Channel Basics
What Are Channels?
To expose your digital assistants and standalone skills to users, you configure channels in Digital Assistant. Channels carry the chat back and forth from users on various messaging platforms to the digital assistant and its various skills. There are also channels for user agent escalation and testing.
Channel Types
You can create and manage the following channel types from the Channels page, which you access by clicking Channels in the left menu. There’s a tab for each type.
| Channel Type | Uses |
|---|---|
| Users |
|
| Agent Integrations |
|
| DA as Agent |
|
| Applications |
|
| System |
|
User Channel Routing
You can route each user-facing channel to a single version of a digital assistant or a skill.
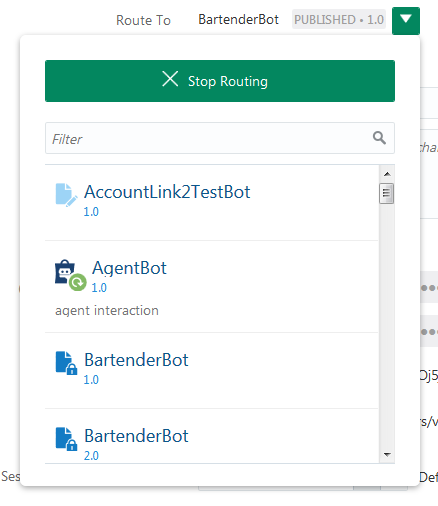
Description of the illustration routing-menu.png
Only one version of a skill or digital assistant can run on a channel at any given time. When you create new version of the skill, you can stop the routing to the old version and then assign the routing to the updated version.
You can support running two versions of a skill or digital assistant concurrently by creating separate channels for each one. For example, beta testers could access the skill through one channel while customers continue to chat through a separate channel uninterrupted.
Route (or Reroute) a Channel
-
Click
 to open the side menu, select Development > Channels > Users.
to open the side menu, select Development > Channels > Users.
- Select the Users tab, and select the channel.
- In the channel, next to the Route To field, select
 and then select the digital assistant or skill that you want to route the channel to.
and then select the digital assistant or skill that you want to route the channel to.
How Digital Assistant User Channel Routing Works
When you register a skill to a digital assistant, both the messages that it sends and receives are relayed through the digital assistant’s user channels. The digital assistant’s routing takes over, even if the skill already has other channels routed to it.
For example, say there two skills, each with their own web channel that have been registered to a digital assistant, which in turn routes to its own web channel and to a Facebook channel. When users send a message to the digital assistant through the digital assistant’s web channel, it determines the intent and sends the message to the appropriate skill. When the skill replies, its message is sent back to the user over the digital assistant’s web channel, not through the skill’s web channel. Likewise, when the digital assistant intercepts a message from a Facebook subscriber, the skill’s response to the user is sent back over the digital assistant’s Facebook channel instead of the skill’s own web channel.
Test Rendering for a Channel
To see how a conversation with a digital assistant or individual skill will render in a given user channel, you can use the tester.
-
Open the digital assistant or skill that you want to test.
-
At the bottom of the left navigation for the digital assistant or skill, click
 .
.
-
In the Channel dropdown, select the channel you plan to deploy the digital assistant or skill to.
-
In the text field at the bottom of the tester, enter some test text.
As you test the channel, you can see how it would display in the channel. In addition, when there are limitations for that channel type that force the conversation to be rendered differently than it otherwise might be, those limitations are described in the Conversations tab.
Zero-Downtime Channel Updates
You can reroute your channel from one skill or digital assistant to another without causing any user downtime.
Here's how you set it up:
- For a channel that is routed to a digital assistant, you:
- Create a new version of the digital assistant.
- In the new version of the digital assistant, make whatever changes are necessary, including adding new versions of existing skills.
- Reroute the channel to the new version of the digital assistant.
- For a channel that is routed to an individual skill, you:
- Create a new version of the skill, make the desired updates, and publish the skill.
- Reroute the channel to the new version of the skill.
Here's what happens after the channel is rerouted:
- If the user doesn't have an open session, they will get the new digital assistant or skill when they next access the channel.
- If the user has an open session with the digital assistant or skill but is not in the middle of a flow in a skill, the session is refreshed with the updated digital assistant or skill.
- If the user is in the middle of a flow in a skill when the channel is rerouted, the user will continue seeing the previous version of the skill or digital assistant. After they finish their flow (which happens when the
returntransition is called in the flow), the session will be updated with the updated digital assistant or skill.
Caution:
If you update an existing digital assistant (instead of creating a new version of the digital assistant and then rerouting to that version), the zero downtime feature will not work. For example, if a new version of a skill has been added to the digital assistant and a user is in the middle of a session with the old version of the skill, the session will be interrupted and the skill will stop working.Rich Text Formatting in Channels
You can use HTML tags to format skill messages, even for channels that have channel-specific markup or markdown. When the message is passed to the channel, the HTML tags you include are replaced with the appropriate markup or markdown for that particular channel. This enables you write messages in one place for multiple channels.
If a tag doesn't have a direct equivalent in a channel, the closest equivalent is used.
For example, if the message has <h1>Title 1</h1> and
<h2>Title 2</h2> tags, those are converted to *Title
1* and *Title 2* when sent to a Slack channel.
If there isn't a rough equivalent for the tag in the channel, the tags are merely stripped from the message when sent to the channel.
| Style | HTML Tags and Attributes |
|---|---|
| bold |
<strong>; <b> |
| italics | <em>; <i> |
| headings | <h1>; <h2>;
<h3> |
| unordered lists (including nesting) | <ul>; <li> |
| ordered lists (including nesting) | <ol>; <li> |
| preformatted text | <pre> |
| blockquote | <blockquote> |
| newline | <newline> |
| hyperlink | <a href="">Note: If your
link includes an ampersand ( |
| image link | <img> |
| table | <table>; <th>;
<tr>; <td> |
| font size | font-size (e.g. <p
style="font-size:large;">Large Font</p>)
|
| font color | color (e.g. <p style="color:red;">Red
Font</p>)
|
| video | <video controls=""
src="link_to_video_source_file">Note:
This tag only works if you link directly to the video file, such as
an |
Session Expiration
For each channel that you configure, you use the Session Expiration field to set the timeout for inactive user sessions. For most channel types, the default value is one day (1440 minutes). When the session has expired, the conversation is terminated and a message is sent to notify the user of that fact.
In addition, any variables that have been set in a skill's dialog flow will be destroyed, unless the variable was declared as a user-scoped variable. See User-Scoped Variables in YAML Dialog Flows.
Change the Session Expiration Prompt
When a session expires, the user is prompted with a message that is set in the Expired Session Error Prompt property for the digital assistant or skill that the channel is routed to. By default, this message is "Your session has expired. Please start again."
To change this message for a digital assistant:
-
Click
 to open the side menu, select Development > Digital Assistants, and open the digital assistant.
to open the side menu, select Development > Digital Assistants, and open the digital assistant.
-
In the left navigation for the digital assistant, click
 and select the Configurations tab.
and select the Configurations tab.
- Scroll down to the Other Parameters section of the page and update the Expired Session Error Prompt property.
To change this message for a standalone skill:
-
Click
 to open the side menu, select Development > Skills, and open the skill.
to open the side menu, select Development > Skills, and open the skill.
-
In the left navigation for the skill, click
 and select the Configuration tab.
and select the Configuration tab.
- Update the Expired Session Error Prompt property.
Reset User Channel Sessions
If needed, you can break off the current conversations in a user channel by clicking its Reset Sessions button.
Caution:
This button is primarily intended for cases when you are developing the skill or digital assistant. If you use it for a channel that is in production, you will disrupt all user conversations that are in progress.To access the Reset Sessions button:
- Click
 to open the side menu, select Development > Channels, and select the user channel.
to open the side menu, select Development > Channels, and select the user channel.
Enable or Disable Channels
From time to time, you may need to disable a channel to perform maintenance or updates to the configuration and then re-enable the channel.
To do so, you can use the these switches:
- Channel Enabled
- Interaction Enabled (for agent integrations)
- Application Enabled (for applications)
Disabling the System channel, which supports the skill tester, alerts developers that the channel is unavailable.
To access these options:
- Click
 to open the side menu, select Development > Channels, and select the channel.
to open the side menu, select Development > Channels, and select the channel.
Channel-Specific Extensions
In addition to the generic elements that you can use in your dialog flows to render
across multiple channels, you can also take advantage of features that are specific to a
channel type. You can do so through the Common Response component's
channelCustomProperties metadata element, which takes the following
form:
...
channelCustomProperties:
- channel: "CHANNEL_NAME" // can be facebook, slack, cortana, twilio, androidsdk, iossdk, websdk, test
properties:
PROPERTY_NAME: "PROPERTY_VALUE"
...You can apply channelCustomProperties in the component's metadata
at the level of globalActions, responseItems, and elements
of responseItems, depending on the given property.
Here is an example of custom properties defined at the response item level and the card level:
responseItems:
- type: "cards"
cardLayout: "vertical"
cards:
- title: "${pizzas.name}"
description: "${pizzas.description}"
imageUrl: "${pizzas.image}"
url: "${pizzas.moreInfo}"
iteratorVariable: "pizzas"
channelCustomProperties:
- channel: "facebook"
properties:
webview_height_ratio: "compact"
fallback_url: "https://www.example.com"
channelCustomProperties:
- channel: "facebook"
properties:
top_element_style: "large"
..The channelCustomProperties element takes an array, where each entry
specifies the properties of a specific channel. Some custom properties are only applicable to
a specific Common Response component element, or even a specific response item type, as in the
above example where top_element_style only applies to response items of type
cards.
You can also use Freemarker expressions to specify the value of a channel custom property.
Here is an example where a date picker is only shown on Slack when prompted for the expense date item while resolving the composite bag entity expense:
responseItems:
- type: "text"
text: "${system.entityToResolve.value.prompt}"
channelCustomProperties:
- channel: "slack"
properties:
showDatePicker: "${system.entityToResolve.value.name=='Date'}"
...The available properties vary by channel. See the following topics for the list of custom properties available for each channel:
Comparison of Channel Capabilities
Here's a non-exhaustive comparison of channels and the features that they support.
| Capability | Facebook Messenger | Slack | Microsoft Teams | Cortana | Twilio | Web , iOS, and Android |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Text | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Images | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes for sending. No for receiving | Partial | Yes |
| Files | Yes | Partial for sending. Yes for receiving | Yes | Yes for sending. No for receiving | Partial | Yes |
| Emojis | Yes | Partial for sending. Yes for receiving | Yes | Yes for sending. No for receiving | Partial | Yes |
| Location | Yes, but deprecated | No | No | No | No | Yes |
| Links | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Postbacks | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Partial | Yes |
| Location Requests | Yes | No | No | No | No | Yes |
| Extensions | No | No | No | No | No | No |
| Custom Properties | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Partial | Yes |
| Carousel | Yes | Partial | Yes | Yes | Partial | Yes |
| List | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Partial | Yes |
| Tables and Forms | No | Yes | Yes (autosubmit is not supported) | No | No | Yes |
To render an emoji from your dialog flow, start with its Unicode representation, replace
+ with 000, and prefix the code with \. For example, for U+1F600, you would enter \U0001F600 in your dialog flow. See https://unicode.org/emoji/charts/full-emoji-list.html for a list of the Unicode codes for each emoji.
Comparison of Channel Message Constraints
Here's a comparison of constraints on messages and action buttons, by channel.
Text Message Constraints
| Text Message Constraint | Facebook Messenger | Slack | Microsoft Teams and Cortana | Twilio | Web , iOS, and Android |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Maximum length of text message | 640 characters. If the length exceeds 640, the text is split over multiple messages. | 3000 characters. If the length exceeds 3000, the text is split over multiple messages. | No limit. | 1600 characters. If the length exceeds 1600, the text is split over multiple messages. | No limit. |
| Maximum length of text action label | 20 characters | 30 characters | 1 line (about 50 characters) | N/A | 128 characters |
| Types of text actions allowed | Postback, Call, URL | Postback, URL | Postback, Call, URL | Postback, Call, URL. These action types are converted to text. For postback actions, the label serves as a keyword that can be used to trigger the postback. | Postback, URL, Location Request, Call (if the device has calling capabilities), and Share (if the platform supports it) |
| Maximum number of text actions | If there are more text actions, the message is converted to multiple horizontal cards, with the same text used as the title on each card, and each card containing up to 3 actions. | No limit. | No limit. | N/A | If there are more text actions, the message is converted to multiple horizontal cards, with the same text used as the title on each card, and each card containing up to 6 actions. |
Horizontal Card Messages
| Horizontal Card Message Constraint | Facebook Messenger | Slack | Microsoft Teams and Cortana | Twilio | Web , iOS, and Android |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Supported? | Yes | No. Card is layout is converted to vertical. | Yes | No, but near equivalent functionality is achieved by converting some action types to text. | Yes |
| Maximum length of title | 80 characters | 3000 characters | 2 lines (about 80 characters) | N/A | 30 characters |
| Maximum length of description | 80 characters | 3000 characters | 25,000 characters | N/A | 128 characters |
| Maximum length of card action label | 20 characters | 30 characters | 1 line (about 50 characters) | N/A | 25 characters |
| Maximum number of cards | 10 | N/A | 10 | N/A | 10 |
| Maximum number of card actions | 3. If the number of card actions exceeds 3, the card is duplicated to render remaining card actions. | N/A | 6. If the number of card actions exceeds 6, the card is duplicated to render remaining card actions. | N/A | 3. If the number of card actions exceeds 3, the card is duplicated to render remaining card actions. |
| Minimum number of card actions | 0 | N/A | 0 | N/A | 1 |
| Maximum number of card list actions | 0 | N/A | 6 | N/A | -- |
| At least one description, image or action required? | Yes | N/A | No | N/A | No |
| Types of card actions allowed | Postback, Call, URL, Share | Postback, URL | Postback, Call,URL | Postback, Call, URL. These action types are converted to text. For postback actions, the label serves as a keyword that can be used to trigger the postback. | Postback, URL |
| Types of card list actions allowed | N/A | Postback, URL | Postback, Call,URL | Postback, Call, URL. These action types are converted to text. For postback actions, the label serves as a keyword that can be used to trigger the postback. | Postback, URL |
Vertical Card Messages
| Vertical Card Message Constraint | Facebook Messenger | Slack | Microsoft Teams and Cortana | Twilio | Web , iOS, and Android |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Supported? | No | Yes | Yes | No, but near equivalent functionality is achieved by converting some action types to text. | Yes.
Note
For 19.4.1, this is not supported. |
| Maximum length of title | N/A | 3000 characters | 2 lines (about 80 characters) | N/A | 30 characters |
| Maximum length of description | N/A | 3000 characters | 25,000 characters | N/A | 128 characters |
| Maximum length of card action label | N/A | 30 characters | 1 line (about 50 characters) | N/A | 25 characters |
| Maximum number of cards | N/A | 100 | 10 | N/A | N/A |
| Maximum number of card actions | N/A | -- | 3 | N/A | N/A |
| Minimum number of card actions | 0 | 0 | 0 | N/A | N/A |
| Maximum number of card list actions | 1 | -- | 6 | N/A | N/A |
| At least one description, image or action required? | Yes | N/A | No | N/A | No |
| Types of card actions allowed | Postback, Call, URL, Share | Postback, URL | Postback, Call, URL | Postback, Call, URL. These action types are converted to text. For postback actions, the label serves as a keyword that can be used to trigger the postback. | N/A |
| Types of card list actions allowed | Postback, Call, URL | Postback, URL | Postback, Call,URL | Postback, Call, URL. These action types are converted to text. For postback actions, the label serves as a keyword that can be used to trigger the postback. | N/A |
Attachment Messages
| Attachment Message Constraint | Facebook Messenger | Slack | Microsoft Teams and Cortana | Twilio | Web , iOS, and Android |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Supported? | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes, if MMS is enabled | Yes |
| Maximum number of attachment actions | 0 | -- | -- | N/A | -- |
| Types of actions allowed | N/A | Postback,URL | Postback, Call, URL. | Postback, Call, URL. These action types are converted to text. For postback actions, the label serves as a keyword that can be used to trigger the postback. | Postback,URL |
Action Buttons
| Action Button Constraint | Facebook Messenger | Slack | Microsoft Teams and Cortana | Twilio | Web , iOS, and Android |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Supported? | Yes | Yes | Yes | No, but near equivalent functionality is achieved by converting some action types to text. | Yes |
| Maximum length of global action label | 20 characters | 30 characters | 1 line (about 50 characters) | N/A | 128 characters |
| Maximum number of global actions | 11 | -- | 6 | N/A | -- |
| Types of global actions allowed | Postback, Location | Postback,URL | Postback, Call, URL | Postback, Call, URL. These action types are converted to text. For postback actions, the label serves as a keyword that can be used to trigger the postback. | Postback, Location |