Test access to your enterprise application after you configure the App Gateway server to communicate with your IAM instance and start the server.
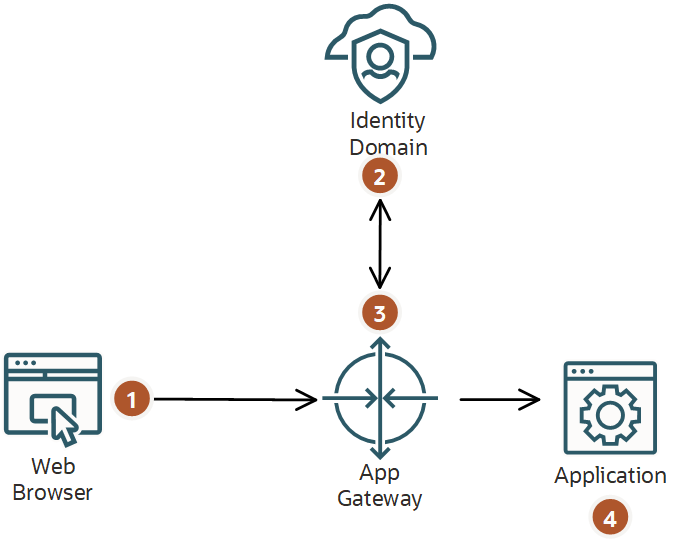
The following diagram provides an example of how App Gateway and IAM interact when the user browser sends an HTTP request to an application resource through App Gateway.
Because App Gateway proxies your web application, use the App Gateway base URL to access the application instead of the application actual URL.
-
Open a new web browser and access your application using the App Gateway URL.
In this example, the URL is: https://myappgateway.example.com:4443/myapp/private/home
The actual application https://myapp.internal.example.com:3266/myapp/private/home isn't accessible by the user browser.
-
App Gateway intercepts the request and communicates with IAM to verify if
the URL corresponds to an enterprise application.
In this example, My Enteprise Application is registered, and
the authentication policy for this enterprise application is Form or Access
Token.
-
App Gateway verifies that the request contains a valid IAM's access token in the
Authorization Bearer header or IAM's session cookie, indicating the user has already signed in to IAM.
-
If the user hasn't signed in to IAM, then App Gateway redirects the user
browser to the IAM Sign In page.
-
If the user has signed in, then App Gateway adds header variables and a cookie to the
request, and then forwards the request to the application.
The application receives the request, uses the header variables to identify the user and
to present the content of the /myapp/private/home page.