Use Azure Service Principal to Access Azure Resources
You can use an Azure service principal with Autonomous AI Database to access Azure resources without having to create and store your own credential objects in the database.
- Enable Azure Service Principal
Enable Azure service principal authentication to allow Autonomous AI Database to access Azure services without providing long-term credentials. - Provide Azure Application Consent and Assign Roles
To access Azure resources from Autonomous AI Database with Azure service principal authentication you must consent the Azure application and assign roles to allow access to your Azure resources. - Use Azure Service Principal with DBMS_CLOUD
When you makeDBMS_CLOUDcalls to access Azure resources and specify the credential name asAZURE$PA, the authentication on the Azure side happens using the Azure service principal. - Disable Azure Service Principal
To disable access to Azure resources from Autonomous AI Database with Azure service principal, useDBMS_CLOUD_ADMIN.DISABLE_PRINCIPAL_AUTH. - Notes for Azure Service Principal
Notes for using Azure service principal.
Parent topic: Configure Policies and Roles to Access Resources
Enable Azure Service Principal
Enable Azure service principal authentication to allow Autonomous AI Database to access Azure services without providing long-term credentials.
To use Autonomous AI Database with Azure service principal authentication you need a Microsoft Azure account. See Microsoft Azure for details.
To enable Azure service principal authentication on Autonomous AI Database:
See ENABLE_PRINCIPAL_AUTH Procedure for more information.
Parent topic: Use Azure Service Principal to Access Azure Resources
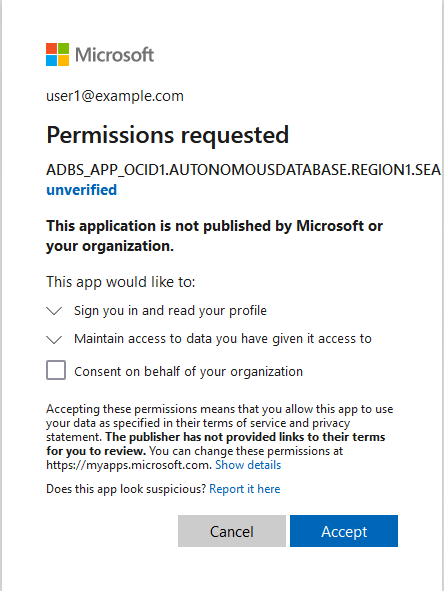
Provide Azure Application Consent and Assign Roles
To access Azure resources from Autonomous AI Database with Azure service principal authentication you must consent the Azure application and assign roles to allow access to your Azure resources.
To provide Azure application consent and assign roles, perform the following steps:
This example shows steps to grant roles for accessing Azure Blob Storage. If you want to provide access for other Azure services you need to perform equivalent steps for the additional Azure services to allow the Azure application (the service principal) to access the Azure service.
Parent topic: Use Azure Service Principal to Access Azure Resources
Use Azure Service Principal with DBMS_CLOUD
When you make DBMS_CLOUD calls to access Azure resources and specify the
credential name as AZURE$PA, the authentication on the Azure side happens
using the Azure service principal.
If you have not already done so, perform the required prerequisite steps:
-
Enable the ADMIN schema or another schema to use Azure service principal authentication. See Enable Azure Service Principal for more information.
-
Consent the application and perform the Azure role assignment grants. See Provide Azure Application Consent and Assign Roles for more information.
To use a DBMS_CLOUD procedure or function with Azure service
principal, specify AZURE$PA as the credential name. For example,
you can access Azure Blob Storage using Azure service principal credentials as
follows:
SELECT * FROM DBMS_CLOUD.LIST_OBJECTS('AZURE$PA', 'https://treedata.blob.core.windows.net/treetypes/');
OBJECT_NAME BYTES CHECKSUM CREATED LAST_MODIFIED
----------- ----- ------------------------ -------------------- --------------------
trees.txt 58 aCB1qMOPVobDLCXG+2fcvg== 2022-04-07T23:03:01Z 2022-04-07T23:03:01ZIf you compare the steps required to access object storage, as shown in
Create Credentials and Copy Data into an Existing Table, notice that Step 1, creating credentials is not required because
you are using an Azure service principal called AZURE$PA.
Parent topic: Use Azure Service Principal to Access Azure Resources
Disable Azure Service Principal
To disable access to Azure resources from Autonomous AI Database with Azure service
principal, use DBMS_CLOUD_ADMIN.DISABLE_PRINCIPAL_AUTH.
To disable Azure service principal on Autonomous AI Database:
BEGIN
DBMS_CLOUD_ADMIN.DISABLE_PRINCIPAL_AUTH(
provider => 'AZURE',
username => 'adb_user');
END;
/When the provider value is
AZURE and the username is
a user other than the ADMIN user, the procedure
revokes the privileges from the specified user. In this case, the
ADMIN user and other users can continue to
use ADMIN.AZURE$PA and the application that is
created for the Autonomous AI Database instance remains on the instance.
When the provider value is
AZURE and the username is
ADMIN, the procedure disables Azure service
principal based authentication and deletes the Azure service
principal application on the Autonomous AI Database instance. In this case, if you
want to enable Azure service principal you must perform all the
steps required to use Azure service principal again, including the
following:
-
Enable the
ADMINschema or another schema to use Azure service principal authentication. See Enable Azure Service Principal for more information. -
Consent the application and perform the Azure role assignment grants. See Provide Azure Application Consent and Assign Roles for more information.
See DISABLE_PRINCIPAL_AUTH Procedure for more information.
Parent topic: Use Azure Service Principal to Access Azure Resources
Notes for Azure Service Principal
Notes for using Azure service principal.
-
Cloning an Autonomous AI Database instance with Azure service principal: When you clone an instance with Azure service principal enabled, the Azure service principal configuration is not carried over to the clone. Perform the steps to enable Azure service principal on the clone if you want to enable Azure service principal on a cloned instance.
Parent topic: Use Azure Service Principal to Access Azure Resources