Data Manufacturing
As a single developer, it can be difficult, or even impossible for you to create a large, varied set of utterances, especially when you need to provide training data for multiple intents or ML Entities. Rather than trying to come up with training data on your own, you can use Oracle Digital Assistant to crowd source this task. Assigning this to the crowd can be particularly useful when you need utterances that only experts in the application or the domain can provide.
What is a Data Manufacturing Job?
Data manufacturing jobs are collections of tasks assigned to crowd workers. The jobs themselves focus on various ways of improving intents and ML entities.
Annotation Jobs
You can assign an Annotation Job when you have logging data that needs to be classified to an intent, or when a single intent is too broad and needs to be broken down into separate intents. You can also assign crowd workers to annotate the key words and phrases from the training data that relate to an ML Entity.
The Data Manufacturing Job Workflow
To create a data manufacturing job, you first create a job and monitor its progress. If you want to access the data before the job has officially finished (say, for example, that the crowd workers are no longer working on the job), then you can cancel the job. Finally, you review the results before you add them to the training data by accepting them, or exclude them from the training data by rejecting them.
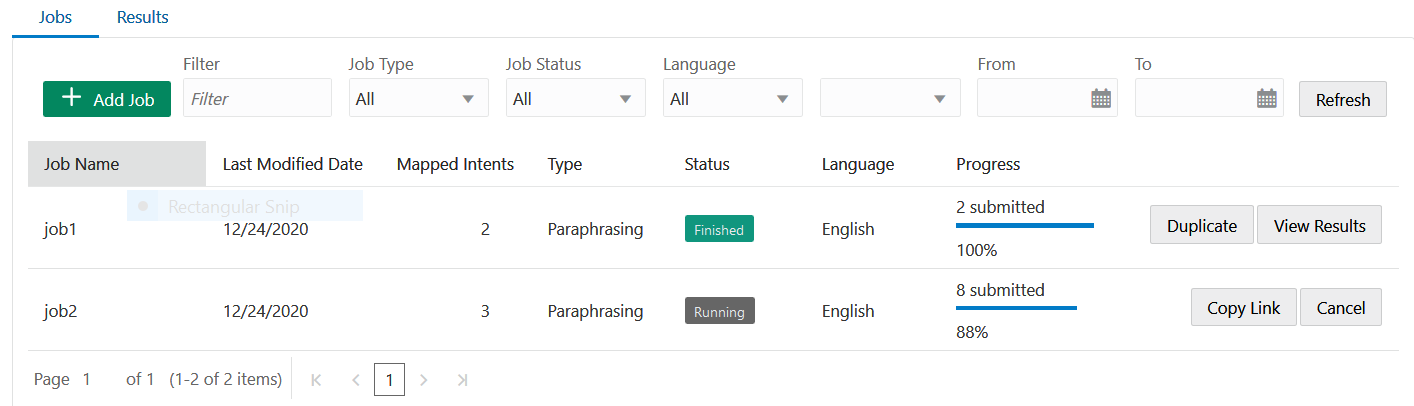
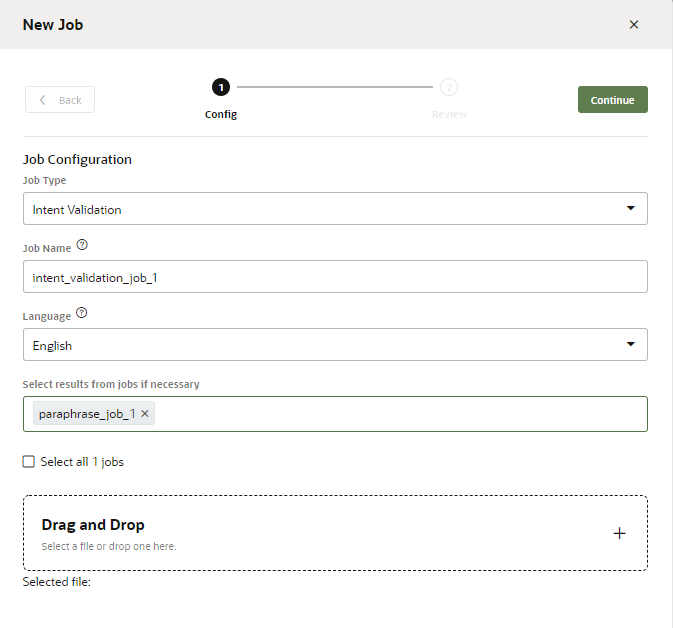
Create the Job
- Click Manufacturing
 in the left navbar.
in the left navbar.
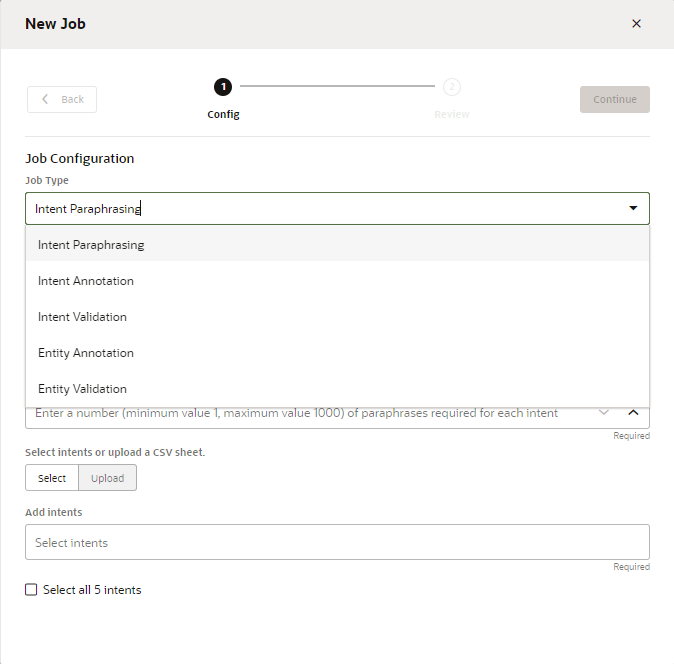
- In the Jobs page, click Add Job.
- Select the job type (Paraphrasing,
Validation, or
Annotation).
- Select the language that's used by the crowd workers. The default language is the skill's predominant language, but you can choose from other natively supported languages. You can't, however, choose a language that's enabled by a translation service.
- Click Launch. After you launch a job, its status is noted as Running in the Jobs page. You can’t edit a job when it's running. If you need to make a change, you need to first cancel the job, duplicate it, and then edit it before relaunching it.
- To send the job to the crowd, click Copy
Link. Then paste the link to an email that's broadcast to the crowd.
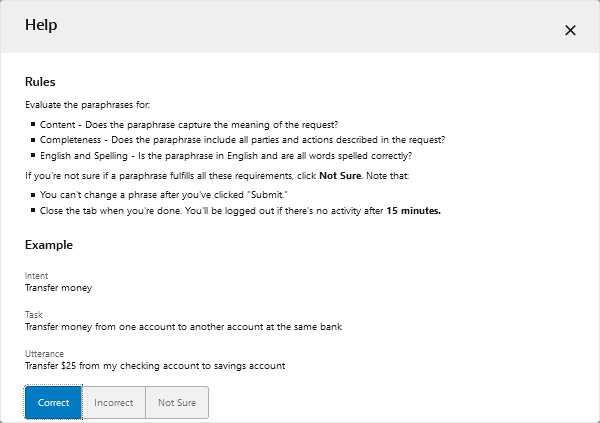
Crowd workers accept the job by clicking this link. After a crowd worker accepts the job, he or she reviews general rules for Paraphrasing, Annotation, or Validation jobs.Note
Crowd workers provide their names and email addresses for tracking purposes. You sort the results by their names to gauge their success in completing the tasks.
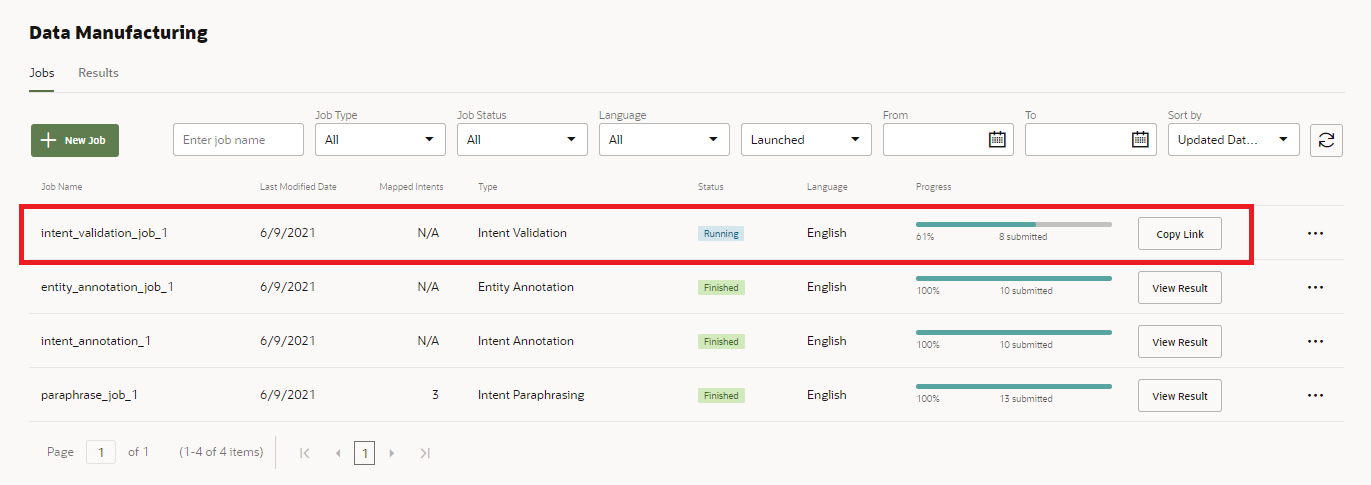
Monitor the Progress of the Crowd Workers
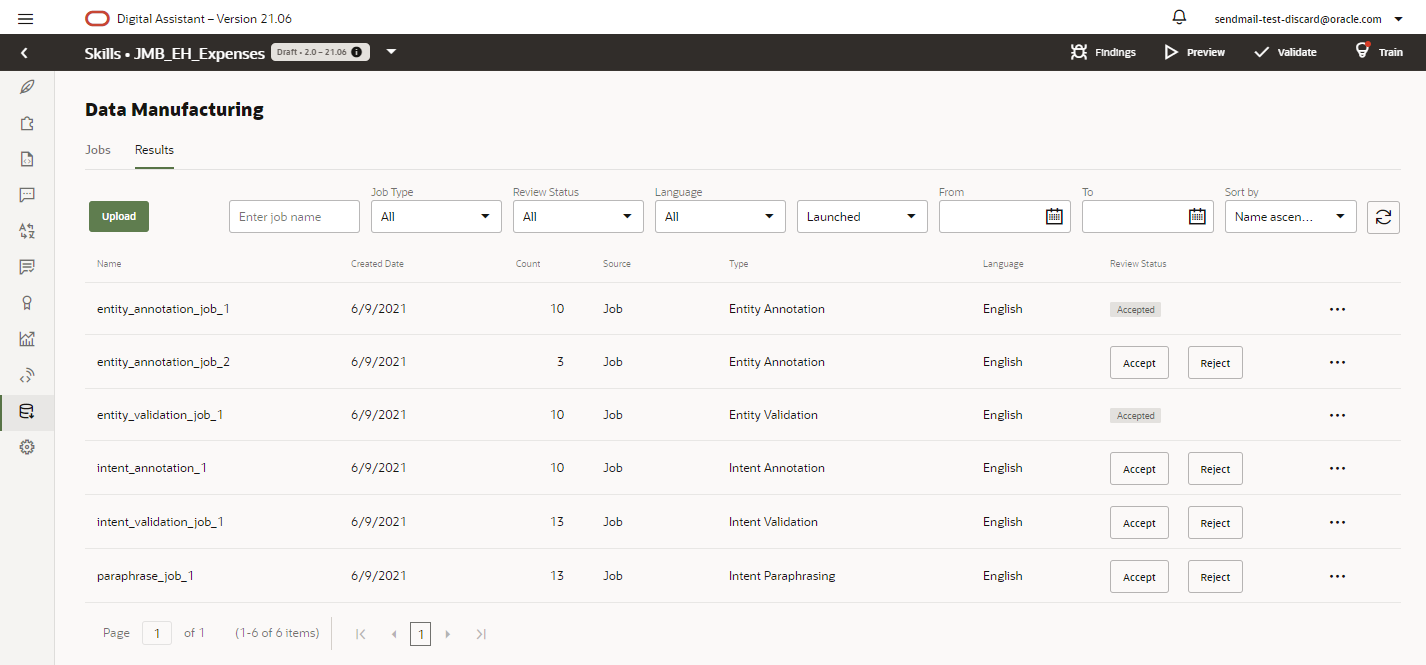
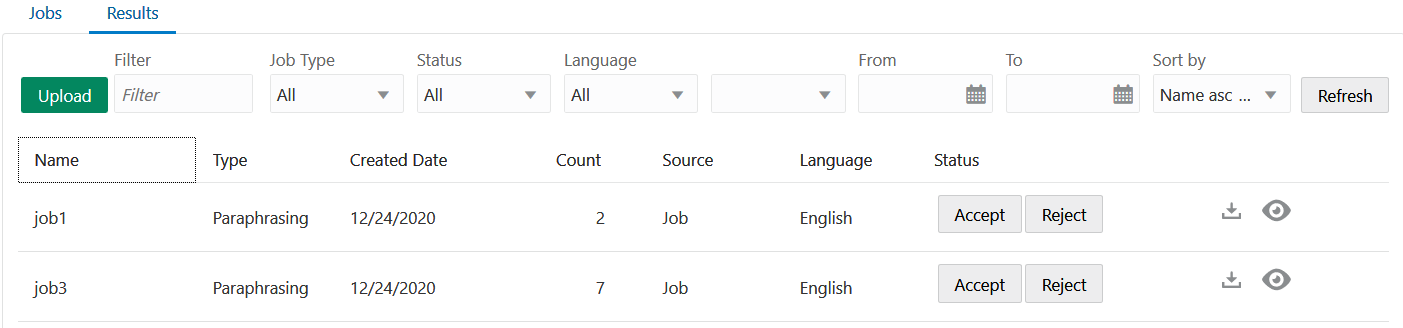
Jobs that have finished, or have been canceled, are available for download in the Results page. Typically, you’d use this page to access and modify results by downloading them as a CSV file that you can manipulate in a spreadsheet program like Excel.
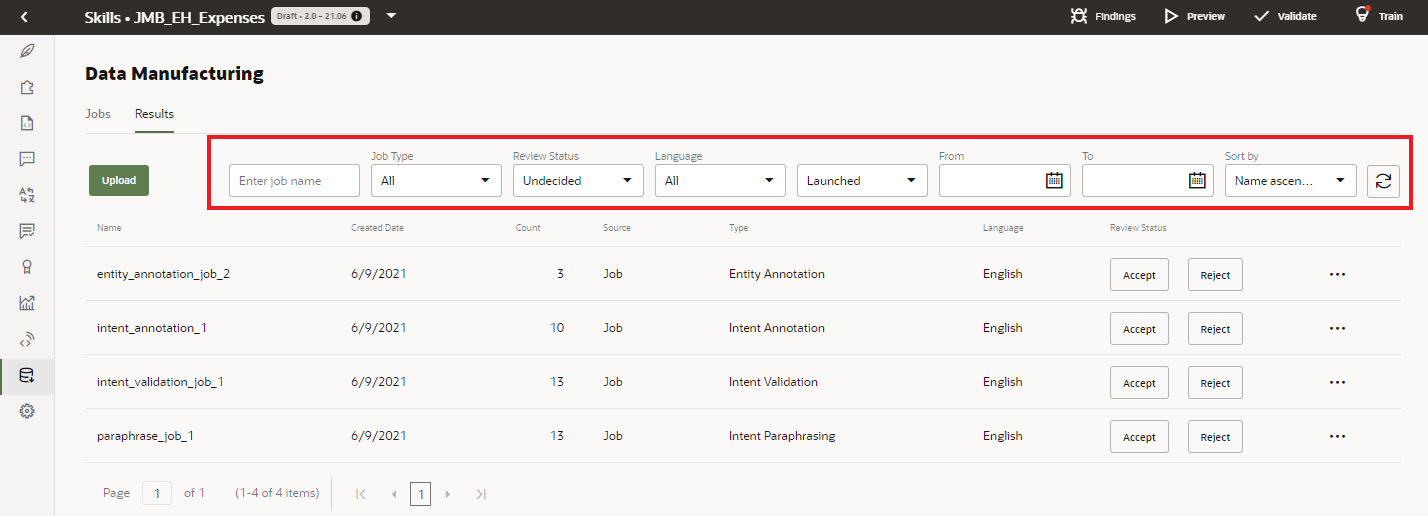
As the number of jobs increases, you can filter them as Accepted, Rejected, or Undecided, which is for jobs that have neither been accepted or rejected.
Tip:
Because the Accepted or Rejected status signifies that your work on a job has concluded, you're likely to filter by Undecided most often.Review the Results
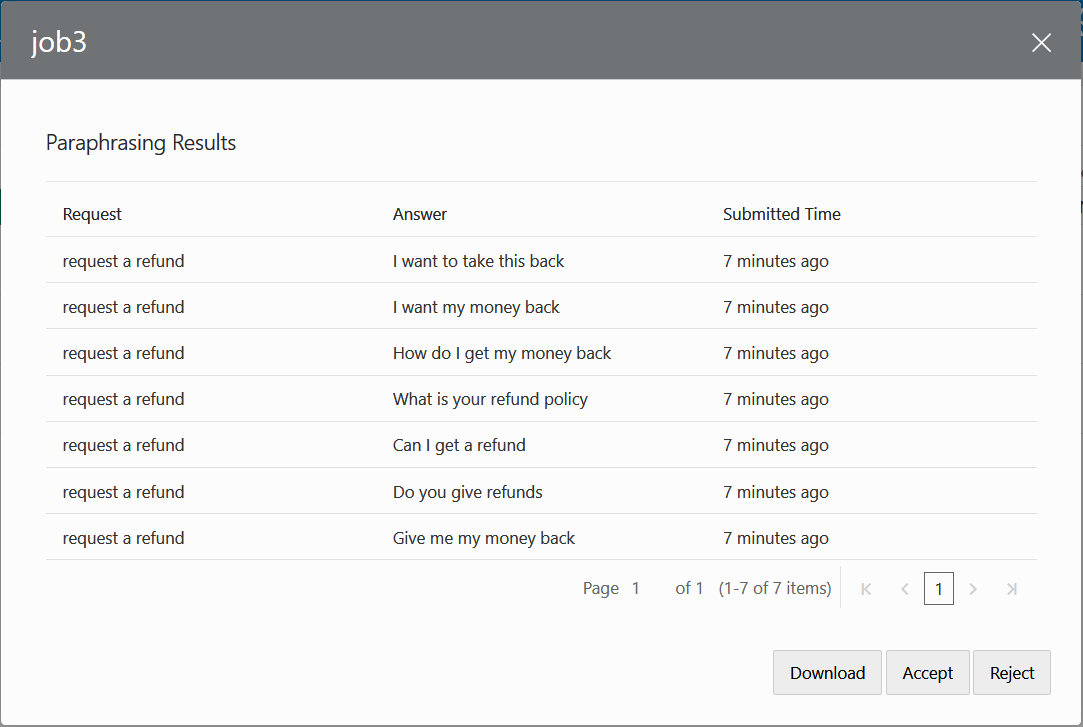
- Click View to examine the results.
If most of the results are uniformly incorrect, then click Reject. You might reject a poorly conceived job that confused or mislead crowd workers, or you might reject a job because it was a test. If you find the results are correct, then you can add them to your training set by clicking Accept. Before you choose this option, keep in mind that you cannot undo this operation, which adds the entire set of results to your training data. Because you may inadvertently add bad utterances that you can only remove by editing the intent, we recommend that you download the results and edit them before accepting them into the training corpus.
Editing the downloaded CSV files enables you to clean up the results. For Paraphrasing jobs, editing the results before committing them to your training set enables you to change utterances or delete the incorrect ones.Note
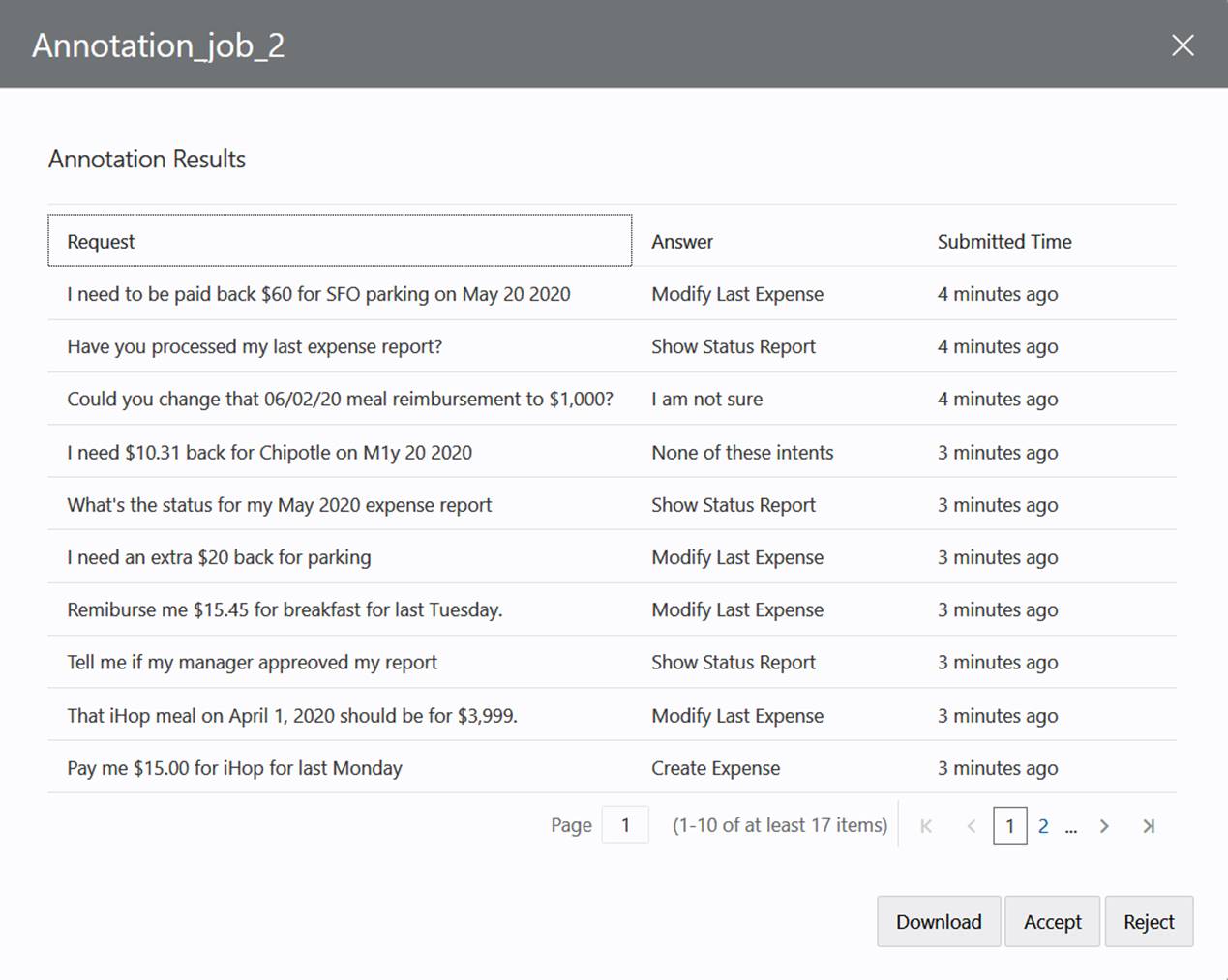
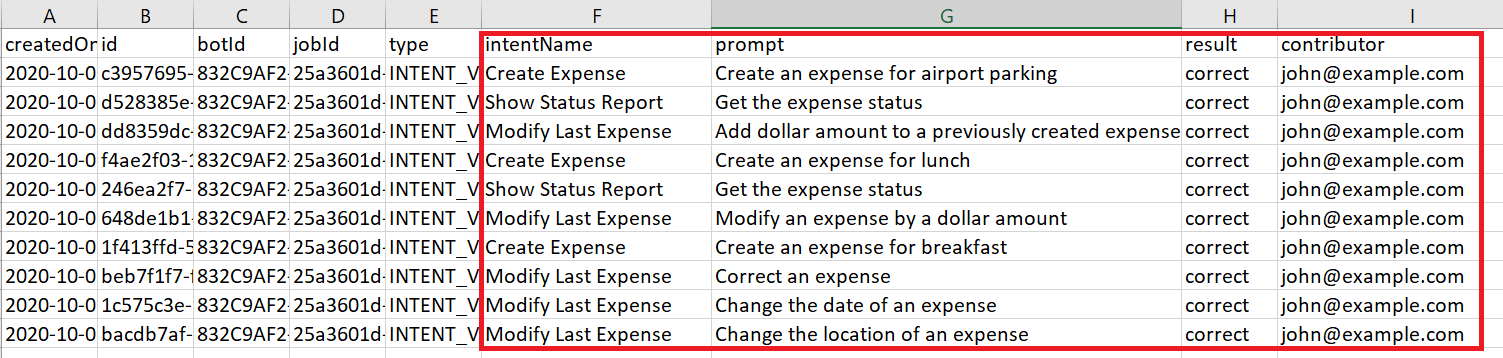
The content in theresultcolumn depends on the Job type. For a Paraphrase job, the crowd worker's utterances populate this column. For a Validation job, it's the worker's evaluation of the utterance against the task (Correct, Incorrect, Not sure), and for an Annotation job, it's the intent that matches the utterance.
To download the job, click Download either in Results page or in the View Results dialog. Save the job to
your local system and then open the CSV with a spreadsheet program.
either in Results page or in the View Results dialog. Save the job to
your local system and then open the CSV with a spreadsheet program.
- After you’ve finished your edits, click
Upload in the Results page.
- Retrain your skill.
Paraphrasing Jobs
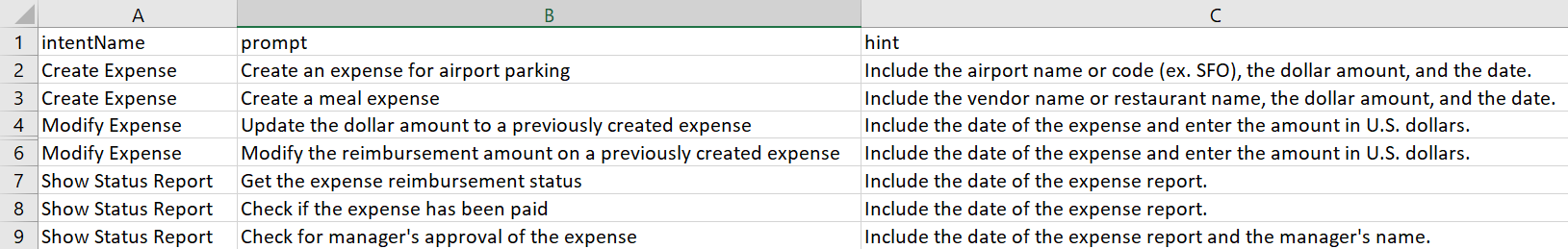
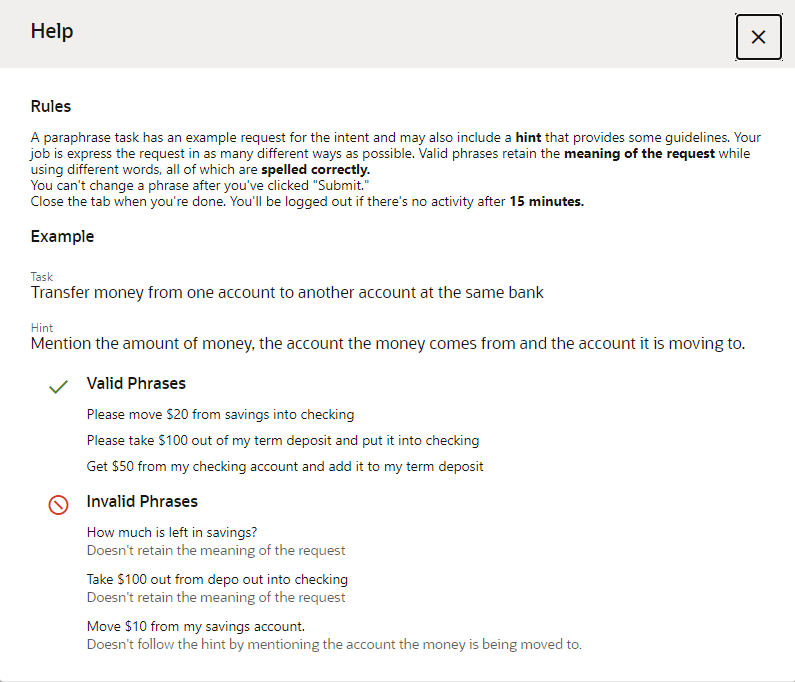
You collect utterances from the crowd workers through Paraphrasing jobs. Workers who accept the Paraphrasing job produce valid utterances using guidelines in the form of prompts and hints that you provide. A prompt captures the essence of what users expect the skill to do for them. A hint, which is optional, provides the crowd worker with further detail, such as wording and entity values. For example, "Create an expense for a merchant using a dollar amount" is a prompt for a Create Expense Report intent. The accompanying hint is "Use the merchant name ACME and a dollar amount of less than $50."
- A prompt is not an utterance. Utterances can stifle crowd worker's creativity because of their specificity. Rather than serve as an example, they instead encourage workers to simply produce slight variations. These redundant phrases add noise to your training corpus and will not improve your skill's cognition.
- If you have more than one prompt for an intent, vary them. Each prompt in a Paraphrase job is likely to be distributed to different crowd workers. Even if a crowd worker gets more than one prompt from the same Paraphrase job, having a different prompt will change the worker's perspective.
- Use hints to encourage variation. You can define hints for anything that you
want the utterances to include (or not include). As you vary your prompts, you
should likewise vary their corresponding hints.
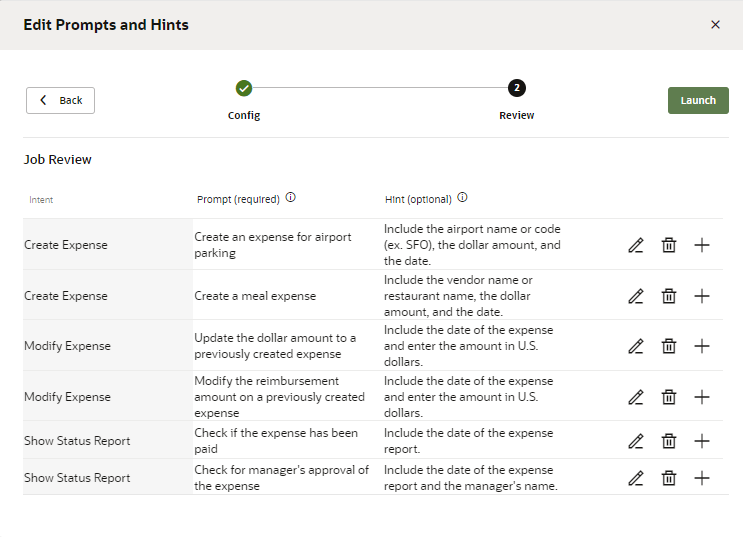
Prompt Hint Create an expense for airport parking Include the airport code (SFO, LAX, etc.), a full date (dd/mm/yyyy), and an amount in US dollars. Create an expense for a meal Include the name of the restaurant, a full date (dd/mm/yyyy), and an amount in US dollars.
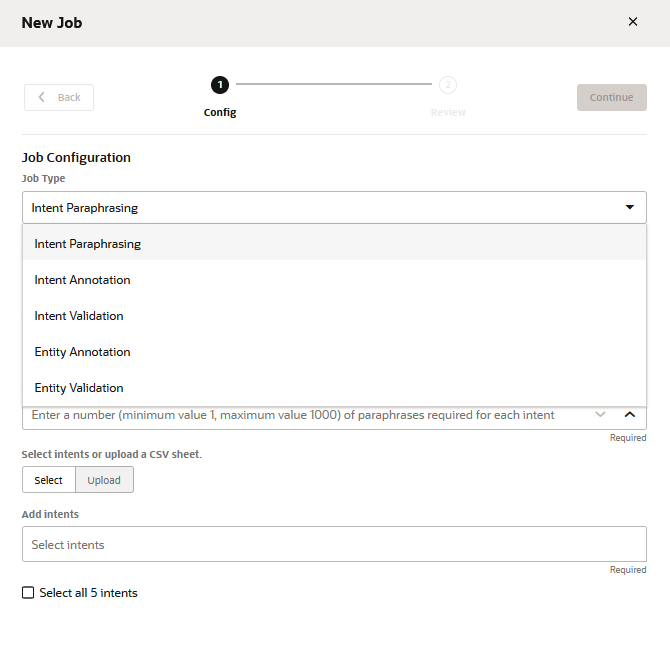
Create the Paraphrasing Job
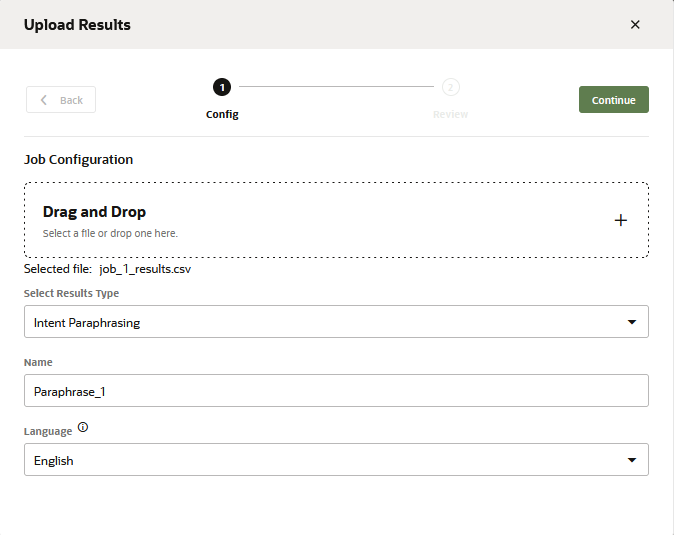
- If you haven't created any jobs yet, click Add Job (either in the landing page if you haven’t created any jobs yet, or in the Jobs tab if there are existing jobs).
- Select Paraphrasing.
- Enter a job name.
- Select the language that's used by the crowd workers. By default, the skill's predominant language displays, but you can choose from other natively supported langauges that have been set for the skill.
- Add your prompts and hints (which are optional) for the intents.
You can create these offline in a CSV file with columns named
intentName,prompt, andhint, and add them as a batch, or you can them one by one with the New Job dialog. You can add these columns in any order in the CSV file.Note
If you selected a language other than the predominant language of the skill, then your prompts and hints must also be in that language. - If you've added the prompts, hints, and intent names to a CSV, click Upload, then browse to, and select, the file. Then click Continue.
- If needed, add additional prompts
 , edit
, edit  , or delete
, or delete  prompts where needed, or change the number of utterances per prompt.
Click Launch.
prompts where needed, or change the number of utterances per prompt.
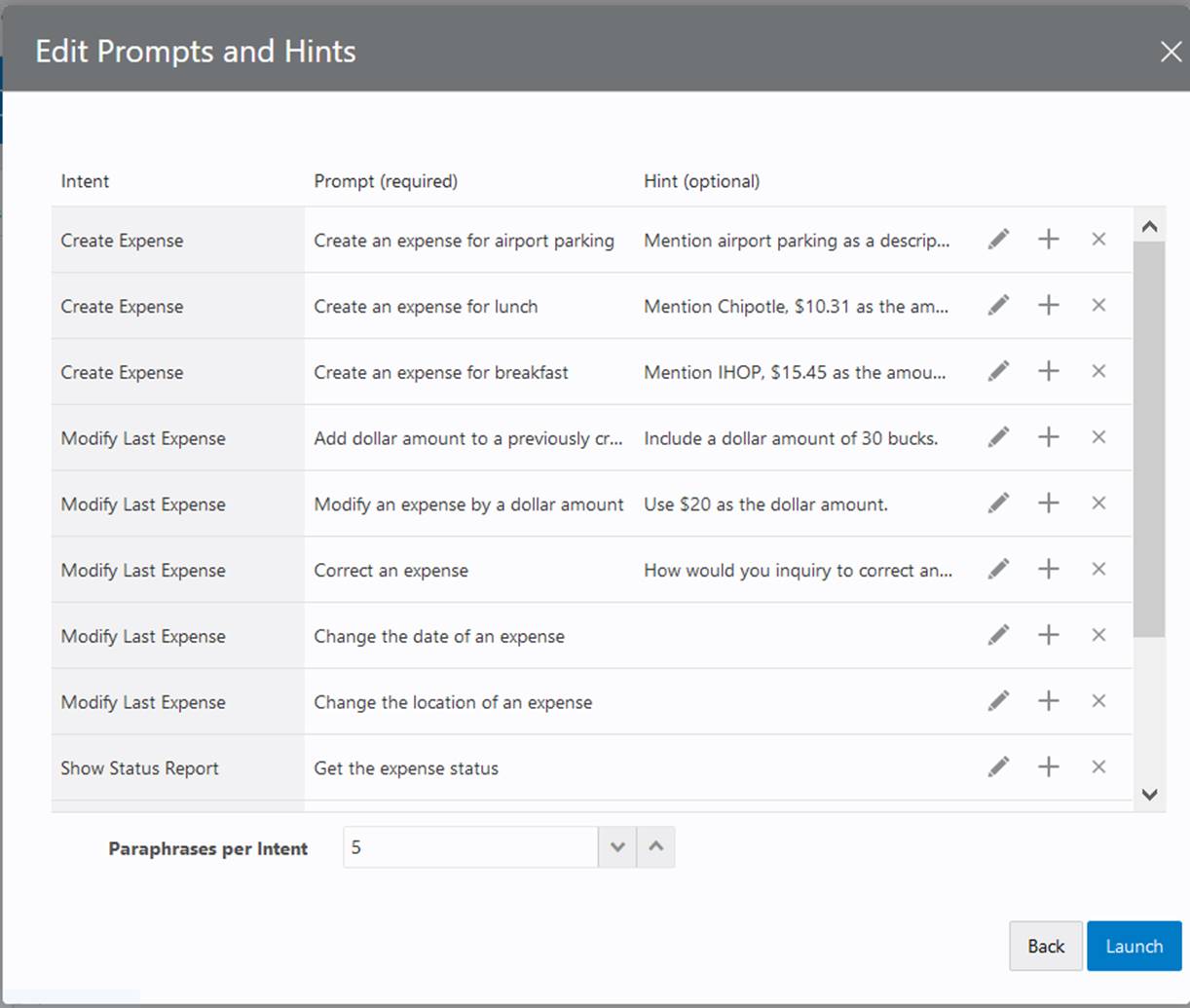
Click Launch. - To create a Paraphrase job manually, click Select.
- Click the Intents field to select and intent from the menu, or
click the Select all ... intents option if you want to
add prompts to your entire set of intents.
- Click Continue.
- Click within the Prompt field, or click Edit
 , to enter your prompt.
, to enter your prompt.
- Click within the Hint field, or click Edit
 , to enter your prompt.
, to enter your prompt.
- Click Add
 to create another prompt. Keep in mind that each new prompt is
potentially a separate job, handled by a different crowd worker.
to create another prompt. Keep in mind that each new prompt is
potentially a separate job, handled by a different crowd worker.
- If needed, delete or revise any prompts or hints.
- Click Add
- Select the number of paraphrases per prompt.
- When you’re finished, click Launch.
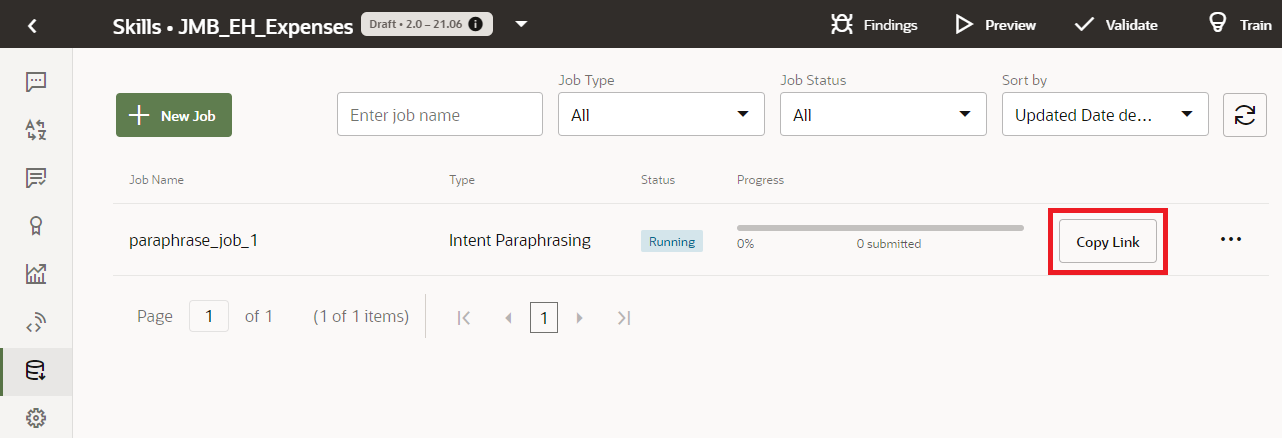
The Paraphrasing job displays as a new row in the Jobs page with its status noted as Running. - Click Copy Link in the row, then paste the
link into an email that you broadcast to the crowd. Crowd workers accept the job
by clicking this link. After a crowd worker accepts the job, he or she reviews
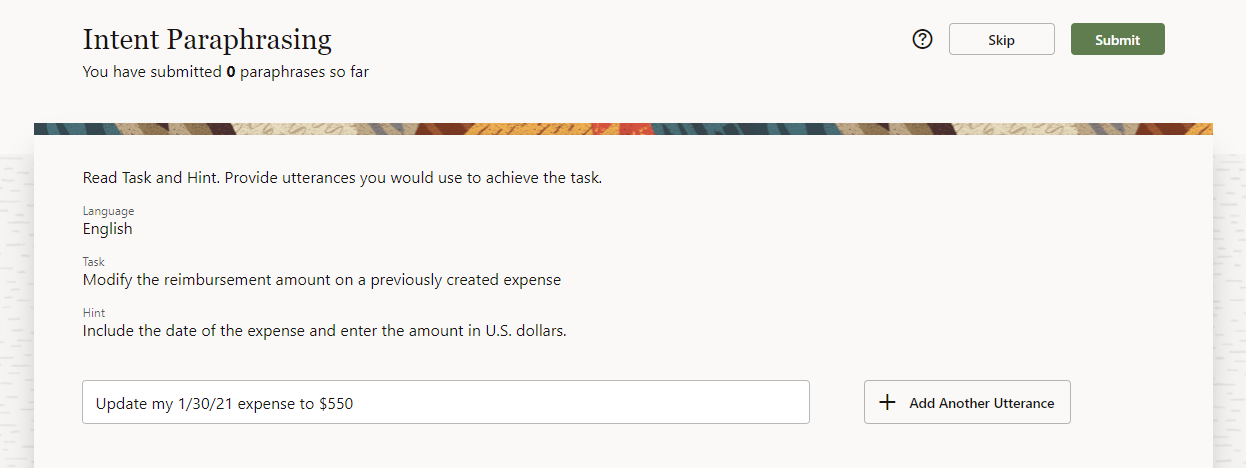
general rules for Paraphrasing jobs.NoteWorkers then submit their paraphrases.
The locale of the worker's browser is set to the language selected in the Create Job dialog.
You can monitor the progress of the running in real time from the Jobs page.
Tips for Paraphrasing Jobs
For the results of a paraphrasing job to truly improve the training corpus, it's important to set it up in a way that will elicit diverse and real-life phrases for the use case. Here are some tips for making your paraphrasing jobs more successful:
- Carefully formulate the use cases that you can use as seeds for the tasks.
- Using the "seed use cases", describe concrete scenarios for which the user should provide utterances instead of merely asking for variations on a phrase.
- Provide multiple scenarios for the same intent.
- Use the Hint field to give tips that might widen perspective. For example, for an expense intent, you might add the hint "include different currencies as if you were travelling".
Review the Paraphrasing Job
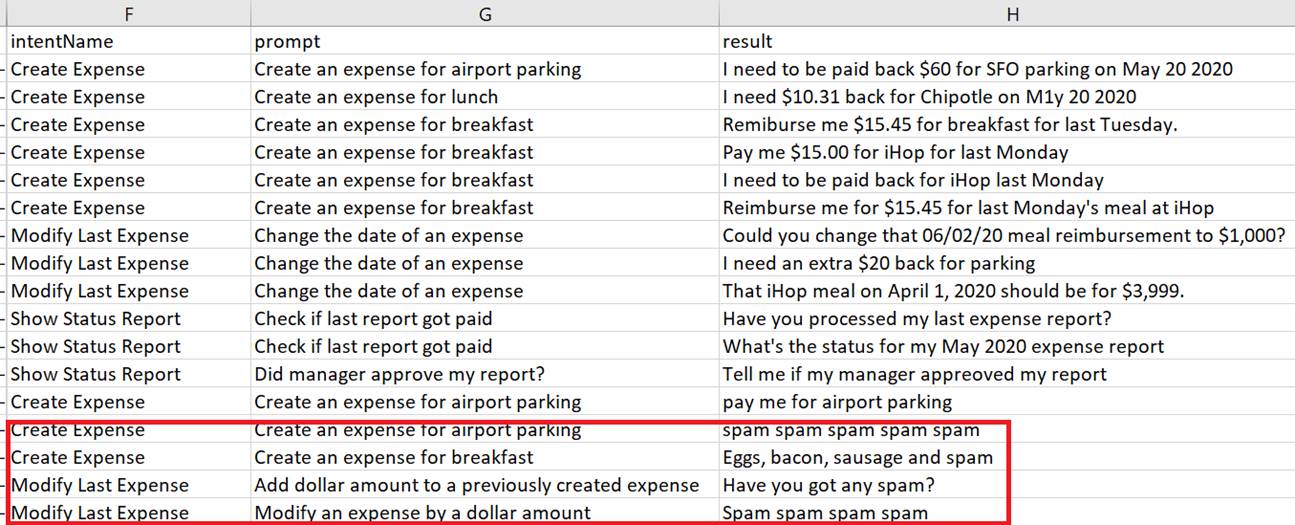
Before adding the utterances to your training set, you probably want to review them for semantics, misspellings, or spam.
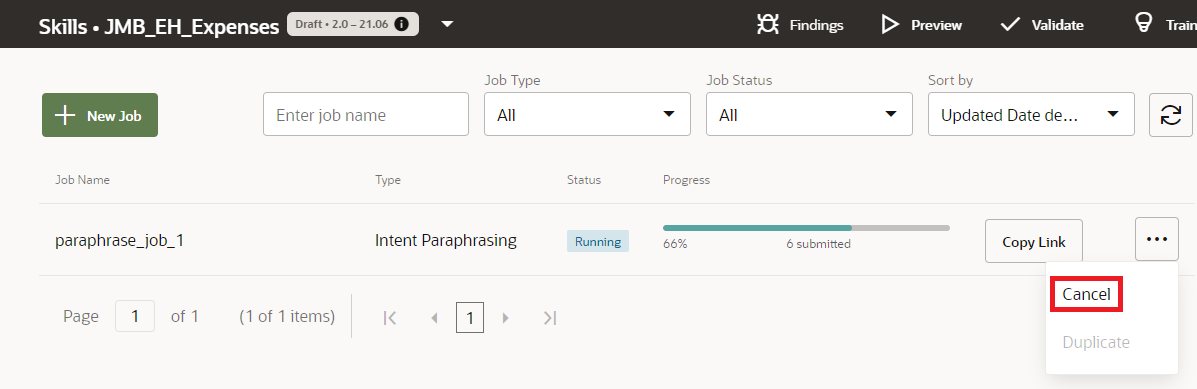
- You can wait for a job to complete, or if you believe that all contributions have been made to a running job, click Cancel in the Jobs page.
- Click Results. Only canceled or completed
jobs display in the Results page.
- Click View for a read only view of the
utterances. Using the options in this dialog, you can download the job as a CSV,
or accept or reject it in its entirety.
Before committing to rejecting or accepting all of the jobs tasks at once (which can't be undone automatically), you may instead want to download the job and clean up the results before adding them to the training set. If you follow this route, click Download either in this dialog or in the Results page.Tip:
Before you can't easily remove utterances after you've accepted them, you may want to create a new version of your skill, or clone it as a precaution. - Open the CSV file with spreadsheet program.
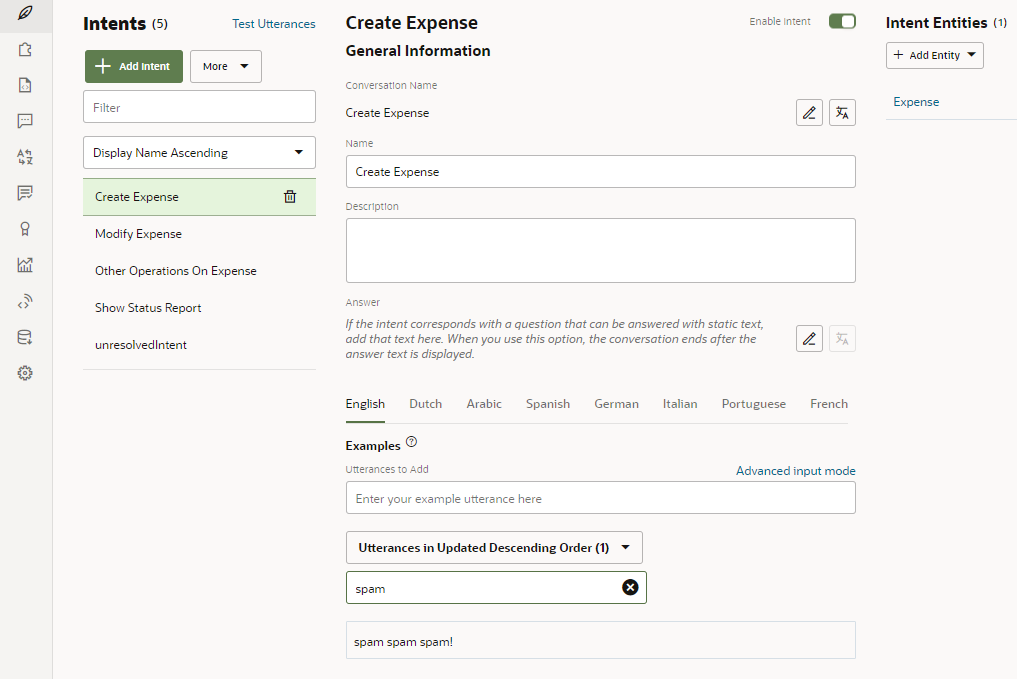
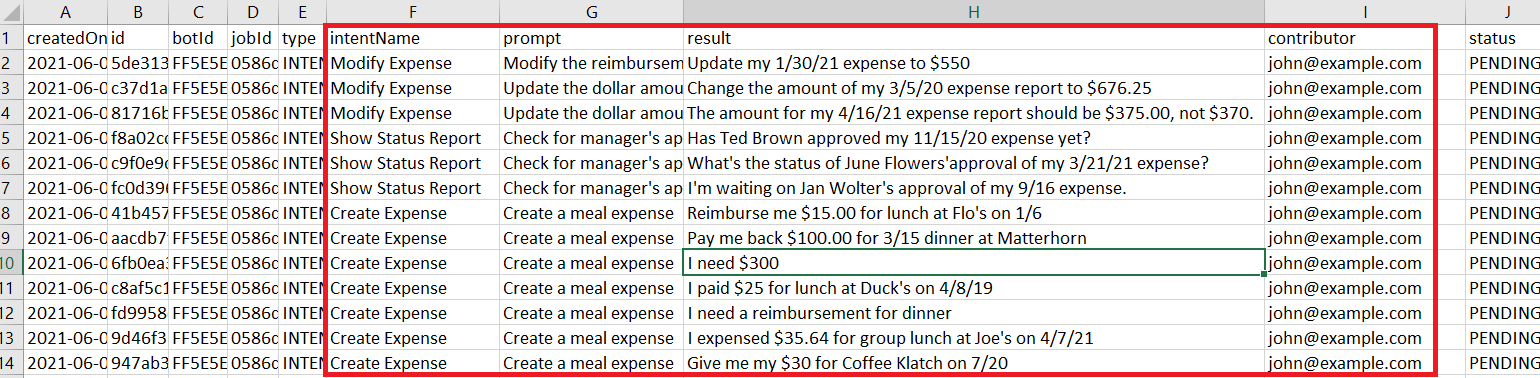
Review the utterances in the result column against the
IntentNameand prompt columns. Update the utterances in the result column where needed or delete an entire row (or rows). If the utterance is beyond repair, you can delete the entire row. If a crowd worker repeatedly enters bad utterances because he didn't understand the prompts or follow the general paraphrasing guidelines, then you can sort the worksheet by the contributor column and then delete rows. If you do delete a row, be sure to delete it completely. You won't be able to upload the file otherwise.Tip:
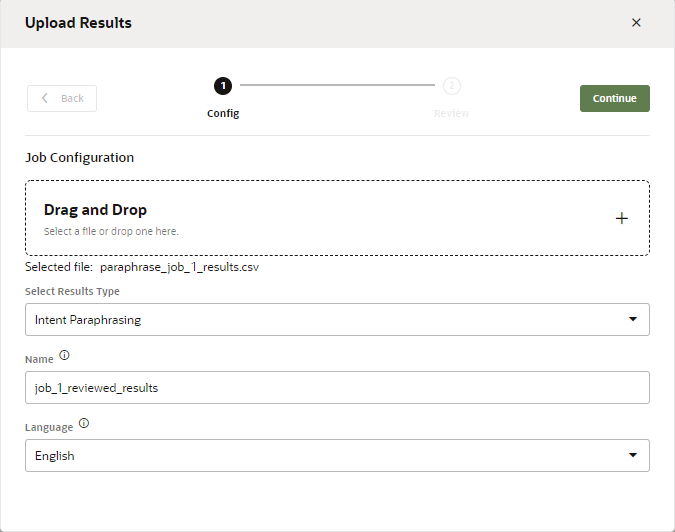
You only need to focus on theintentName,prompt,result, andcontributorcolumns of the spreadsheet. You can ignore the others. - When you're finished, click Upload in the
Results page. Browse to, then select, the CSV file. Select Intent
Paraphrasing, enter a name, then click
Upload.
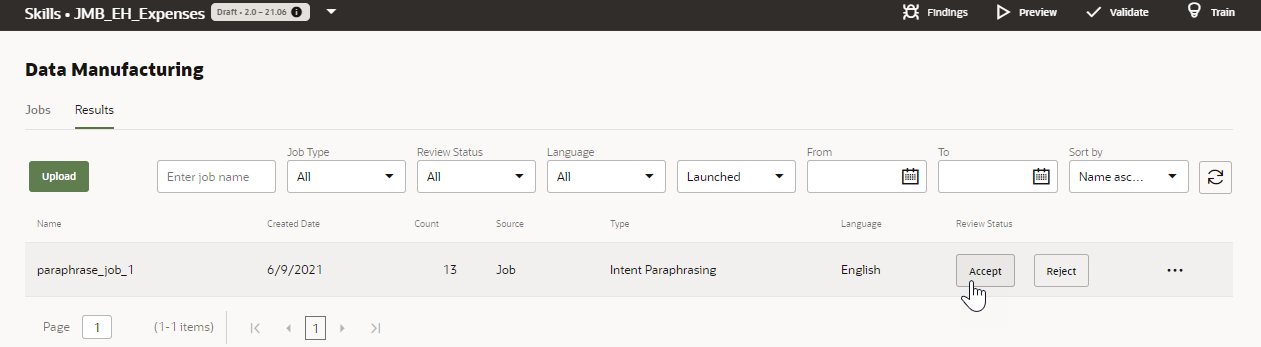
- If you want to add the utterances to an intent's training data,
click Accept in the Results page. Click Reject
if you don't want to add them to the training set. You might want to
reject a job if it's a test, or if it can't be salvaged because of ill-conceived
prompts and hints.
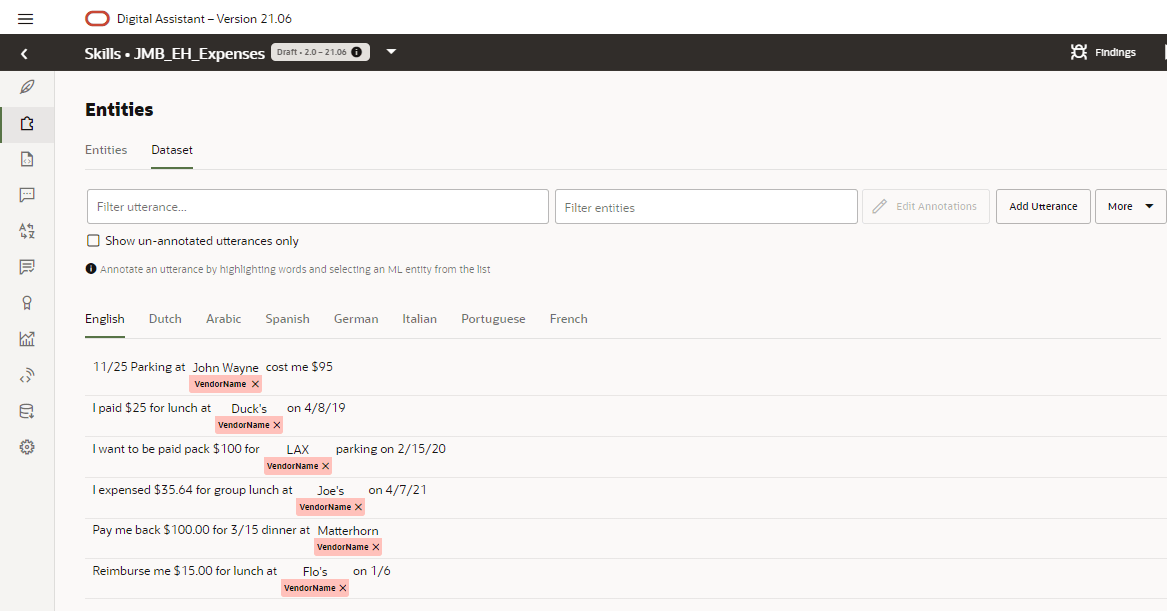
Annotation Jobs
Whenever you have chat data that needs to be mapped to an intent or annotated for ML
Entities, you can create an Annotation job. Workers complete annotation jobs for intents
by matching an utterance to an intent. For entity annotation jobs, workers label the
text in the utterance for an ML Entity. You can create these jobs using a CSV file with
an utterance column, previously completed annotation jobs, or by
combining the two approaches. You can also create an intent annotation job from the utterances collected in the Retrainer.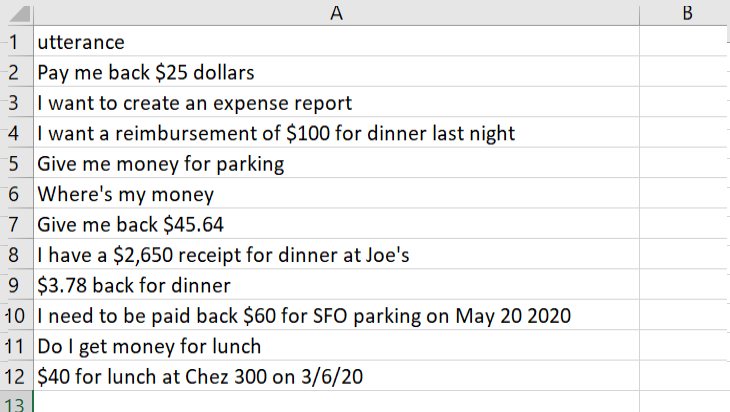
Description of the illustration annotation-csv.png
Create the Intent Annotation Job
- Click + New Job in the Jobs page.
- Select Intent Annotation.
- Enter a name.
- Enter the language that's used by the crowd workers.
- Upload the file, click Continue, note the number of items for the job, then click Launch.
- Click Copy Link and then paste the link into
an email that’s broadcast to crowd workers. Workers accept the job by clicking
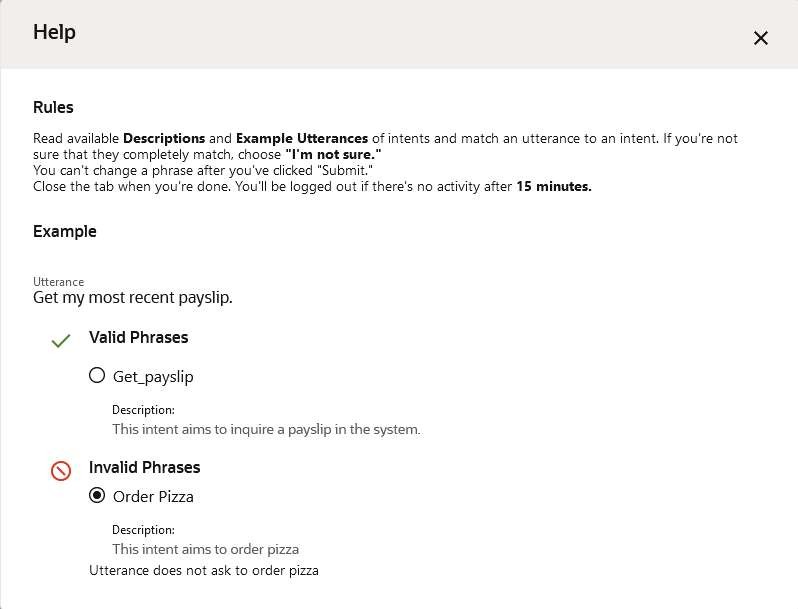
this link. After they sign in, crowd workers review basic rules on how to
classify utterances.
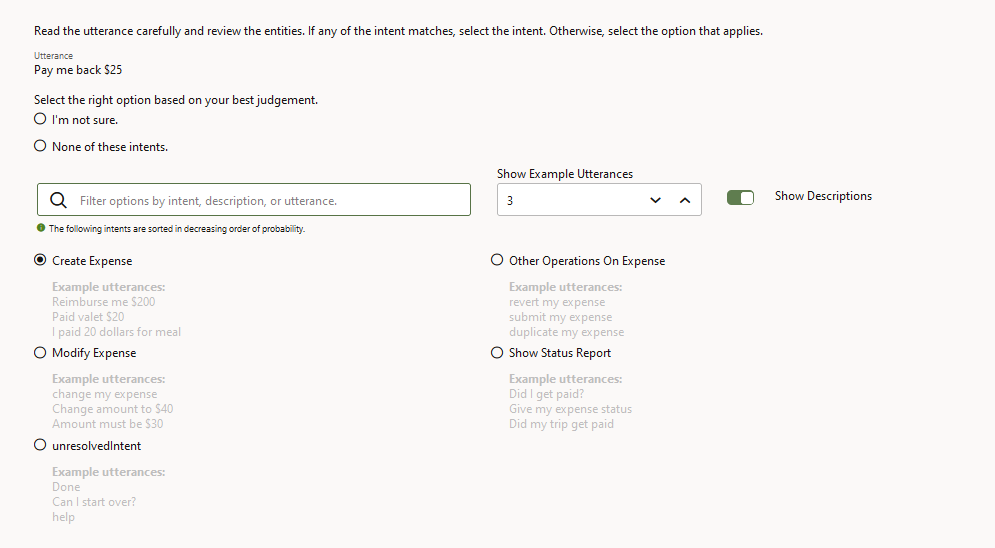
Active learning helps crowd workers out by ranking all of the skill's intents by their likelihood to match the utterance. The intent that has the highest potential to match the utterance is first. Likewise, the utterances that are currently in the corpus, which crowd workers use as a guide, are also ranked by their likelihood to match the utterance.
You can monitor the progress in the Jobs page.
Review the Annotation Job
- After the job has completed, or when you've clicked
Cancel because you think that job is as complete as
it can be, click View.
- If you disagree with some of the crowd worker's decisions, click Download to download a CSV of the results to your local system.
- In the CSV, enter the intent name that you expect in the
intentNamecolumn. - Override the intent chosen by the crowd worker in the
resultcolumn by entering the Conversation Name for the intent that you entered in theintentNamecolumn. - When you've finished your review, click
Upload in the Results page. Then select the file,
enter a name, and then click Upload.
NoteThe results will be merged into the current job.
You can't remove an entry from the results. The results retain all of the entries, even if you delete a row from the CSV before you upload. If you want to remove bad entries (because you don't want to reject the entire job), then you need to create a separate set of results that do not belong to any job by removing the contents from thejobIdandIdcolumns before you upload the file. - Retrain the skill.
Note
Only the utterances that match an intent get added to the training data. The ones classified as None of these Intents or I’m not sure are excluded.
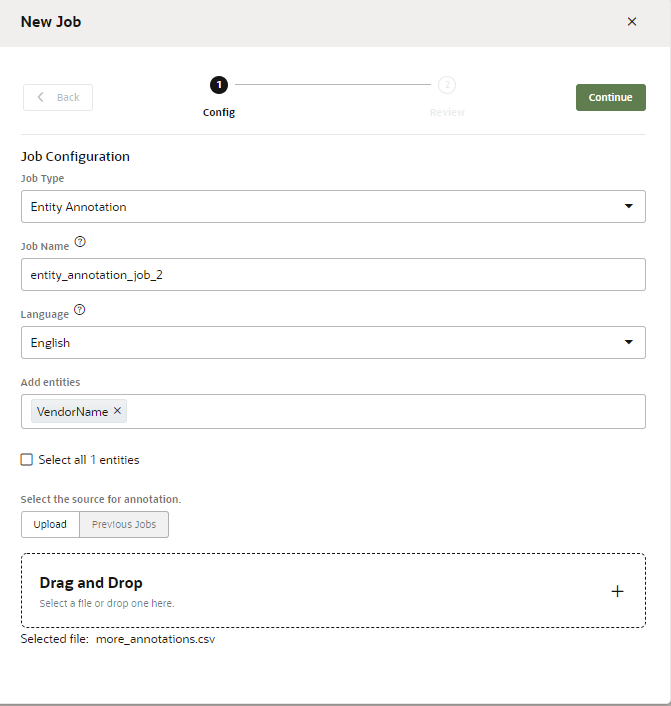
Create the Entity Annotation Job
Your skill needs at least one ML Entity for this job. You can't create an Entity Annotation Job with non-ML Entities.
- Click + New Job in the Jobs page.
- Select Entity Annotation.
- Enter a name.
- Enter the language that's used by the crowd workers.
- Select the ML Entity (or ML Entities) that crowd workers will select from. Ideally, these entities will have helpful names and succinct descriptions.
- If this is your first Entity Annotation job, browse to, then select
a CSV file. You can provide workers with either annotated or unannotated
utterances, depending on the format of this file:
- For unannotated utterances, upload a CSV that organizes the
plain utterances under a single column,
utterance:utterance I want to order a family size pepperoni pizza with thin crust and mozzarella cheese I want to order a large supreme pizza with regular crust and provolone cheese I want to order a medium size meat-lover pizza with gluten-free crust and goat cheese - For annotated utterances, upload a CSV with a single
column,
annotationwith each utterance represented as a JSON object. ThebeginOffsetandendOffsetproperties represent the beginning and end of the text labeled for the ML Entity. Create ML Entities describes the other properties in this object.
Crowd workers will review the existing labels defined by these offsets, and change them when they're incorrect.annotation "[ { ""Utterance"":{ ""utterance"":""I want to order a family size pepperoni pizza with thin crust and mozzarella cheese"", ""languageTag"":""en"", ""entities"":[ { ""entityValue"":""family"", ""entityName"":""MLPizzaCrust"", ""beginOffset"":18, ""endOffset"":24 }, { ""entityValue"":""mozzarella"", ""entityName"":""MLCheeseType"", ""beginOffset"":66, ""endOffset"":76 }, { ""entityValue"":""pepperoni"", ""entityName"":""MLPizzaType"", ""beginOffset"":30, ""endOffset"":39 } ] } } ]" "[ { ""Utterance"":{ ""utterance"":""I want to order a large supreme pizza with regular crust and provolone cheese"", ""languageTag"":""en"", ""entities"":[ { ""entityValue"":""supreme"", ""entityName"":""MLPizzaType"", ""beginOffset"":24, ""endOffset"":31 }, { ""entityValue"":""provolone"", ""entityName"":""MLCheeseType"", ""beginOffset"":61, ""endOffset"":70 }, { ""entityValue"":""regular"", ""entityName"":""MLPizzaCrust"", ""beginOffset"":43, ""endOffset"":50 }, { ""entityValue"":""large"", ""entityName"":""MLPizzaSize"", ""beginOffset"":18, ""endOffset"":23 } ] } } ]"
- For unannotated utterances, upload a CSV that organizes the
plain utterances under a single column,
- Click Continue, verify the number of records, then Launch.
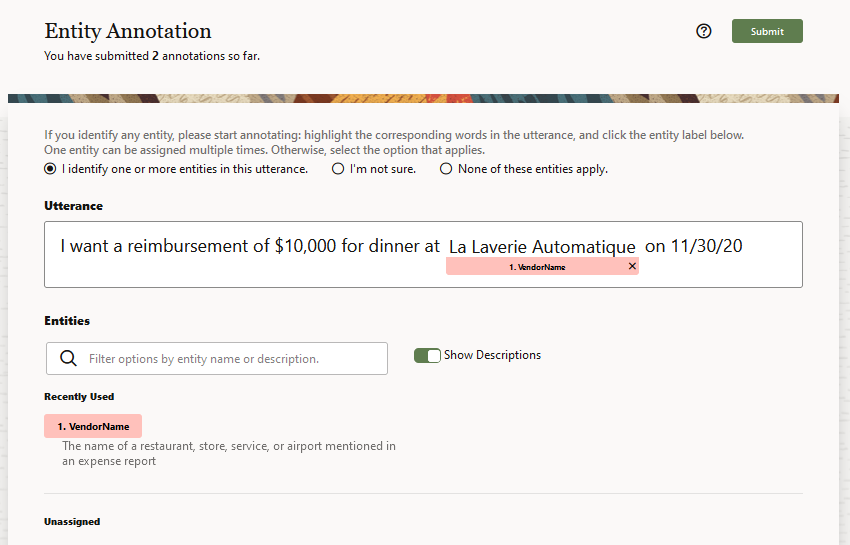
- Copy then paste the link into an email that’s broadcast to crowd
workers. Workers accept the job by clicking this link. Before they begin
labeling the utterances with annotations, they review basic rules on how to
label content with annotations. If the utterance includes text that matches one
the ML Entities listed in the page, a crowd worker highlights the applicable
text and applies the ML Entity label. If the utterance is already annotated,
workers can review the labels and adjust them when needed.
- When the job completes (either because workers have completed the
annotations or because you canceled it), you can view the results and accept it
into the ML Entity's training corpus.
Before adding the results, however, you can have crowd workers verify them by launching an Entity Validation Job. Only the correct results from a validation job are added to the corpus. If needed, you can make additional corrections and additions to the job results in the ML Entity's Dataset tab.
Validation Jobs
For Validation jobs, crowd workers review the results from Paraphrase jobs, Entity Annotation jobs, or Intent Validation jobs generated from the Retrainer. To validate a Paraphrase Job, they compare the utterances (the results of a Paraphrasing job or from ) against a task, the Paraphrasing job's prompt. For Entity Annotation Jobs, they review the utterances to ensure that the correct ML entity has been identified and that the text has been labeled completely.
Create an Intent Paraphrasing Validation Job
- Click Add Job in the Jobs page.
- Select Intent Paraphrase Validation.
- Enter a name.
- Enter the language that's used by the crowd workers.
- Add Paraphrasing jobs that have not yet been accepted (that is, the Finished or Canceled jobs). You can either upload a CSV file from your local system, select one or more Paraphrasing jobs, or create a job from both.
- Click Continue, verify the number of records,
then Launch.
- After the row for the Validation job is added to the Jobs page (you
may need to click Refresh ), click Copy
Link.
- Paste the link into an email that's broadcast to crowd workers.
After the crowd workers accept the job, they review basic rules for evaluating
the utterances.
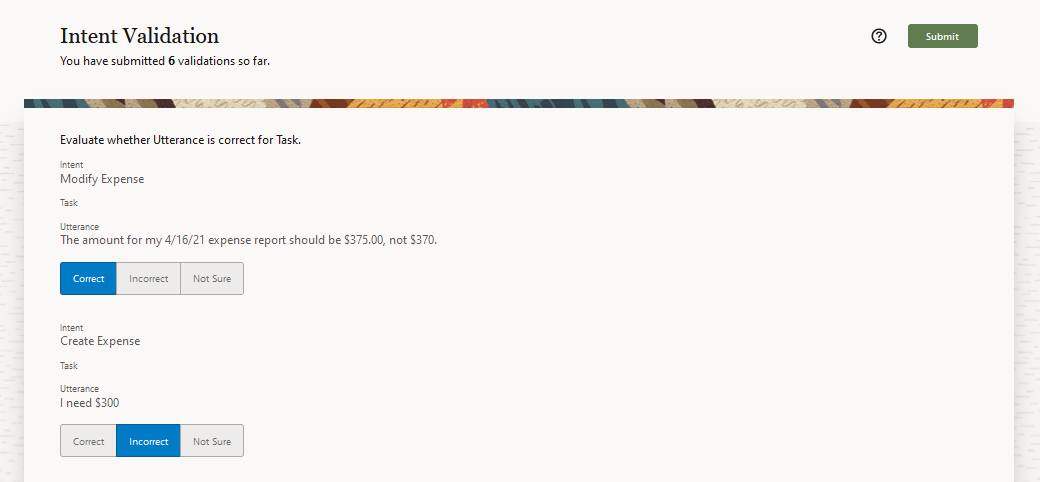
They then evaluate an utterance.
You can monitor the worker’s progress from the Jobs page.
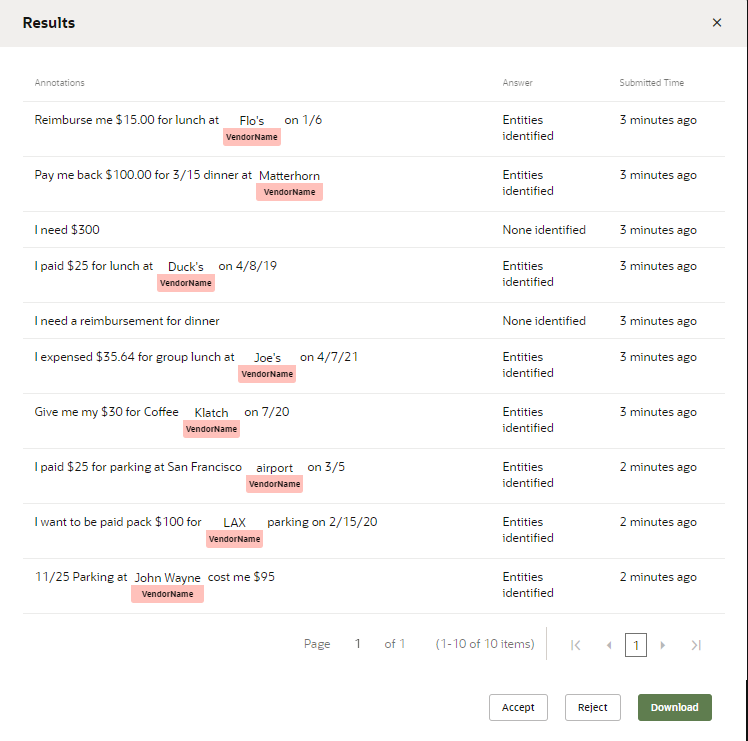
Review a Validation Job
After workers complete the Validation job (or if you cancel the job because it's
close enough to completion), you can view it, accept or reject the job in its entirety.
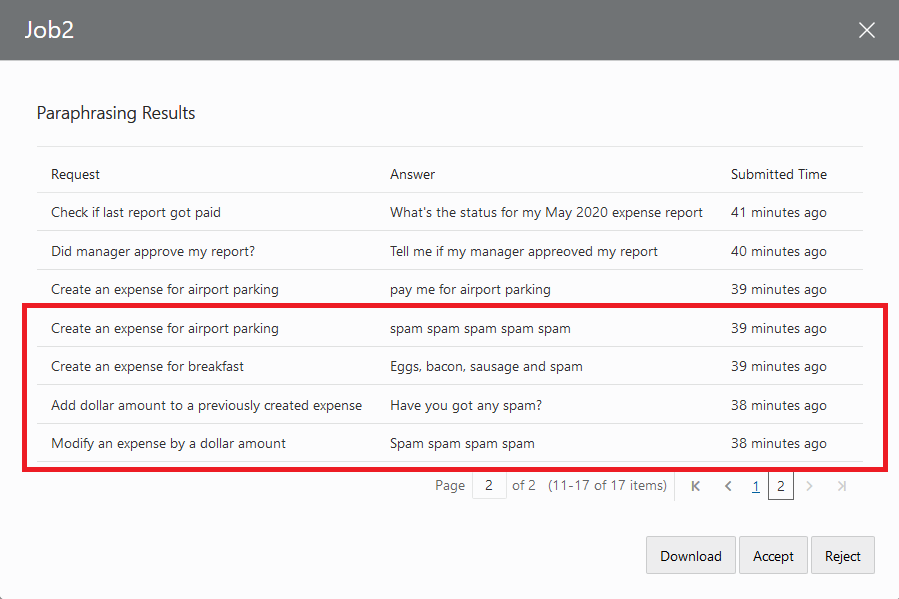
Even though Validation jobs may contain thousands of results (which is why you'd source
them to the crowd), you may still want to review them individually. For example, you
might see answers in the View Results dialog that you disagree with. You'll want to
change or remove them before committing the results to your training data.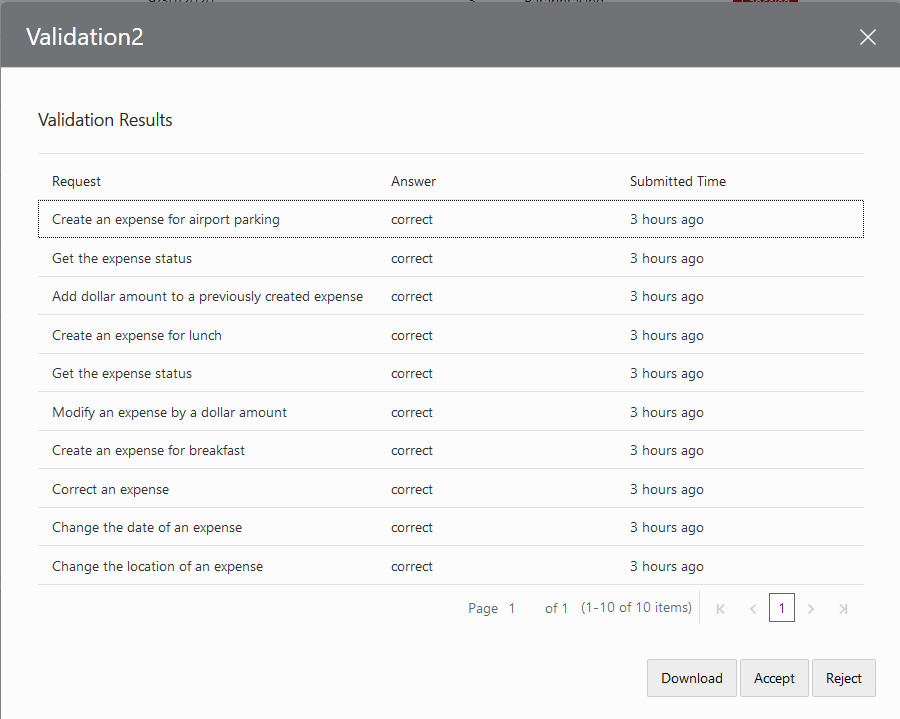
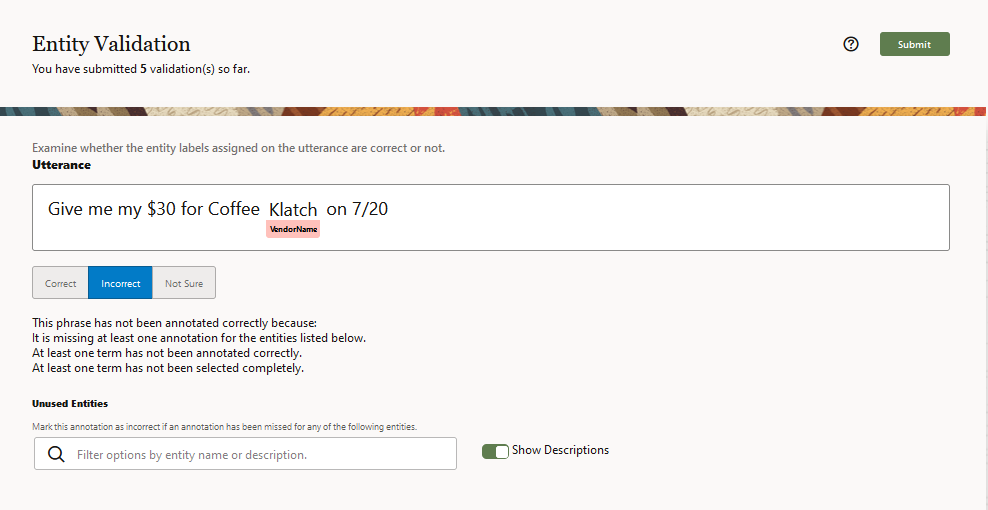
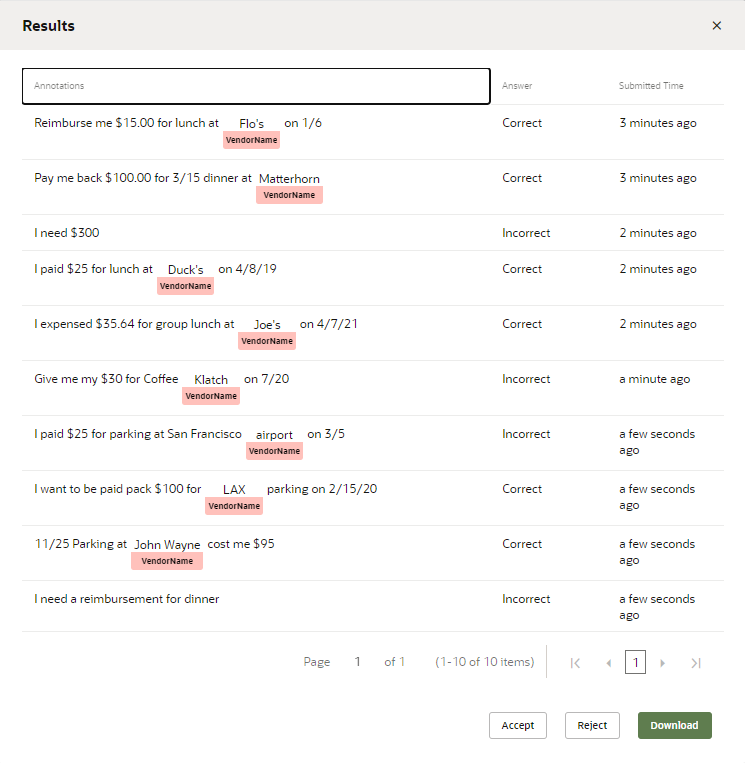
Description of the illustration review-validation-job.png
- Download the job as a CSV, either from the View Results dialog, or by clicking Download in the Results page.
- Open the CSV in a spreadsheet program.
- Compare the entries in the
IntentNameand prompt columns and then change the results entry when needed. You can edit just this column, or remove an entire row.
In general, you only need to focus on these three columns. That said, you can sort by the contributor column to isolate the work of a particular crowd worker. If this worker's decisions are consistently unreliable, then you can delete all of the rows for this contributor.Note
If you delete a row, make sure that you delete it entirely. You can't upload a CSV with a partial row. - When you’re finished, click Upload in the Results page. Browse to, then select, the CSV file. Select Validation, enter a name, then click Upload.
- Click Accept or Reject. If you accept the job, only the "correct" utterances are added to the training set. You can't undo this operation. You can only remove these utterances manually.
- Retrain the skill.
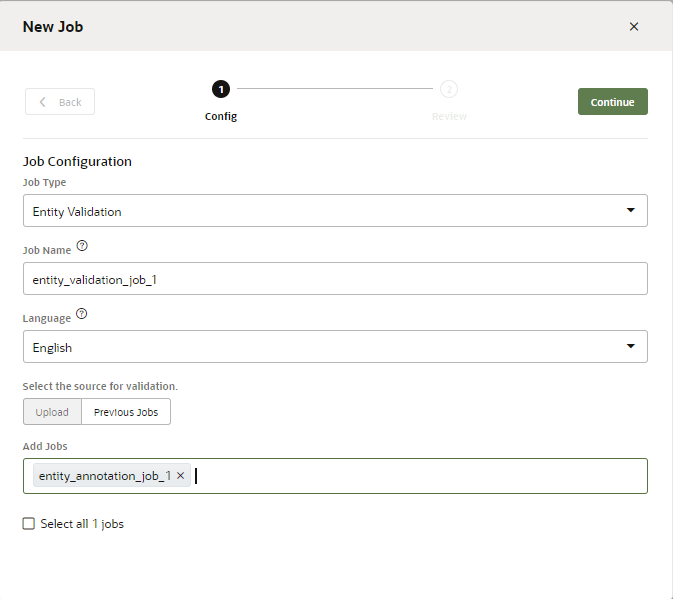
Create an Entity Annotation Validation Job
- Click New Job in the Jobs page.
- Select Entity Validation.
- Enter a name.
- Enter the language that's used by the crowd workers.
- You can either upload a CSV file from your local system, select one
or more completed Entity Annotation Jobs (which includes jobs that workers have
completed or that you canceled), or combine them to create a single job. The CSV
has the same format as the one used to add annotated utterances to an Entity Annotation Job: it has the single
annotationcolumn and JSON objects for utterances:annotation "[ { ""Utterance"":{ ""utterance"":""I want to order a family size pepperoni pizza with thin crust and mozzarella cheese"", ""languageTag"":""en"", ""entities"":[ { ""entityValue"":""family"", ""entityName"":""MLPizzaCrust"", ""beginOffset"":18, ""endOffset"":24 }, { ""entityValue"":""mozzarella"", ""entityName"":""MLCheeseType"", ""beginOffset"":66, ""endOffset"":76 }, { ""entityValue"":""pepperoni"", ""entityName"":""MLPizzaType"", ""beginOffset"":30, ""endOffset"":39 } ] } } ]" ... - Click Continue, verify the number of records,
then click Launch.
- Paste the link into an email that's broadcast to crowd
workers.
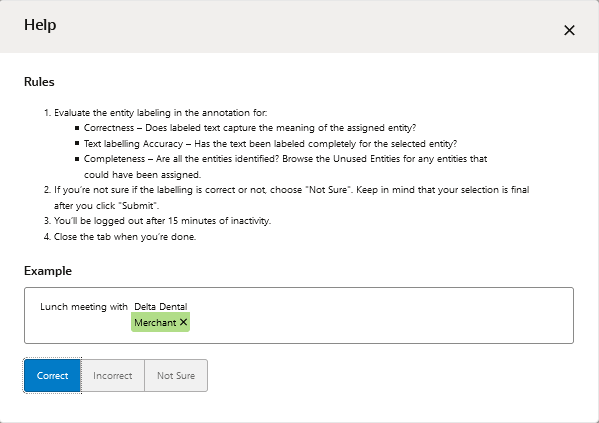
After the crowd workers accept the job, they review basic rules for evaluating the annotations. From there, they review the annotations by classifying them as correct, incorrect, or not sure.
You can monitor the worker’s progress from the Jobs page. When the job completes, you can review the results before accepting or rejecting it.
By clicking Accept, you add the correct results to the ML Entity's training set. If needed you can edit them further in the Dataset tab.
Create Test Suites
- Select the report in the Results page, then Click

- select Test Suite.
- Complete the dialog by giving the test suite and name and selecting the language that the utterances will be tested in. Then click Create.
- Open the Utterance Tester to run the test suite.