributed across many fault domains within a single specified availability domain.
- Availability domain-specific firewalls might cause redirection of traffic if it comes from a regional subnet.
Network Firewall Concepts
- Firewall
- A firewall is a resource that exists in a chosen subnet and controls incoming and outgoing network traffic based on a set of security rules. Traffic is routed to and from the firewall from resources such as internet gateways and dynamic routing gateways (DRGs). To create a firewall, you must have at least one policy that you can attach to the firewall. For information about how to create and manage this resource, see Creating and Managing Firewalls.
- Firewall policy
- A firewall policy is a resource that contains the rules that control how a firewall inspects, allows, or denies network traffic. You can associate a firewall policy to one or more firewalls. To create or manage this resource, see Creating and Managing Firewall Policies.
- Firewall policy component
- Firewall policy components such as lists, secrets, and decryption profiles help you build rules for a firewall policy. To create or manage firewall policy components, see Creating and Managing Firewall Policies.
- availability domain
- The data center within a geographical region that hosts cloud resources. For more information, see Regions and Availability Domains. A firewall exists in a single Availability domain in a region.
Creating Automation with Events
Next Steps
To set up the Network Firewall service, see Setting Up the Network Firewall Service