Clone an Autonomous AI Database from a Backup
Shows the options to select a backup as the clone source for cloning Autonomous AI Database.
Perform the following prerequisite steps as necessary:
-
Open the Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Console by clicking the
 next to Cloud.
next to Cloud.
- From the Oracle Cloud Infrastructure left navigation menu click Oracle Database and then click Autonomous AI Database.
To clone an Autonomous AI Database instance from a backup:
- Choose your region. See Switching Regions for information on switching regions and working in multiple regions.
- Choose your Compartment. See Compartments for information on using and managing compartments.
- Select an Autonomous AI Database instance from the list in your compartment.
- On the Details page, from the More actions drop-down list, select Create clone.
- On the Create Autonomous Database clone page, choose the clone type from the choices:
- Full clone: creates a new database with the source database’s data and metadata.
- Refreshable clone: creates a read-only full clone that can be easily refreshed with the source database’s data.
See Use Refreshable Clones with Autonomous AI Database for more information.
- Metadata clone: creates a new database with the source database’s metadata without the data.
- In the Configure clone source area, select the
Clone source option:
-
Clone from database instance: This creates a clone from a running database. See Clone an Autonomous AI Database Instance for details and steps with this selection.
-
Clone from a backup: This selection creates a database clone using a backup. Select this option.
-
- In the Configure clone source area, select the
Backup clone type:
-
Point in time clone: Enter a timestamp to clone in the Enter Timestamp field.
-
Select the backup from a list: Enter From and To dates to narrow the list of backups then select a backup to use for the clone source.
-
Latest backup timestamp: See Clone an Autonomous Database from Latest Backup for information on this clone option.
Point in time clone
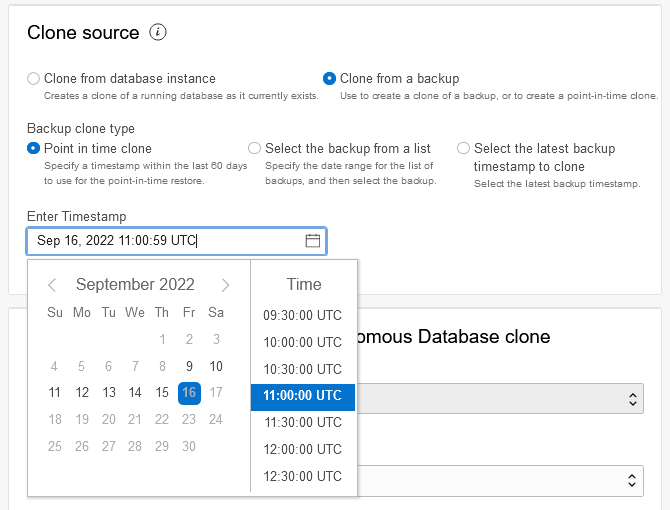
Description of the illustration adb_clone_source_backup.pngSelect the backup from a list
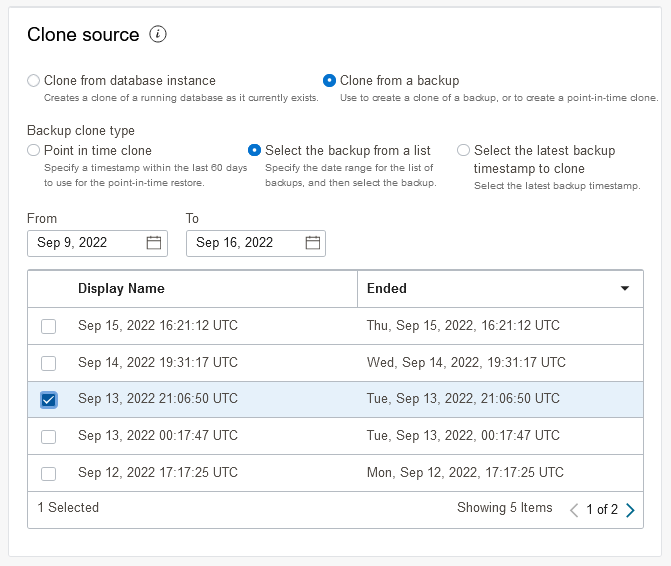
Description of the illustration adb_clone_source_list.png -
- Provide basic information for the Autonomous Database.
-
Choose your preferred region: from the list, select the region where you want to create the clone.
Note: the list only shows the regions that you are subscribed to.
For the clone type Clone from a backup as the clone source, when you choose another region other than the current region for your clone target, using either the Oracle Cloud Infrastructure CLI or Terraform you can only perform such a cross-region clone from the remote region. That is, call the create clone API from the remote region to which you want to clone, with the source database OCID as that of the source that you want to clone from.
-
Create in Compartment: See Compartments for information on using and managing compartments.
-
Display name: Specify a user-friendly description or other information that helps you easily identify the resource.
You can use the name provided, of the form: Clone-of-DBname or change this to the name you want to use to identify the database. The supplied DBname is the name of the source database that you are cloning.
-
Database Name: Specify the database name; it must consist of letters and numbers only. The maximum length is 30 characters. The same database name cannot be used for multiple Autonomous AI Databases in the same tenancy in the same region.
The default database name is a generated 16-character string.
-
- Select a value for Choose a workload type from the following options.
-
Lakehouse: This creates an Autonomous AI Lakehouse type clone.
-
Transaction Processing: This creates an Autonomous Transaction Processing type clone.
-
JSON: This creates an Autonomous AI JSON Database type clone.
-
APEX: This creates an APEX type clone.
Note
The unavailable cloning options are grayed out. See Clone Autonomous AI Database to Change Workload Type for more information on cross workload cloning. -
- Configure the database (ECPU compute model)
-
Always Free: Select to show Always Free options.
You can only create a free instance in the tenancy's Home region.
-
Choose database version: Select the database version. The available database versions are Oracle AI Database 26ai and Oracle Database 19c.
Notes for selecting a database version:
-
In regions where Oracle AI Database 26ai is not available, Oracle Database 19c is the only choice.
-
Autonomous AI Database with Oracle AI Database 26ai in the Paid tier is available in all commercial public cloud regions.
-
Always Free Autonomous AI Database with Oracle AI Database 26ai is available in all commercial public cloud regions except the following regions: Colombia Central: Bogota (BOG), Saudi Arabia Central (RUH), Singapore West: Singapore (XSP)
-
If the source database version is Oracle Database 19c, in regions where Oracle AI Database 26ai is available, you can choose either Oracle Database 19c or Oracle AI Database 26ai for the clone.
-
If the source database version is Oracle AI Database 26ai, you can select Oracle AI Database 26ai for the clone.
-
-
ECPU count: Specify the number of CPUs for your database. The minimum value for the number of ECPUs is 2.
-
Compute auto scaling: By default compute auto scaling is enabled to allow the system to automatically use up to three times more CPU and IO resources to meet workload demand. If you do not want to use compute auto scaling then deselect this option.
See Use Auto Scaling for more information.
-
Storage: Specify the storage you wish to make available to your database. Depending on your workload type you have these options:
-
Lakehouse: Specify your storage in Terabytes (TB).
For a Full Clone, the minimum storage that you can specify is the source database's actual used space rounded to the next TB.
-
Transaction Processing or JSON: Specify your storage in Gigabytes (GB) or Terabytes (TB). Enter the size in the Storage field. Select GB or TB for the Storage unit size.
For a Full Clone, the minimum storage that you can specify is the source database's actual used space rounded to the next GB.
-
-
By default, the IO capacity of your database depends on the number of ECPUs you provision. When you provision 384 TB of storage, your database is entitled to the full IO capacity of the Exadata infrastructure, independent of the number of ECPUs you provision.
Autonomous AI Database uses Exadata Smart Flash Cache to automatically cache frequently accessed data, delivering the high I/O rates and fast response times of flash. The amount of flash cache for your database depends on the amount of storage you provision, or the amount of allocated storage if you enable storage auto scaling.
If you want to provision more than 384 TB of storage, file a Service Request at Oracle Cloud Support.
-
Storage auto scaling: By default storage auto scaling is disabled. Select if you want to enable storage auto scaling to allow the system to automatically expand to use up to three times more storage.
With storage auto scaling disabled, the guaranteed minimum flash cache size is 10% of your database's provisioned storage size.
With storage auto scaling enabled, the guaranteed minimum flash cache size is 10% of your database's provisioned base storage size or its allocated storage size, whichever is higher.
See Use Auto Scaling for more information.
-
Show advanced options: Click to show the compute model options or if you want to create or join an elastic pool:
-
Enable elastic pool:
See Create an Elastic Pool While Provisioning or Cloning an Instance for more information.
-
Compute model: Shows the selected compute model.
See Compute Models in Autonomous Database for more information.
-
Bring your own license: If you want to Bring Your Own License to the database, click Enable to show the Update license and Oracle AI Database Edition page.
See Choose Bring Your Own License Option While Provisioning or Cloning for more information.
-
-
- Backup retention
By default the automatic backup retention is 60 days.
Automatic backup retention period in days You have the option to select the automatic backup retention period, in a range from 1 to 60 days. You can restore and recover your database to any point-in-time in this retention period.
Select Immutable backup retention to lock the backup retention period.
After setting the immutable backup retention option, you cannot disable this option or change the retention period. To disable immutable backup retention or to change the backup retention period, file a Service Request at Oracle Cloud Support.
See About Backup and Recovery on Autonomous AI Database for more information.
- Create administrator credentials.
-
Username This is a read-only field.
- Password Set the password for the Autonomous AI Lakehouse Admin user. The password must meet the strong password complexity criteria based on Oracle Cloud security standards. For more information on the password complexity rules see Create Users on Autonomous AI Database - Connecting with a Client Tool.
- Confirm password Specify a value to confirm the password.
-
- Choose network accessNote
After you clone your Autonomous AI Database you can change the network access option you select for the cloned instance.-
Secure access from everywhere
By default all secure connections are allowed from everywhere.
-
Secure access from allowed IPs and VCNs only
This option restricts connections to the database according to the access control rules (ACLs) you specify. To add multiple ACLs for the Autonomous AI Database, select this option and click Add access control rule.
See Configure Access Control Lists When You Provision or Clone an Instance for more information.
-
Private endpoint access only
This option assigns a private endpoint, private IP, and hostname to your database. Specifying this option allows traffic only from the VCN you specify; access to the database from all public IPs or VCNs is blocked. This allows you to define security rules, ingress/egress, at the Network Security Group (NSG) level and to control traffic to your Autonomous AI Database.
See Configure Private Endpoints When You Provision or Clone an Instance for more information.
See IP Address Ranges for information about the public IP address ranges in Oracle Cloud Infrastructure. You must allow traffic to these CIDR blocks to ensure access to an Autonomous AI Database instance on a public endpoint.
-
- (Optional) Provide contacts for operational notifications and
announcements
Click Add contact and in the Contact email field, enter a valid email address. If the database you are cloning has a customer contact list, the list is copied. To enter multiple Contact email addresses, repeat the process to add up to 10 customer contact emails.
See View and Manage Customer Contacts for Operational Issues and Announcements for more information.
- (Optional) Click Show advanced options to select advanced options.
- Encryption Key
Encrypt using an Oracle-managed key: By default Autonomous AI Database uses Oracle-managed encryption keys. Using Oracle-managed keys, Autonomous AI Database creates and manages the encryption keys that protect your data and Oracle handles rotation of the TDE master key.
Encrypt using a customer-managed key in this tenancy: If you this option, a master encryption key from a Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Vault in the same tenancy is used to generate the TDE master key on Autonomous AI Database.
Encrypt using a customer-managed key located in a remote tenancy: If you this option, a master encryption key in the Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Vault located in a remote tenancy is used to generate the TDE master key on Autonomous AI Database.
See Use Customer-Managed Encryption Keys on Autonomous Database for more information.
- Maintenance
Patch level By default the patch level is the patch level of the source database. Select Early to configure the instance with the early patch level. Select Regular to configure the instance with the regular patch level.
See Set the Patch Level for more information.
- Management
Shows the character set and national character set for your database.
See Choose a Character Set for Autonomous AI Database for more information.
- Tools
If you want to view or customize the tools configuration, select the tools tab.
See Configure Autonomous AI Database Built-in Tools when you Provision or Clone an Instance for more information.
- Security attributes
Add a security attribute to control access for your resources using Zero Trust Packet Routing (ZPR) policies. To enter security attributes during provisioning you must already have set up security attributes with Zero Trust Packet Routing. You also can add security attributes after provisioning.
Note
You can apply Oracle Zero Trust Packet Routing (ZPR) policies to a private endpoint.Specify a Namespace, Key, and Value security attribute.
Click Add security attribute to add additional security attributes.
See Overview of Zero Trust Packet Routing for more information.
- Tags
If you want to use Tags, enter the Tag key and Tag value. Tagging is a metadata system that allows you to organize and track resources within your tenancy. Tags are composed of keys and values which can be attached to resources.
See Tagging Overview for more information.
- Encryption Key
- Click Create Autonomous Database Clone.
On the Oracle Cloud Infrastructure console the State shows Provisioning... until the new database is available.
See Notes for Cloning an Autonomous Database from a Backup for additional information on cloning.
See Cloning an Autonomous Database for information on using the API.
- Clone an Autonomous Database from Latest Backup
When you choose to clone from latest backup, this selects the latest backup as the clone source. You can choose this option if a database becomes unavailable or for any reason when you want to create a clone based on the most recent backup.
Clone an Autonomous Database from Latest Backup
When you choose to clone from latest backup, this selects the latest backup as the clone source. You can choose this option if a database becomes unavailable or for any reason when you want to create a clone based on the most recent backup.
Follow the steps in Clone an Autonomous AI Database from a Backup and in the Clone source area, select Clone from a backup and Select the latest backup timestamp to clone to create a clone that recovers the most recent backup data that is available for the Autonomous AI Database instance (the clone source) from the database backup and logs backup.
After Autonomous AI Database
has finished provisioning the clone, query the view
dba_pdbs to see the
last_recover_time and
last_recover_scn columns. These columns provide the
saved timestamp and the saved SCN of the data from which the cloned database
was created.
For example:
SELECT last_recover_time, last_recover_scn FROM dba_pdbs;Parent topic: Clone an Autonomous AI Database from a Backup