Analyze SQL with SQL Tuning Advisor
You can use SQL Tuning Advisor to analyze and tune SQL statements.
SQL tuning is an important aspect of database system performance tuning. SQL Tuning Advisor is a mechanism for resolving problems related to sub-optimally performing SQL statements. It takes one or more SQL statements or one SQL Tuning Set (STS) as input and invokes the Automatic Tuning Optimizer to analyze the statements. The output is in the form of findings and recommendations, along with a rationale for each recommendation and its expected benefit. Tuning recommendations include the following and you can choose to accept the recommendations to complete the tuning of the SQL statements.
- Collection of object statistics
- Creation of indexes
- Rewriting SQL statements
- Creation of SQL profiles
- Creation of SQL plan baselines
For more information on:
- SQL Tuning Advisor, see About SQL Tuning Advisor in Oracle Database SQL Tuning Guide.
-
STS and how to create one, see Capturing Workloads in SQL Tuning Sets in Oracle Database SQL Tuning Guide.
In Database Management Diagnostics & Management, you can use SQL Tuning Advisor to analyze the SQL statements in a Managed Database.
SQL Tuning Advisor is only available for Oracle Database Enterprise Edition version 12.2 and later and if the
COMPATIBLE initialization parameter is set for the database, then
it should match version 12.2.0 and later. For information on database compatibility, see
What Is Oracle Database
Compatibility? in Oracle Database Upgrade
Guide.
Here are the main steps involved in using SQL Tuning Advisor in Diagnostics & Management:
- Select the input and run SQL Tuning Advisor: The input (SQL
statements or an STS) for SQL Tuning Advisor can be selected using one of the
following options and submitted as a SQL tuning task:
-
Go to Performance Hub, select one or more SQL IDs on the ASH Analytics tab, and click Tune SQL.
-
Click Tune SQL in the SQL Tuning Advisor tasks section and select SQL statements or an STS. Note that to be able to select individual SQL statements as the input, the SQL statements must first be selected on the ASH Analytics tab in Performance Hub.
-
Enable automatic SQL tuning on the database. Note that Diagnostics & Management does not support the automatic configuring of SQL Tuning Advisor, however, if SQL Tuning Advisor is configured to run automatically on the database, then the automatic SQL tuning task and the findings and recommendations are also displayed in Diagnostics & Management. For information on how to configure SQL Tuning Advisor as an automated task, see Managing the Automatic SQL Tuning Task in Oracle Database SQL Tuning Guide.
-
- View the findings: The SQL Tuning Advisor findings are displayed in the SQL Tuning Advisor tasks section on the Managed database details page.
- Implement the recommendations: The SQL Tuning Advisor findings and recommendations are available on the SQL Tuning Advisor task details page and you can review this information and opt to implement the recommendations.
Role and Privileges Required to Use SQL Tuning Advisor
You require Oracle Database administrative privileges to perform the tasks in the SQL Tuning Advisor workflow. In addition, the following role and privileges must be assigned:
GRANT SELECT_CATALOG_ROLE <following privileges> TO <admin user>ADVISORCREATE JOBCREATE SESSIONSELECT ANY DICTIONARYINHERIT ANY PRIVILEGESADMINISTER SQL TUNING SET TO <SQLTUNEUSER>
For more information on Oracle Database roles and privileges, see Configuring Privilege and Role Authorization in Oracle Database Security Guide.
Run SQL Tuning Advisor
As a first step, you must run SQL Tuning Advisor on selected SQL statements or an STS.
You can use one of the following options to access the Run SQL Tuning Advisor panel on the Managed database details page of the Managed Database:
-
Click Performance Hub and on the ASH Analytics tab, scroll down to the SQL IDs listed in the SQL ID by Wait Class section (default view), select one or more SQL statements, and click Tune SQL.
Note
Performance Hub for Managed Databases only supports the Oracle Database Enterprise Edition and the availability of Performance Hub features depends on the Oracle Database type and version, and requires certain additional privileges. For information on all the conditions that impact the use of Performance Hub for Managed Databases, see OCI: Prerequisite Conditions for Performance Hub (KB59684) in My Oracle Support. -
Click SQL Tuning Advisor on the left pane under Resources and click Tune SQL in the SQL Tuning Advisor tasks section.
In the Run SQL Tuning Advisor panel:
View SQL Tuning Advisor Findings
On running SQL Tuning Advisor, you can view its findings and recommendations in Diagnostics & Management.
After you run SQL Tuning Advisor on selected SQL statements or an STS, the
SQL tuning task is displayed in the SQL Tuning Advisor tasks
section. Note that if SQL Tuning Advisor is configured to run automatically on the
database, then the automatic SQL tuning tasks are also displayed. For each of the SQL
tuning tasks, you can click the Actions icon (![]() ) and click the Re-run SQL tuning task option to rerun
the SQL tuning task, if required.
) and click the Re-run SQL tuning task option to rerun
the SQL tuning task, if required.
Click the name of the SQL tuning task to go to the SQL Tuning Advisor task details page. The SQL Tuning Advisor findings and recommendations are displayed on the following tabs on the SQL Tuning Advisor task details page:
- Summary tab: View a graphical summary of the task
and the findings provided by SQL Tuning Advisor:
- Distinct SQL statements examined: The SQL statements examined by SQL Tuning Advisor are grouped into the SQL examined with findings, SQL skipped due to errors, and SQL examined without findings categories and displayed in a donut chart. Note that if the SQL statement was executed multiple times, then only one (distinct) execution during the analysis time period is considered.
- Benefit for SQL profile recommendations: The benefit of the SQL profile recommendations in DB time (in seconds) is displayed in bar charts. The bar charts have before and after bars, which denote the actual DB time and improved DB time respectively. If the SQL profile recommendations are provided but not implemented, then a single Potential benefit chart is displayed, if the SQL profile recommendations are implemented partially, then the Potential and Implemented benefit charts are displayed, and if the SQL profile recommendations are implemented completely, then only the Implemented benefit chart is displayed.
- Findings with recommendations by type: The SQL Tuning Advisor findings with recommendations are categorized by type and displayed in a bar chart.
- SQL findings tab: View the findings and implement the recommendations of SQL Tuning Advisor. You can view the list of SQL statements and the corresponding information based on the analysis done by SQL Tuning Advisor. This includes estimated performance benefit and findings with recommendations. You can select a single SQL statement to view the specific recommendations for each finding, the rationale, and the expected benefit if a recommendation is implemented. On this tab, you can use the available options to implement all SQL profile recommendations, implement a single recommendation, and compare explain plans.
- SQL without findings tab: View the SQL statements that were skipped owing to their not being any findings or recommendations, errors, or if the task timed out.
Implement SQL Tuning Advisor Recommendations
You can create jobs to implement SQL Tuning Advisor recommendations.
To do so, go to the SQL Tuning Advisor task details page, and view the findings and recommendations of the SQL Tuning Advisor analysis on the SQL findings tab. On this tab, you can create a job to implement all SQL profile recommendations or implement a single SQL profile, index, or statistics-related recommendation, and compare explain plans. You can also view restructure SQL, alternative plan, and miscellaneous findings, however, the option to implement restructure SQL and alternative plan recommendations is not available. For information on restructure SQL and alternative plans, see SQL Structural Analysis and Alternative Plan Analysis in Oracle Database SQL Tuning Guide.
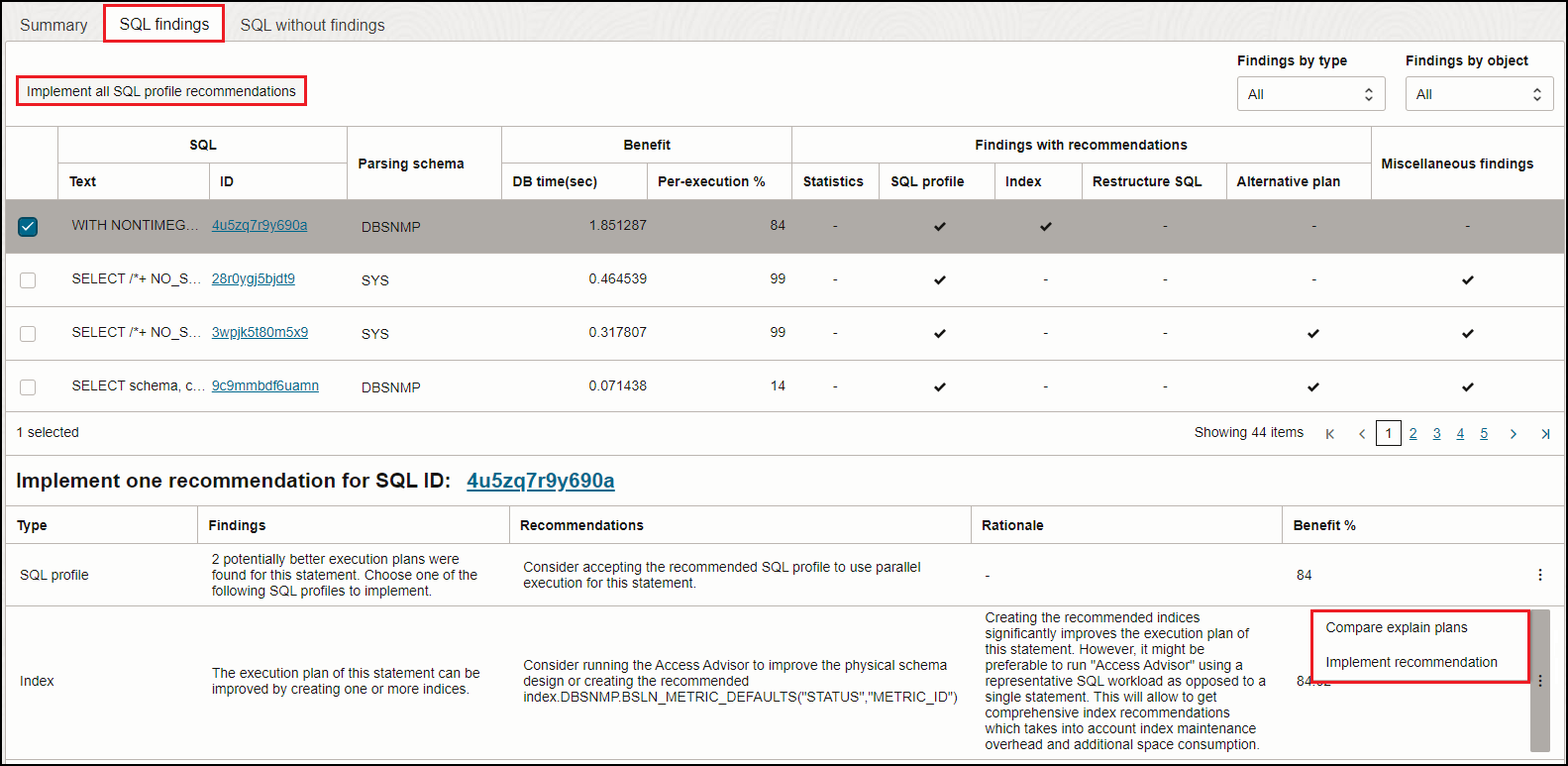
Implement all SQL Profile Recommendations
To implement a single SQL profile recommendation, select a single SQL
statement, scroll down to the Implement one recommendation for SQL ID: <SQL
ID> section and click the Actions icon
(![]() ) in the SQL profile row and click
Implement recommendation.
) in the SQL profile row and click
Implement recommendation.
For information on SQL profiles, see About SQL Profiles in Oracle Database SQL Tuning Guide.